Hypodermic tubing refers to small-diameter, thin-walled stainless steel tubes that are mostly used in medical fields. These have wall thicknesses as minimal as 0.002″ and outer diameters ranging from 0.008″ to 0.072″. Usually made from 304 or 316L stainless steel, hypodermic tubing gives extraordinary corrosion resistance, strength and biocompatibility.
This tubing acts as the central component in catheters, hypodermic needles and other medical devices. It facilitates precise sampling or fluid delivery in these devices.
How is Hypodermic Tubing Manufactured?

The manufacturing of hypodermic tubing involves a complicated multi-stage process using precision engineering with strict quality control. Let’s discuss the important production stages:
- Raw Material Preparation: Producers select premium metal alloys like stainless steel (316 or 304) or polyethylene and shape them into hollow tubes with diameters larger than the end product.
- Cold Drawing: Next the tube is pulled through a series of progressively smaller diamond dies. This decreases its wall thickness and diameter.
- Annealing: Between drawing phases, heat treatment preserves tube ductility and decreases internal stresses for further processing.
- Precision Finishing: To acquire accurate outer diameters, centerless grinding is used with fine grits of abrasive material like aluminum oxide or silicon. Whereas electropolishing increases corrosion resistance and makes surfaces smooth.
- Quality Control: Thorough testing guarantees material integrity and dimensional accuracy. This stage also includes visual checks for defects like scratches or dents along with verifications for adherence to industry standards for technical and medical uses.
Types of Hypodermic Tubing Based on Different Variables

Hypodermic tubing differs greatly because of many important factors. These variations provide for distinct needs of medical and industrial areas. Here are some main types of tubing and their unique characteristics.
Materials
Austenitic stainless steels like 304 and 316L are the preferred materials for hypodermic tubing because of their good biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. For particular operations, manufacturers usually use materials like cobalt-chromium, Nitinol (NiTi) and titanium alloys. Each of these alternatives gives distinct advantages such as improved MRI compatibility, shape memory and increased strength.
Gauge Sizes
Hypodermic tubing gauge sizes range from 7G (largest) to 34G (smallest). The gauge number is inversely proportional to tube diameter. For example, 18G tubing has an outer diameter of 0.050 inches, while 30G has 0.012 inches OD. Accurate size hypodermic tubes are important in medical operations to guarantee patient comfort and proper fluid flow during procedures.
Table: Common hypodermic tubing gauge sizes and their outer diameters in inches and millimeters
| Gauge Size | Outer Diameter (inches) | Outer Diameter (mm) |
| 7 | 0.144 | 3.6576 |
| 10 | 0.109 | 2.7686 |
| 14 | 0.064 | 1.6256 |
| 18 | 0.040 | 1.0160 |
| 22 | 0.020 | 0.5080 |
| 26 | 0.010 | 0.2540 |
| 30 | 0.005 | 0.1270 |
| 34 | 0.0015 | 0.0381 |
Wall Thickness (Standard wall (RW), Thin wall (TW), Extra-thin wall (XX))

Wall thickness in hypodermic tubing varies largely. Standard wall (RW) thickness of 0.015 inches gives a balance between flow and strength, while thin wall (TW) tubing usually with 0.010-inch thickness increases the inner diameter for higher flow rates. Extra-thin wall (XX) tubing as thin as 0.002 inches gives the largest possible inner diameter. This is important for specialized uses like neurovascular devices and microcatheters.
Precision and Application-Specific Tubing
Precision hypodermic tubing is known for its strict tolerances mostly within ±0.0001 inches to cover special operation needs. Micro-tubing permits minimally invasive procedures like neurovascular interventions with diameters under 0.1 mm while high-pressure tubing with tolerances around ±0.001-±0.005 can handle pressures over 20,000 psi in HPLC systems and chromatography.
High-temperature tubing gets used in medical sterilization processes and surgical instruments as it can tolerate temperatures up to 500°F in medical operations.
Welded vs. Seamless Tubing

Welded tubing is generally fabricated by rolling flat stock and welding the seam and this method gives adaptability and cost-effectiveness in sizes. On the other hand, seamless tubing is drawn from solid bar stock. This tubing method provides better strength and uniformity.
Seamless tubing is mostly preferred for high-pressure uses while welded tubing is the right choice for lower-pressure needs. Welded tubing usually cost less than seamless tubing.
Applications of Hypodermic Tubing

These tubes are adaptable and used for different operations beyond medical applications. Its distinct properties and accuracy make it important for different industries. Now, we will cover the different uses of hypodermic tubing for different areas.
Medical Uses:
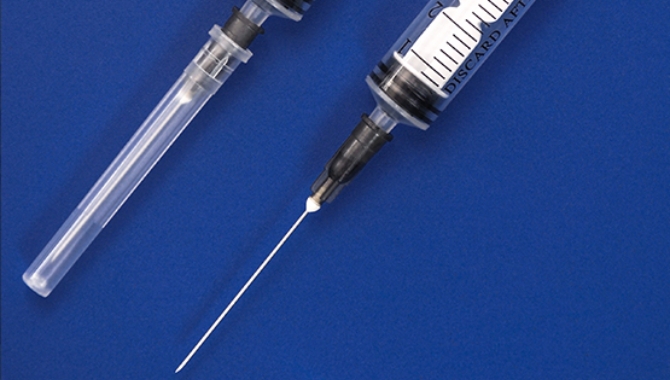
Needle Production
Hypodermic tubing is important for biopsy needles and syringe needles due to its smooth surfaces and precise dimensions. This facilitates accurate tissue sampling and painless injections in medical procedures.
Catheters and Cannulas
For epidural cannulas and central venous catheters, hypodermic tubing is frequently used. Its flexibility and precision provide accurate fluid delivery and drainage in anesthesia and sensitive care.
Surgical Instruments
Endoscopes and arthroscopic shavers use hypodermic tubing as its durability and small diameter contribute to visualization and accurate tissue removal during minimally invasive surgeries.
Non-medical uses:

Aerospace Fluid Transfer Systems
In hydraulic actuators and aircraft fuel systems, hypodermic tubing is mostly preferred. The accuracy and durability of these tubes guarantee reliable fluid transfer which is important for proficient and safe flight operations.
Chromatography and Lab Equipment
In autosampler needles and HPLC columns, hypodermic tubing’s 0.010″-0.030″ inner diameter allows precise sample handling. Its corrosion resistance also ensures accuracy in analytical chemistry uses.
Mechanical Cable Assemblies
Robotic surgical systems use hypodermic tubing for precise control due to its tight tolerances, high-strength properties and accurate transmission of the surgeon’s movements to laparoscopic instruments.
Custom Prototyping
Hypodermic tubing helps with rapid prototyping in microfluidic device development as its material flexibility and precise dimensions allow engineers to make custom flow channels for novel diagnostic tools.
Precision Instrumentation
Gas chromatography systems and Micro-pipettes depend on hypodermic tubing for accurate sample handling. There its smooth surface finish and accurate inner diameter give minimal contamination and consistent fluid flow.
Top 5 Benefits of Hypodermic Tubing

There are many advantages of this tubing that make it important for industrial and medical uses. We will cover its benefits one by one.
1. Precision
Hypodermic tubing shows tolerances as tight as ±0.0001 inches and gives fantastic accuracy. This guarantees constant outer and inner diameters which is very important for operations like microfluidics and drug delivery systems. Modern laser cutting technology is used to further increase its accuracy which allows complicated geometries and intricate shapes in medical devices.
2. Strength and Durability
With tensile strengths of 150 KPS, hypodermic tubing shows superb strength-to-weight ratios. The cold-working processes during manufacturing give hypodermic tubing amazing durability. Its ability to go through repeated sterilization cycles without structural damage increases its longevity and cost-saving value.
3. Biocompatibility
Hypodermic tubing is usually produced from 316 or 304 stainless steel as these materials have outstanding biocompatibility. They also help to decrease adverse reactions and resist corrosion in biological systems. Biocompatibility is vital for long-term medical operations, implantable devices and drug delivery systems. It permits prolonged contact with fluids and tissues without compromising patient health or device functionality.
4. Customizability
In hypodermic tubing, manufacturers can change hardness levels, OD and ID dimensions and wall thicknesses to meet accurate specifications. Advanced production methods also allow custom lengths up to 2 meters, mirror-finish IDs and electro-polished ODs. This flexibility allows for operation-specific designs in both industrial and medical components.
5. High Tolerance
Hypodermic tubing sets itself apart due to its ability to reach outstanding tolerances. It can attain ID tolerances of +0.001/-0.0005 inches and OD variations of ±0.0005 inches. This level of precision guarantees constant performance in instruments like microfluidic devices, drug delivery and neurovascular interventions. It also allows smooth integration of hypodermic tubing with other components. This makes it suitable for high-precision medical tools like minimally invasive surgical instruments and biopsy needles.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Hypodermic Tubing

Choosing the right hypodermic tubing is very important for better performance. Some important factors to consider when selecting are:
Material Choice
For general medical uses, stainless steel (304/316) gives great corrosion resistance and nitinol provides super elasticity. This elasticity is very useful for intricate anatomies. Titanium is generally appropriate for aerospace operations because of its better strength-to-weight ratio. When you are choosing materials for medical devices, consider compliance with regulatory standards like ASTM F138 or ISO 10993, biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
Gauge Size and Wall Thickness
Hypodermic tubing comes in a broad range of gauge sizes from 7 (largest, 0.180″ OD) to 34 (smallest, 0.007″ OD). Larger gauges are usually best for sampling and fluid transfer, while smaller ones are preferred for precise microinjections. Wall thickness options are TW, RW and XTW. Regular Wall is for strength, Thin Wall is suitable for adaptability and Extra Thin Wall is selected for increased flow.
These specifications also adhere to standards like ISO 9626 or ASTM A908 for medical devices to meet different application needs.
Temper
The temper of hypodermic tubing greatly determines its mechanical properties. Full-hard temper is suited for needles as it provides maximum rigidity and strength. On the other hand, quarter-hard temper gives balance between formability and strength. This makes it appropriate for bent components. For complicated forming processes, soft or annealed tempers give the highest ductility.
Conclusion

Hypodermic tubing is very important in different fields as it gives strength, precision and adaptability. Its different operations range shows its importance in aerospace, laboratory machines and medical devices. Learning about its different types, manufacturing processes and materials guarantees better selection for your particular needs and will increase product reliability and performance.
If you need guidance and skilled advice on hypodermic tubing procedures, consider KDM fabrication. Contact us today to discuss your particular needs and projects.
FAQs
Can hypodermic tubing be customized?
Yes, hypodermic tubing can be customized. Manufacturers offer different tempers, sizes and materials according to your particular application needs. Coatings and custom surface treatments are also available.
How is hypodermic tubing sized?
It is sized using gauge numbers which indicate the outer diameter. Lower gauge numbers represent larger diameters and the wall thickness of tubing is specified separately, for example, TW, XTW and RW.




