A breaker box has circuit breakers, and a fuse box contains fuses. Both do the same job. They provide a weakness in an electrical circuit.
When there is a problem with the circuit, such as an overload or damaged wiring, the weak spot breaks, effectively protecting the circuit and the user.
Main Differences Between Breaker Box and Fuse Box

The Way They Break the Electrical Circuit
- Breaker box
Inside a breaker box are several rows of circuit breakers. Each row has a connection to the main electrical supply via a master circuit breaker. Smaller circuit breakers are connected to this via solid pins. Typically, the pins are connected across the top. This is where the load comes in.
Each of the smaller circuit breakers will have wires leaving from the base. Each circuit breaker represents one circuit in your home, such as lighting, or your living room power outlets.
Circuit breakers contain a magnet. Electricity passes through the magnet, completing the circuit. If the electrical current surges or reaches a dangerous level, the breaker will ‘trip’. In short, it will turn off.
You can turn it back on. However, if the fault isn’t resolved, it will simply trip again.
- Fuse box
Fuse boxes typically have a master fuse and between six and twelve standard fuses. As with a breaker box, the power to each fuse comes from the master fuse and the fuse will ‘blow’ when the circuit is damaged or overloaded.
The fuse is a cartridge. Inside is a metal wire or filament. When too much current goes through the wire, it will melt, effectively turning off the circuit. That prevents the overload from causing a fire or electrical injury.
The wire inside the fuse isn’t visible. While it is possible to check a fuse with a multimeter, once it has blown it will need to be replaced.
Which Faults are Detectable

- Breaker box
Circuit breakers can protect against ground faults, arcing issues, short circuits, and overloads. It’s possible to get double-pole, single-pole, molded cases, instantaneous trip, and others.
- Fuse box
A fuse can only detect current overload, caused by a faulty appliance, power surge, or even damage to the circuit.
In short, the circuit breaker detects a much wider range of faults than the fuse.
Level of Maintenance Required

- Breaker box
Circuit breakers are complicated inside. They use magnets and bimetal strips to ensure current issues are detected and issues prevented. Unfortunately, the greater the level of equipment, the more often it will need to be maintained.
A circuit breaker will have a 15-20 year life expectancy. However, they should be checked at least once a year
- Fuse box
Fuses in a fuse box are simply pieces of wire. It will last indefinitely unless blown. Fuses need no maintenance.
Replacement Period

- Breaker box
A circuit breaker can last 15-20 years. Unfortunately, it will degrade if it is tripped frequently, meaning it could need replacing sooner. The breaker box itself can last indefinitely.
- Fuse box
Fuses can be easily changed but they, and the fuse box, are made out of plastic which becomes brittle over time. This can cause them to fail and the entire fuse box will need to be replaced.
Pros and Cons of Breaker Boxes

When deciding which to offer your clients it’s worth noting that breaker boxes generally have more pros than cons.
Pros
- Fast
Circuit breakers use more advanced technology and tend to trip faster than fuses, increasing safety for consumers.
- Easy to reset
Resetting a circuit breaker is simple, just turn the switch from off to on. Of course, if the fault hasn’t been fixed it will likely trip again.
The ability to constantly reset the breaker can help you identify the fault.
- Multiple protection levels
There are many different types of circuit breakers, you can choose the one that suits the risk you’re dealing with. For example, you can choose between single or double pole, arc protection, surge protection, or ground protection. That’s just some of the options.
- Can be tested to ensure working
If you’re not sure whether a breaker is working you can simply press the test button or deliberately overload a circuit. You can then just reset the breaker.
Cons
- Shuts off the entire circuit
The most common cause of a tripped circuit breaker is a faulty appliance plugged into it. Unfortunately, when the breaker trips, it shuts the power to everything in the circuit.
You’ll need to figure out which appliance is causing the issue. Unplugging it should allow you to successfully reset the breaker.
This can be a real issue if the fault triggers the master breaker and all the power is down inside a house.
- Longer installation time
While breakers are generally considered superior to fuses, they do take longer to install. The casing will need to be removed to allow access to the breakers. In addition, the power will need to be shut off to allow the safe removal of the breaker and the installation of a new one.
- Can wear out faster than a fuse
Because fuses are essential a piece of wire they won’t wear out and can last for years. Circuit breakers can wear out if they are constantly tripped.
That’s an additional unwanted expense.
Pros and Cons of Fuse Boxes

Although older technology, it’s still permissible to fit fuse boxes. Some homes even have a breaker box and a fuse box. However, fuse boxes are older technology and the cons generally outweigh the pros.
Pros
- Lower cost
The cost of a fuse is significantly lower than a circuit breaker. It’s also much easier to install a fuse box, meaning less time on site for the electrician and a reduced cost for customers.
- No maintenance required
Fuses are very simple. If they aren’t blown then no maintenance is required.
- Can trip faster
This isn’t true of all fuses, but some are capable of tripping faster than a circuit breaker giving you additional protection. It will depend on the sensitivity level of your circuit breaker as to whether the wires in the fuse heat and melt before the breaker trips.
Cons
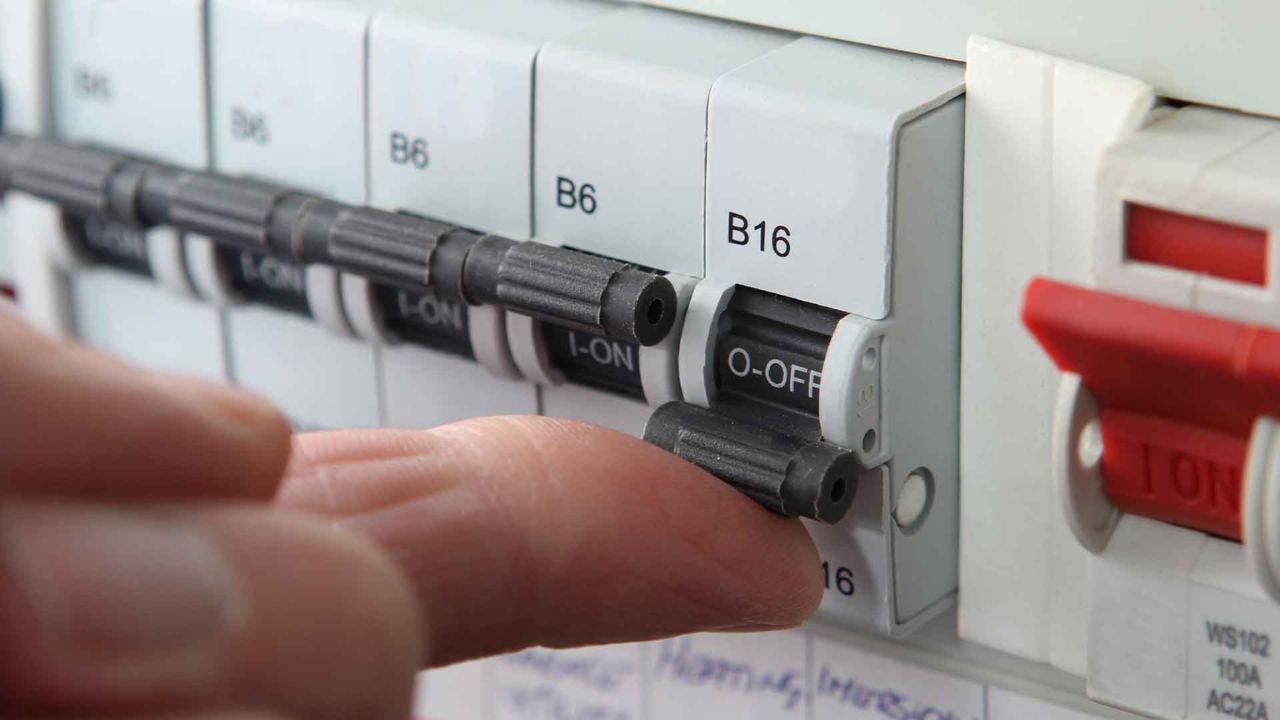

- Limited number
A fuse box can hold between six and twelve fuses. Modern wiring regulations require a fuse/breaker per circuit. That’s each room of the house, lights, exterior circuits, and individuals for heavy-duty appliances.
According to studies, the average home has between 20 and 30 breakers. A fuse box may not offer enough circuits to properly power your home.
Breaker boxes can have up to 42 circuit breakers.
- Needs replacing after blowing
Every time a fuse blows you need to remove the fuse and replace it. Homeowners may not wish to do this which means a call to an electrician and the purchase of an additional fuse.
Even if the homeowner can do it themselves, they may not have a spare fuse and the local store could be closed.
- Only offers thermal protection
Fuses offer thermal protection, that’s overloaded circuits. They don’t offer any of the other types of protection that you can get with circuit breakers.
- Replacing can be tedious and dangerous
Replacing a fuse requires you to remove the fuse and replace it. In principle, this is simple. However, fuses connect to the electricity supply, meaning that you can accidentally touch live parts.
The power must be shut off every time and proper precautions taken. It’s much more complicated than resetting a circuit breaker by flipping a switch.
- Larger wires
Fitting a fuse box requires additional space as the wires feeding to it must be larger than for a breaker box. This is to allow for inrush currents.
Conclusion

As a business, you need to be able to explain the differences between breaker boxes and fuse boxes to your customers. It also helps to understand the differences as this will help you select the right option for your consumers.
Remember, there is no right option, only the right option for your consumer. Weigh up all the pros and cons before deciding or making a recommendation.
FAQs
How many fuses can a fusebox accommodate?
Fuse boxes can handle up to 12 fuses. If the property needs more circuits than this you’ll either have to choose a breaker box or have a breaker box and fuse box working together.
Should the age of the property influence my decision?
The older the property the more likely needs a rewire. That’s an additional expense but the perfect time to switch to a breaker box.
Newer homes may not need rewiring, you can keep the costs down by choosing a fuse box, provided it will do the job properly.
How can I tell the fuse box needs replacing?
It likely needs replacing if the fuses are blowing regularly and there is no obvious reason for this.




