A breaker is a device incorporated into your electrical system as a safety mechanism.
One of the most common way to classify circuit breaker is the number of poles. Today, we are going to compare double pole and single pole circuit breakers.
From, basic definition, advantages, limitations to application, you will find all information right here:
What is a Double-pole Breaker?
This is a variation of the circuit breaker that is designed to provide protection for two circuits at the same time.
Featuring a double-switch toggle, this device occupies two slots in your system electric panel, and wiring the system requires a neutral wire and a pair of hot wires. Even if one of the hot wires is tripped, the other is automatically tripped.

What is a Single Pole Breaker?
Featuring an individual toggle switch, this breaker variation is most commonly utilized for small everyday appliances. Wiring requires one hot wire and its complimentary neutral wire, making it compatible with your standard electrical circuits. It is important to note that this breaker is compatible with only low-power systems.

Advantages
Both of these breaker variations offer you several benefits which can vary depending on the application of the device and the type of device. These benefits include;
Advantages of Double-pole Breaker
- This device provides you with complete disconnection as it functions by interrupting all its hot neutral wires.
- Complete disconnection is also advantageous because it removes the possibility of personnel getting electrocuted due to residual currents in the circuit.
- Designed to handle the increased voltage and current of 240 volts, this device is suitable for larger appliances. This increases the range of applications in which you can utilize the device.
- Given that the device is fitted with two separate breakers, this device helps you reduce the number of units required for larger systems. It halves the number of individual units required to ensure your electrical system is well protected.
- It also ensures that uniform protection is provided throughout the entire circuit as well as a collective of devices.
Advantages of Single-pole Breaker
- This breaker variation is more economical as it is much cheaper than its alternative. It provides you with a cost-effective method of safeguarding our circuits.
- Power is dispensed according to your device’s requirements, this helps optimize energy efficiency. It also reduces the overall power consumption which helps you save on energy costs.
- Featuring a singular switch regulating one circuit, the straightforward design does not require any skill and is easy to operate. Installing and maintaining the device is equally simple to undertake.
- In the event that the breaker is tripped, it is fairly easy to troubleshoot and identify the affected areas. This immediate feedback allows you to quickly rectify the affected areas.
- Designed for low-power systems, this device can be applied to a wide range of domestic appliances.
- If space is a limiting factor, this device features a compact design that allows you to integrate it in limited spaces.
Limitations
There are a few limiting factors that you may encounter when using either one of these devices. These factors include;
Limitations of Double-pole Breaker
- With its additional features, this variation occupies a larger space compared to its alternative. This can pose a challenge if your electrical system has smaller panels.
- Installing this device may require some skill as it is more complex in design. When installing you need to look out for size and configuration to ensure that is compatible with your system and can be safely integrated.
- Economically it may prove to be a challenge if you have a limited budget. The device costs more than its counterpart. Installing the device may require the help of experts which further drives up its overall cost.
- If you are using a low-power system, incorporating this device can be excessive. They are better suited for high-voltage systems.
- Complete disconnection can be limiting as a problem in one area will end up affecting the entire system. This can in turn cause your devices to malfunction.
Limitations of Single-pole Breaker
- Designed to process 120 volts, this breaker can only be used for low-power uses, which limits its range of applications to domestic uses.
- If you have a high-demand circuit, multiple units are required to make it functional. This can in turn drive up operation costs for such systems.
- The device’s safety features extend only to the individual circuit it is connected to. It cannot protect other devices even if they are connected.
- Space can be a limiting factor if you require more than one unit to maintain optimal functionality.
- There is a risk of the device being overloaded if you use too many devices at once. Overloading often leads to damage or reduced functionality of the device.
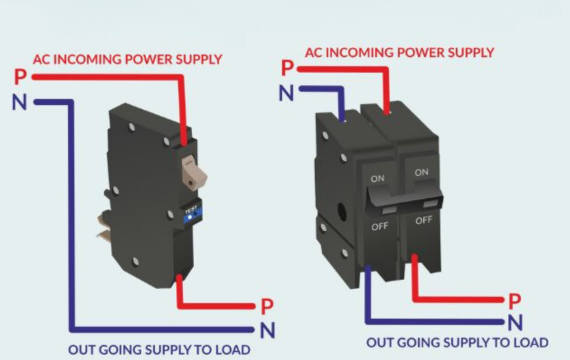
Double-pole vs. Single-pole Breaker Working Principle
Double-pole breaker design features a pair of integrated single-pole breakers that are each connected to a separate hot bus car.
Equipped with double units that also have two hot wires, the arrangement allows it to process 240- voltage making it compatible with high voltage systems.
It is important to note that both systems are linked. Therefore if a problem is detected in one unit both units are tripped leading to a complete shutdown of the systems.
On the other hand, the single variation comprises one hot and one neutral wire that is designed to handle 120- volts. It features a single switch and a slimmer design that allows it to be incorporated in limited space. It protects the circuit that it is directly connected to.
Comparing Applications
The applications of these devices are numerous and may vary with the type of breaker you have. Depending on the scale and demand of your system, you may need more than one unit of either one of the breaker variations. These applications include
Double-pole Breaker Applications
- Large Appliances
- Electric Ranges and Ovens
- Clothes Dryers
- Water Heaters
- Central Air Conditioning Units
- Heat Pumps
- Electric Furnaces
- Heavy Machinery
- Telecommunications Equipment
- Subpanels
- Solar Power Systems
Applications of Single-pole Breaker
- General indoor lighting
- Outdoor lighting
- TVs, computers, and small electronics
- Vacuums, hair dryers, and curling irons
- Power tools and air compressors
- General-purpose outlets
- Dedicated appliance outlets
Conclusion
It is important to consider all the advantages and limitations as well as key features of each breaker variation. This information is key as it will help you determine the most suitable device for your system. You should also consider their standard application as it helps guide you on the proper use of the device.
Related Resources:
How often to Circuit Breaker go Bad – Source: KDMFAB
What is Circuit Breaker Panel – Source: KDMFAB
DC Circuit Breaker – Source: KDMSTEEL
Static Circuit Breaker – Source: KDMSTEEL




