Pipe nipples can be confusing with all the different types, materials and sizes out there. It’s a big issue as picking the wrong pipe nipple could cause leaks, rust or even full system failures. It would waste your money and time.
In this complete guide, we’ll decode pipe nipples. We’ll cover the types, sizes, materials and uses so you can select the right nipple for your particular projects.
What is a Pipe Nipple?
A pipe nipple is a short threaded pipe fitting that connects pipes and other fittings in piping systems. These handy components extend pipe length, adapt sizes and can change flow direction. Typically, 1/8” to 12” in diameter, these nipples can handle pressures up to 3,000 PSI depending on material and size. They have external threads on both ends for secure connections.
These nipples feature external threads on both ends which allows them for secure connections. They can act as a bridge between two fittings to lengthen pipes. They use reducer nipples to adapt sizes or work with elbows/tees to alter flow direction. This flexibility optimizes layouts and efficiency across industries.

Top 10 Types of Pipe Nipples
Knowing the different types of nipples is important for optimizing piping systems. Each has specific functions and benefits. Let’s look at the top 10, starting with the barrel nipple.
1. Barrel Nipple
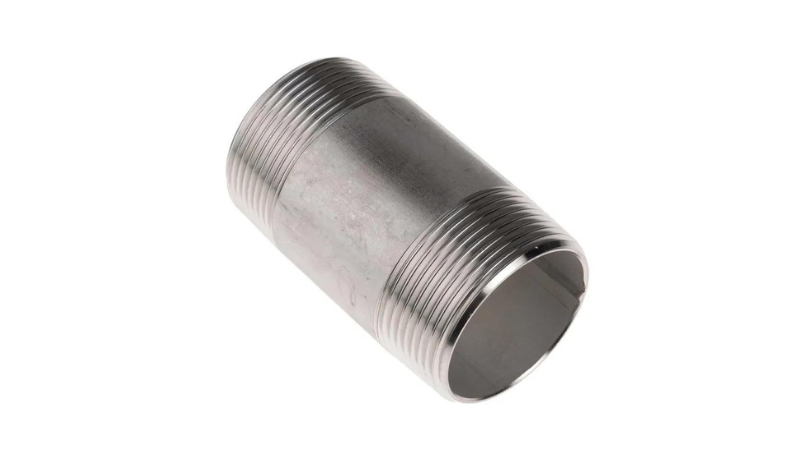

These types of nipples are standard fittings threaded on both ends, with a smooth middle section. They are commonly used in plumbing and industrial settings at 2-12″ lengths. It can handle up to 2,000 PSI pressure and are perfect for extending pipe runs. In HVAC systems, barrel nipples improve flow by up to 15% over close nipples.
2. Hex Nipple
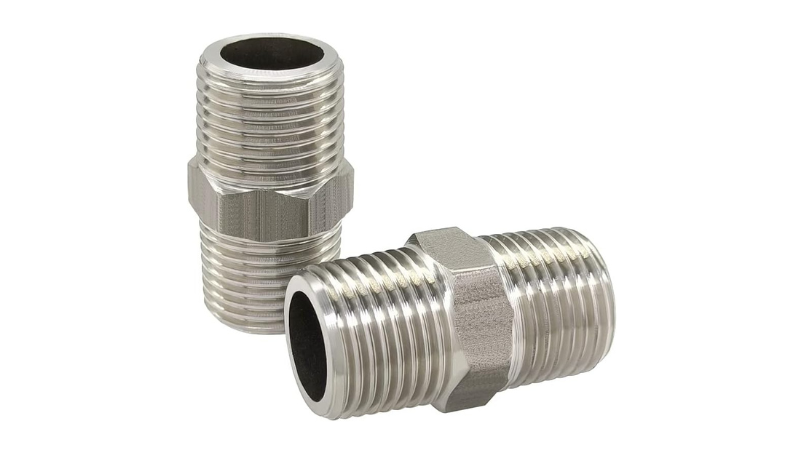

This typehas a hexagonal center part for secure wrench gripping during installation or removal. This design allows 150 ft-lb torque which is 30% more than standard nipples. Commonly used in high-pressure systems, hex nipples can handle pressures up to 3,000 PSI. Their unique shape cuts installation time by approximately 25% compared to standard nipples which makes them perfect for tight spaces in industrial applications.
3. Close Nipple
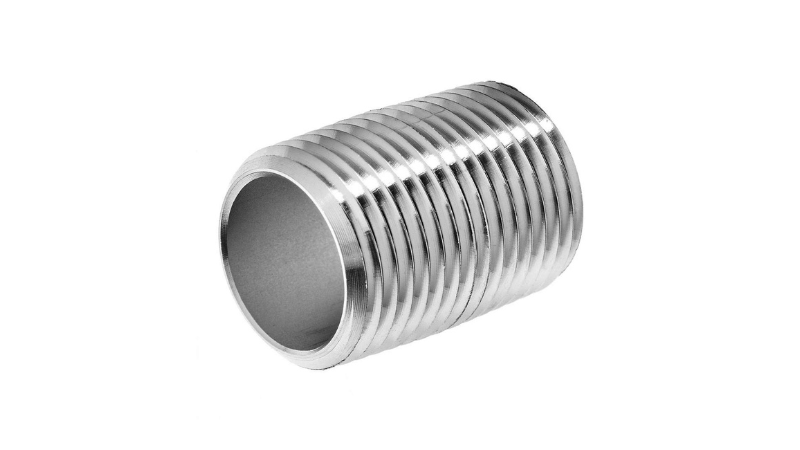

These nipples are very short, with no unthreaded part between the ends. These compact fittings are important in tight installations, cutting overall system length by up to 15%. While they can handle pressures up to 2500 PSI, their short length can make installing challenging. Close nipples are broadly used in pneumatic systems, where they can increase airflow efficiency by up to 10% compared to longer nipples.
4. Swage Nipple
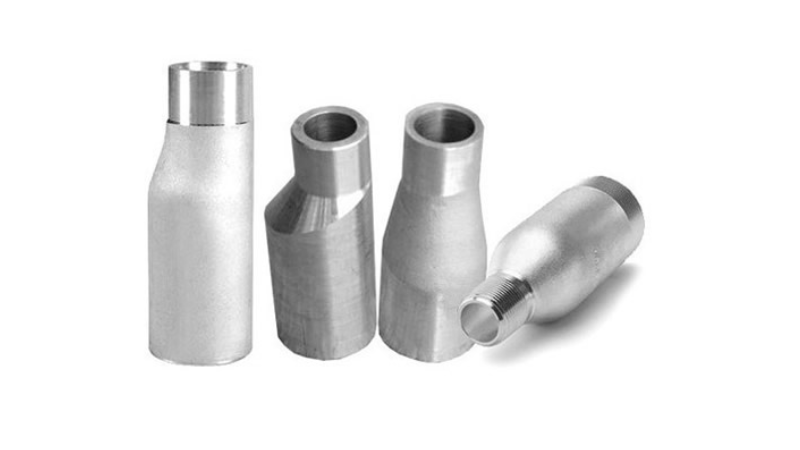

These are built to connect pipes of different diameters. They are commonly available in concentric and eccentric types. They can reduce pipe size by up to 50% in one fitting which simplifies system design. Concentric swage nipples keep centerline alignment, while eccentric types offset it. In oil and gas uses, right-sized swage nipples can improve flow rates by up to 20% which makes them important for optimizing production efficiency.
5. Hose Nipple
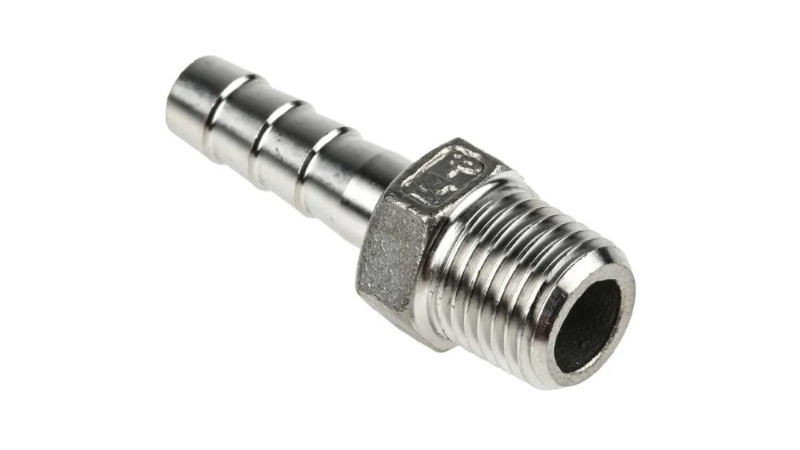

Hose nipples have one threaded end and one barbed end for secure hose connection. These versatile fittings can handle pressures up to 150 PSI and are important in fluid transfer uses. The barbed end gives a grip strength 40% stronger than smooth connections which reduces the risk of leaks. In chemical processing, hose nipples can increase transfer efficiency by up to 15% over standard fittings which makes them important for optimizing fluid handling systems.
6. Welded Nipple
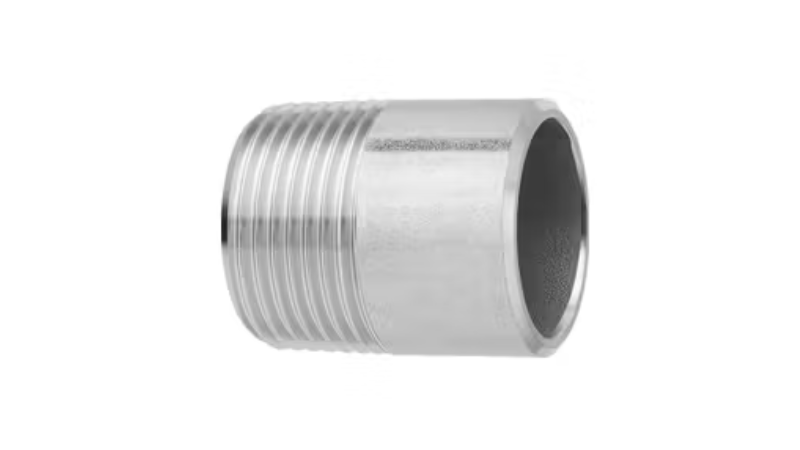

These nipples have one threaded end and one plain end for welding which gives a permanent and leak-proof connection. These fittings can handle pressures up to 3,500 PSI which is 25% higher than standard threaded connection. In high-temp uses, welded nipples keep integrity up to 1,000°F. They are broadly used in petrochemical industrieswhere they can cut maintenance costs by up to 30% compared to fully threaded connections.
7. Extension Nipple

These types of nipples are longer than standard nipples, typically ranging from 12″ to 72″ long. They are very important for bridging gaps in piping systems where they are able to span distances up to 6 feet without extra support. These nipples can reduce the number of joints in a system by up to 50% which minimizes potential leak points. In industrial cooling systems, extension nipples can increase heat transfer efficiency by up to 10% by optimizing fluid flow paths.
8. Threaded Nipple with Thread on End

T.O.E nipples have threads on one end only which offers unique benefits in specialized applications. These fittings can cut installation time by up to 40% compared to fully threaded nipples. With pressure ratings up to 2,000 PSI, T.O.E nipples are perfect for dead-end service in process piping. Threaded nipples are particularly effective in chemical plants, where they can improve system flexibility by allowing for easier future expansions without compromising integrity.
9. Grooved Pipe Nipple

Grooved pipe nipples use mechanical coupling for connection which provides fast assembly in large-scale industrial systems. This design can cut installation time by up to 60% compared to welded connections. Able to handle pressures up to 1,000 PSI, grooved nipples excel in fire protection systems. They provide 30° of angular flexibility which is important for earthquake-resistant designs. It can also absorb up to 0.75 inches of linear movement which improves system longevity.
10. Galvanized Nipple

Galvanized nipples have a zinc coating that gives superior corrosion resistance which extends service life by up to 50 years in moderate environments. These fittings can withstand temperatures up to 225°F and pressures up to 2,500 PSI. In outdoor and marine uses, galvanized nipples reduce maintenance costs by up to 40% compared to standard steel nipples. They are important in water treatment facilities where they maintain system integrity in harsh chemical environments.
Pipe Nipple Sizes and Measurements
Having explored the multiple types of pipe nipples, let’s examine their sizes and measurements. Understanding these specifications is very important to make sure of optimal system compatibility and performance.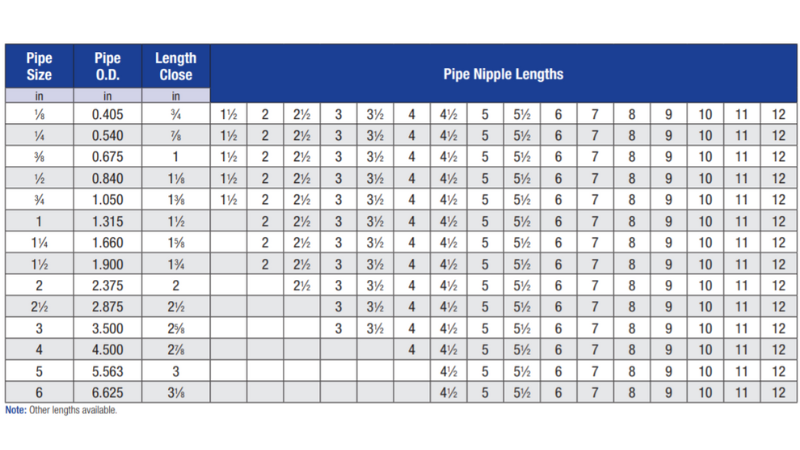
Standard Sizes
Pipe nipple sizes usually range from 1/8” to 12” in diameter. Lengths go from short versions to extended types up to 72”. The most popular sizes fall between 1/2” and 2” which make up 70% of industrial applications. When selecting pipe nipples, consider that real outer diameters are around 1/8” which is larger than normal sizes. For example, a 1” nipple has an actual OD of 1.315” which is important to make sure of proper fit in your piping system.
Pipe Nipple Lengths and Diameters
Pipe nipple lengths are measured from end to end (from one end of thread to the other end). Pipe nipple dimensions ranges from short (1/8” to 1/4”) to long at up to 72”. Diameters play a very important role in matching with other components. For example, a 2” nominal pipe has an actual OD of 2.375”with wall thickness varying based on schedule. This precision is very important for maintaining system integrity.
Thread Types in Pipe Nipples
Getting the thread types right is very important for leak-free connections. NPT (National Pipe Thread) is the most popular standard for threaded nipples in North America. A 1⁄2” NPT nipple can take pressures up to 2,000 PSI. BSP (British Standard Pipe) threads are common in Asia and Europe while metric threads are used globally.
When selecting a threaded nipple, consider that a 2-inch NPT nipple has 11.5 threads per inch compared to 14 threads for a 3⁄4″ one. This difference impacts, torque requirement and sealing efficiency. For high-pressure uses, a properly put in NPT nipple can maintain 99.9% seal integrity at pressures up to 1,500 PSI.
Materials of Nipple Pipe Fittings
The material chosen for nipple pipe fitting greatly affects their lifespan and performance. Let’s look at the most common materials used to make these important parts.
Copper
Copper pipe nipples provide superb thermal conductivity and corrosion protection which makes them perfect for plumbing and HVAC systems. With a melting point of 1,984°F (1,085°C), copper pipe nipples handle high temperature. They have a thermal expansion coefficient of 9.2 × 10-6 in/°F for stability in different conditions. Copper’s antimicrobial properties reduce bacteria by up to 99.9% which increase system cleanliness. In residential plumbing, copper pipe nipples can last up to 50 years which gives cost-effectiveness and long-term reliability.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel pipe nipples combine strength with superior corrosion resistance. Grade 316 SS pipe nipples provide up to 10 times better corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel. With a melting point of 2,550°F (1,400°C), these nipples excel in high-temperature uses. Stainless steel’s low thermal expansion rate of 9.6 × 10-6in/°F make sure of dimensional stability. In chemical processing industries, stainless steel nipples can increase system lifespan by up to 40% over carbon steel alternatives which justifies their higher initial cost.
Brass
Brass pipe nipples provide excellent machinability and corrosion resistance which is perfect for marine applications and water systems. With a tensile strength of up to 60,000 PSI, brass pipe nipples can withstand pressures up to 1,500 PSI. Brass has a thermal conductivity of 70 BTU/(hr·ft·°F) which 4.5 times higher than stainless steel. This property increase heat transfer efficiency by up to 20% in HVAC systems. Brass nipples also show antimicrobial properties which decreases bacterial growth by up to 99.9% within two hours of contact.
PVC
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipe nipples provide great cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance. With a tensile strength of 7,500 PSI, PVC pipe nipples work for low-pressure uses up to 250 PSI. PVC’s thermal expansion rate of 3.0 × 10-5in/°F is higher than metals which is required for careful installation. These nipples reduce system weight by up to 70% compared to other metal options. In chemical handling, PVC nipples can extend system life by up to 50 years which gives long-term reliability in corrosive environments.
Selecting the right nipple material is important for system durability and performance. Consider factors like chemical compatibility, pressure ratings and conditions to make a better choice tailored to your application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Material
When selecting pipe nipple materials, consider chemical compatibility, environmental conditions and pressure needs. Give attention to these factors:
- Temperature ranges can affect material performance by up to 30%.
- Pressure ratings vary greatly; stainless steel can take up to 3,000 PSI while PVC is limited to 250 PSI.
- Chemical compatibility is important because choosing the wrong material can reduce system life by up to 70%.
Always check compatibility charts and standards like ASME B31.3 for process piping to make sure of longevity and optimal performance for your application.

What are the Common Uses of Pipe Nipples?
These nipples find many applications across different industries because of their flexibility and efficiency in connecting pipes and fittings. Let’s look at the common uses of pipe nipples in different sectors, starting with residential plumbing.
Residential Plumbing
For household plumbing, pipe nipples are important parts used in water supply lines, fixture connections and drain systems. Brass and copper nipples are preferred for drinkable water systems because they have antimicrobial properties and corrosion resistance. These nipples can handle pressures up to 150 PSI in standard residential applications.
For drain system, PVC nipples are usually used which offers chemical resistance to household cleaners and waste. Close nipples are particularly valuable in tight spaces like under sinks where they can reduce connection lengths by up to 2 inches compared to standard fittings.
Industrial Pipelines
In industrial pipelines, pipe nipples are important for connecting gauges, valves and instruments. Carbon steel nipples, conforming ASTM A106 Grade B, are preferred for high-pressure applications up to 3,000 PSI. Stainless steel nipples, particularly grade 316, are used in corrosive environments which provides resistance to over 70 different chemicals.
Swage nipples play an important role in diameter transitions which reduces turbulence by up to 30% compared to sudden contractions. In steam systems, pipe nipples with a schedule 80 wall thickness are very important because they are capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1,000°F (538°C).
Oil and gas industry
In the oil and gas sector, pipe nipples are important parts in pipelines, wellheads and processing facilities. At wellheads, they connect production casings to surface facilities to withstand pressures up to 15,000 PSI. In pipelines, swage nipples facilitate diameter transitions which reduces turbulence by up to 30 ft3/s compared to sudden contractions.
Processing facilities use corrosion-resistant stainless steel nipples which are capable of handling over 70 different chemicals. Threaded nipples in blowout preventers can handle temperatures up to 350°F (177°C) which make sure of safety in high-pressure zones above 20,000 PSI.
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing, pipe nipples play an important role in connecting reactors, storage tanks and distillation columns. Stainless steel 316L nipples are preferred for their resistance to over 70 corrosive chemicals and temperatures up to 1600°F (871°C). These nipples can take pressures up to 5,000 PSI in high-pressure reactors.
For highly corrosive environments, Hastelloy C276 nipples provide better protection with a corrosion rate below 0.1 mm/year in concentrated hydrochloric acid at 150°F (66°C).
Irrigation Systems
Pipe nipples are important to connect main lines, sprinklers and valves in irrigation. PVC nipples are preferred for their ability to handle pressures up to 200 PSI and for their corrosion resistance. Brass nipples are used in control valves for durability and preventing dezincification.
For large-scale systems, grooved pipe nipples allow quick installation which reduces labor time by up to 50%. These fittings handle flow rates of 500 GPM in 6-inch lines which makes sure of better water distribution over huge agricultural areas.
Marine applications
For marine environments, pipe nipples are very important for seawater intake, fuel lines and ballast systems. Corrosion-resistant materials like Monel 400 or 316L stainless steel are preferred which can handle saltwater for up to 25 years. These nipples can withstand pressures up to 5,000 PSI deep underwater applications.
For fuel systems, special nipples with fire-resistant coatings maintain integrity for up to 30 minutes at 1,000°C which meets marine regulations. In ballast systems, large nipples allow flow rates of up to 5,000 cubic meters/hour for better water management.
Food and beverage industry
In this industry, pipe nipples are very important in processing gear, packaging lines and CIP systems. 316L stainless steel nipples, with 0.8 μm or better surface roughness are preferred for their sanitation properties. These fittings handle CIP pressures up to 1,000 PSI and temperatures up to 200°F (93°C).
In dairy processing, specialized nipples with 3-A Sanitary Standards certification make sure of product safety. For high-volume beverage lines, large-diameter nipples allow flow rates up to 500 GPM which increases production efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Nipple Fitting
Selecting the correct pipe nipple fitting is very important for optimal system performance and life. Let’s explore the important factors to keep in mind when making your choice.
Assessing Your Needs
When selecting a nipple, consider the application specifics. Assess pressure needs ranging from 150 to 3,000 PSI. Account for temperature changes which are typically from -20°F to 400°F (-29°C to 204°C). Evaluate environmental conditions and fluid compatibility. These factors collectively affect material selection and can impact system efficiency by up to 30%.
Material Compatibility
Matching pipe nipple materials with your piping system is important to prevent galvanic corrosion. Mismatched metals can increase the speed of corrosion by up to 30 times. For example, coupling copper with steel can cause rapid deterioration. Always consult galvanic series charts when selecting materials. In important applications, using the same material throughout can extend system lifespan by up to 40%.
Correct Sizing
Proper sizing is important for best performance. Make sure that nipple diameters precisely match your pipes and fittings. Even a 1/16 inch mismatch can give a substantial drop in flow efficiency. Thread types must also line up; mixing BSP and NPT threads can cause leaks in 95% of cases. Consider flow needs; oversized nipples can decrease velocity by up to 30%, while undersized ones may significantly increase pressure loss.
Thread Type and Compatibility
Choosing the right thread type is very important for leak-proof connections. BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Thread) are not interchangeable; mismatching can result in complete failure. BSP threads have a 55° thread angle, while NPT uses a 60° angle. This 5° difference can mean up to 30% less sealing surface contact. Always check thread compatibility to prevent expensive leaks and make sure of system integrity.
Conclusion
Pipe nipples are very important parts of many industries. They provide efficiency and flexibility in piping systems. To get a proper knowledge about their sizes, types, materialsand uses is important for best performance. When picking pipe nipples, keep in mind factors like temperature ranges, pressure needs and chemical compatibility to guarantee safety and durability for your particular application.
For high-quality pipe nipples tailored to your requirements, KDM Fabrications is a trustworthy choice. Contact us today to improve your piping systems with top products and expert solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to measure a pipe nipple?
To measure a pipe nipple, use a tape measure to find the total length fromone end of thread to the other end. For diameter, measure the outside diameter with calipers or check standard pipe size charts based on the nominal pipe size.
2. What is the difference between a pipe nipple and coupling?
The main difference is that pipe nipples have external (male) threads on both ends while couplings have internal (female) threads on both ends. Nipples connect two female-threaded fittings and couplings join two male-threaded pipes or fittings.




