Pipe fittings are an important part of different piping systems. They have a great role in adapting, connecting, and controlling fluid and gas flow. But selecting the right fittings is absolutely necessary for everyday construction, plumbing, and industrial uses to assure performance, safety, and longevity.
Today we will discuss the Top 15 pipe fitting types and their applications in multiple industries. So let’s start.
What Are Pipe Fittings?

Pipe fittings have an important role in piping systems to direct, connect and control fluid flow. These particular parts join pipes, adapt to different sizes, and regulate flow. Common types include tees, couplings, elbows and valves and each serves a particular purpose.
In industrial settings, pipe fittings assure the safe and best transport of gases, liquids and slurries. Therefore a complete understanding of these components is important to design and maintain effective piping networks across different industries.
Top 15 Pipe Fitting Types and Their Applications
To make good piping systems, you need to understand the variety of pipe fittings. Let’s survey the top 15 fittings that are commonly used in different industries.
1. Elbow Fittings

Elbow fittings are L-shaped connectors that, usually at 45° or 90° angles, change the direction of pipe flow. They come in different radii with long-radius elbows providing less flow resistance than short-radius ones.
Materials
You will find elbow fittings made from materials like stainless carbon steel, PVC, steel, copper, and brass. The material choice depends on aspects such as corrosion resistance, temperature requirements and pressure ratings.
Applications
In the oil and gas industry, refineries use elbow pipe fittings to move fluid in complex piping networks. Chemical processing plants use them in reactor feed systems. HVAC systems use elbows for plumbing and ductwork. Power plants and water treatment facilities use these fittings in their steam distribution systems.
2. Tee Pipe Fittings

They have a T-shaped design with one inlet and two outlets that allow for the combining or branching of fluid flows. Tee pipe fittings have equal or reducing outlets known as reducing tees or straight tees.
Materials
Common materials for tee fittings include stainless steel, copper, PVC, CPVC, carbon steel and cast iron. The application requirements such as chemical compatibility and pressure ratings determine material selection.
Applications
You will encounter tee fittings in different industries. The petrochemical industry uses them in distillation columns for fluid distribution while water treatment plants put tees in filtration systems. Fire sprinkler systems depend on these types of pipe fittings for branch line connections.
In the food and beverage industry, tees are important in process piping for ingredient mixing. HVAC systems also benefit from tees in refrigerant distribution for multi-zone air conditioning units.
3. Pipe Couplings

Among the different pipe fitting types, the pipe coupler is important for joining two pipes of the same diameter. These fittings come in styles like compression, slip and grooved couplings. Each pipe coupling is suited for particular situations.
Materials
Pipe couplings are usually made from materials like carbon steel, PVC, stainless steel, copper, and malleable iron. The choice depends on factors like temperature resistance, pressure rating and chemical compatibility.
Applications
The oil and gas industry depends on pipe couplings to connect long pipeline stretches. In chemical processing plants, these fittings join pipes in corrosive environments. Municipal water systems use couplings for quick repairs and extensions. You will find these versatile fittings in practically every industry that depends on piping systems.
4. Pipe Union

Pipe unions stand out among fitting types due to their unique design for easy disassembly and reassembly. A union nut and two end pieces are the three main parts of a union pipe fitting. This setup permits for appropriate modifications and maintenance without cutting pipes.
Materials:
You will find pipe unions made from different materials like brass, PVC, stainless steel, and malleable iron. The choice depends on factors like pressure requirements, corrosion resistance and thermal expansion properties.
Applications:
Refineries use pipe unions to remove equipment for replacement or cleaning. In HVAC systems, they connect cooling and heating units. The pharmaceutical industry uses unions in sanitary piping systems. These fittings facilitate easy fixture replacement and system upgrades even in your home.
5. Pipe Adapter Fittings

Adapter fittings connect the gap between pipes of different materials, sizes or thread types. They come in many arrangements such as female-to-female, male-to-female and reducing adapters. This flexibility assures compatibility between diverse piping parts.
Materials:
Common materials for adapters include brass, PVC, stainless steel and cast iron. The specific choice depends on the pressure rating, corrosion resistance and temperature requirements of the situation.
Applications:
You will spot pipe adapters fitting in petrochemical plants that connect pipes of different sizes in complex processing units. Water treatment facilities use them to join pipes of different materials. HVAC technicians depend on adapters to connect copper refrigerant lines to steel compressor fittings. Many industrial machines require adapters to interface with standardized piping systems.
6. Reducer Pipe Fitting
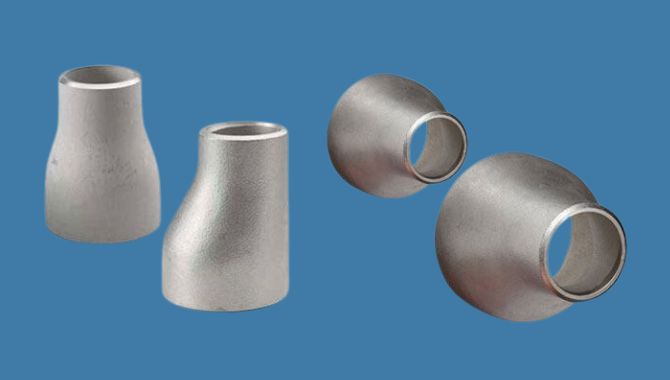
Reducer fittings are important in decreasing pipe diameter which allows for transitions between different pipe sizes. They come in two main types, first one is concentric reducers which maintain a centered flow, and the second one is eccentric reducers which keep one side of the pipe aligned.
Materials:
Manufacturers usually produce reducer pipe fittings from carbon steel, PVC, stainless steel and copper. The material selection depends on the pressure requirements of the system, temperature range and chemical compatibility.
Applications:
Oil refineries use pipe reducer fittings to manage flow rates between processing units of varying capacities. In chemical plants, they control pressure in reactor feed lines. Municipal water systems use reducers to transition from main lines to smaller distribution pipes. HVAC engineers optimize airflow in ductwork systems with these fittings.
7. Pipe Caps

Pipe caps serve as important fittings to seal the end of a pipe or fitting. They provide a tight, pressure-resistant closure and come in different styles including threaded, weld-on and slip-on caps.
Materials:
You will find pipe caps made from carbon steel, PVC, stainless steel and brass. The material choice depends on pressure rating, corrosion resistance and temperature requirements of the situation.
Applications:
In oil and gas pipelines, caps seal off unused branches or provide temporary closures during maintenance. Chemical processing plants use them to isolate sections of piping systems. Water treatment facilities depend on pipe caps to protect pipe ends from impurities. During servicing or installation, HVAC technicians use caps to seal refrigerant lines.
8. Pipe Plugs

Pipe plugs are small fittings that are built to seal openings in valves, pipes or other fittings. They come in different types which include expansion, threaded, and mechanical plugs. Each type is suited for particular situations.
Materials:
Manufacturers usually make plugs from materials like brass, stainless steel, and rubber. The choice depends on chemical compatibility, pressure rating and if the seal is temporary or permanent.
Applications
In refineries, pipe plugs are used for pressure testing newly installed piping systems. In automotive industries, they are used to seal transmission housings and engine blocks. Plumbers use pipe plugs for temporary closures and leak testing in the plumbing system. Likewise, hydraulic systems depend on pipe plugs to seal unused ports in valves and manifolds.
9. Pipe Bushings

Pipe bushings perform an important role in connecting pipes of different diameters. These pipe fittings have male threads outside and female threads inside which permits smooth transitions between pipe sizes.
Materials
You’ll find pipe bushings made from many different materials like carbon steel, PVC, brass and stainless steel. The choice depends on factors such as pressure rating, corrosion resistance and chemical compatibility with the fluid that is being transported.
Applications
In oil refineries, pipe bushings connect instruments to process lines of varying sizes. You’ll find them in chemical plants and use them to adapt small sampling lines to bigger process pipes. HVAC technology depends on bushings to join different refrigerant line sizes. In hydraulic systems, these fittings adapt parts to ports on pumps and valves.
10. Pipe Nipples

Pipe nipples are short pipe pieces of pipe with threads on both ends. They come in different lengths and thread configurations like long, short and close nipples.
Materials
The main materials that are used to manufacture pipe nipples are carbon steel, stainless steel, PVC and brass. The choice depends on the needs for temperature range, pressure and corrosion resistance.
Applications
You’ll see pipe nipples in different industries. Petrochemical industries use them to connect instruments and valves to process lines. In plumbing systems, nipples connect fixtures to supply lines and create offsets for proper alignment. You can also find them in water treatment facilities for the joining of pumps to piping systems. HVAC engineers use them to extend pipe runs in tight spaces.
11. Pipe Flange
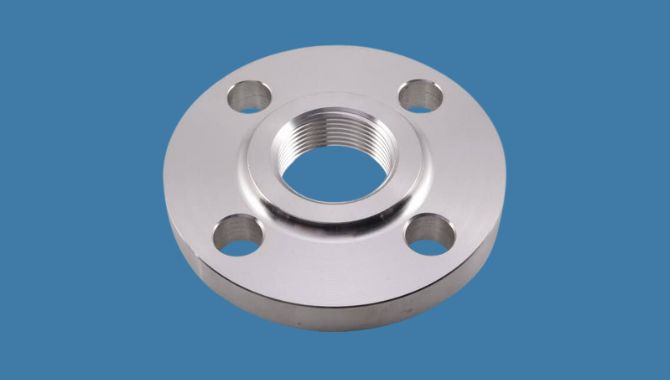
Pipe flange is one of the important types of pipe fitting. It makes strong, leak-proof links between valves, pipes and other equipment. They come in different types which include slip-on, weld neck and blind flanges. Each type fits for different uses.
Materials:
It is mainly manufactured from materials like carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel and cast iron. The choice depends on the required uses of temperature resistance, pressure rating and corrosion protection.
Applications
Oil refineries use pipe flanges to connect large pipes that carry refined products and crude oil. In chemical processing plants, this type of pipe fittings joins reactor vessels to piping systems. Power plants depend on flanges to connect high-pressure steam lines. Water treatment facilities use them to join valves, pumps and filtration machinery to main pipelines.
12. Valves

Valves regulate the pressure, flow and direction of fluids in piping systems. They come in different types such as globe, butterfly, gate and ball valves. Each type gives distinctive flow control features.
Materials:
You’ll find valves made from materials like carbon steel, brass, stainless steel and PVC. The selection depends on pressure rating, corrosion resistance and compatibility with the controlled fluid.
Applications
The oil and gas industry uses valves to regulate flow in pipelines and processing units. Chemical plants use them to manage product distribution and regulate reactant flow. HVAC systems depend on valves to control refrigerant and water flow. Municipal water systems use these pipe fittings to isolate sections for the management and maintenance of water distribution.
13. Cross Fittings

Cross fittings have four openings arranged in a cross shape that lets you connect four pipes at right angles. This flexible type of pipe fitting permits combination or distribution of fluid flows in multiple directions.
Materials:
Main materials for cross pipe fittings manufacturing include carbon steel, stainless steel, copper and PVC. The selection of this type of pipe fitting is based on corrosion resistance, pressure rating and compatibility with the fluid that is being transported.
Applications
Fire protection systems use cross fittings to distribute water to multiple sprinkler lines. In chemical processing plants, they distribute or combine reactants and products. Oil refineries also use them in manifold systems for proficient fluid distribution. HVAC systems create multiple branch lines from one main supply.
14. Y-Fittings
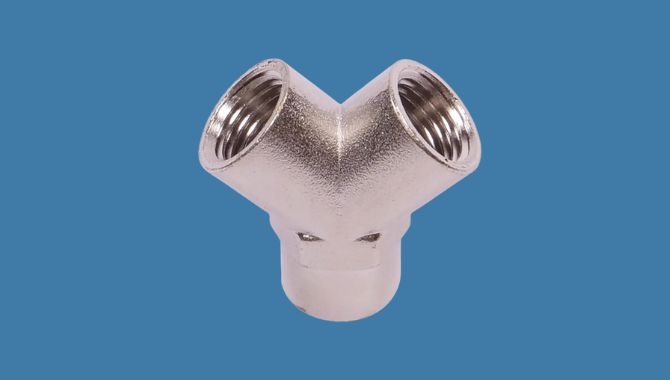
Y-fittings focus on pipe components that split or merge fluid flows at a 45-degree angle. These fittings offer smoother flow characteristics than T-fittings which helps reduce pressure drop and turbulence in piping systems.
Materials:
You will find Y pipe fittings made from different materials including ductile iron, PVC, stainless steel and HDPE. The choice of material depends on pressure requirements, chemical compatibility and particular application needs.
Applications:
In wastewater treatment plants, Y-fittings combine multiple inlet streams into a single process line. Brewing industries use them to split product flows for different packaging lines. HVAC systems use Y-fittings to merge return air ducts. Hydraulic systems use these fittings to create bypass loops or combine multiple pump outputs.
15. Pipe Olet

Pipe olets are particular fittings designed for branch connections on larger diameter pipes. They come in different styles such as threadolets, weldolets and sockolets. Each style is suited for particular joining methods and uses.
Materials:
Common materials for pipe olets include stainless steel, carbon steel and alloy steel. The selection depends on factors like temperature resistance, pressure rating and corrosion resistance required for the specific situation.
Applications:
Oil refineries use pipe olets to create branch connections for instrumentation and sampling points on large process lines. In power plants, these fittings connect small-bore pipes to main steam lines. Chemical processing facilities add injection points for additives or catalysts using olets. Natural gas pipelines contain olets to install pressure relief valves and monitoring equipment on high-pressure mains.
Conclusion
To craft the best and reliable piping systems, knowing about different types of pipe fitting is a must. From tees and elbows to fittings like olets, each part assures proper fluid flow, system integrity and pressure management. You can maximize performance and minimize possible issues by choosing the right pipe fittings for your particular use.
If you need the best quality of pipe fittings to upgrade your projects, contact KDM Fabrications today. Our experts can advise and deliver many options to you for industrial-grade fittings to meet your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How to Choose the Right Kind of Pipe Fittings?
To choose the right kind of pipe fittings consider the material size, compatibility and dimensions. Also know about the temperature and pressure ratings, and the requirements of your plumbing system. Select fittings that match the pipe diameter, material and intended use. Make sure the fittings can withstand the pressure and temperature conditions of the system and follow the relevant industry standards for safety and quality.
How to Identify the Pipe Fitting Size?
To identify pipe fitting size, measure the inside diameter of female threads or the outside diameter of male threads with a caliper or ruler. Subtract 1/4 inch from this measurement to find the nominal pipe size. Consult a pipe size conversion chart to match your measurement with the fitting nominal size for accurate results.
How to Choose the Right Material for Pipe Fittings?
Consider the operating temperature and pressure, fluid transported, corrosion resistance requirements and environmental factors. Match the fitting material to the pipe material for compatibility. Evaluate durability, ease of installation and cost-effectiveness for your particular use.




