Although you might overlook the magnetic capabilities of aluminum, you cannot downplay the number of aluminum components you interact with daily.
Well, the magnetic traits of aluminum have been a source of controversy prompting scientists to study this metal more keenly.
In this article, we dig deeper into it in an attempt to answer your question, is aluminum magnetic or non-magnetic?
How Magnetic is Aluminum?
Aluminum boasts a range of impressive features including:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Good conductivity

Another feature contributing to aluminum metal tremendous usage is its magnetic capabilities or lack of.
Aluminum alongside other prominent metals like platinum and titanium falls under a unique category of magnetic materials. They are referred to as paramagnetic materials and they are characterized by a relatively weak pull to a magnetic field.
This unique aluminum magnetic behavior is a consequence of the solitary electrons that make up their energy orbitals.
Compared to ferromagnetic metals like iron magnetism or even nickel magnetism, aluminum’s magnetic properties are significantly inferior.
For instance, when you put an iron bar and an aluminum sheet within the vicinity of a relatively strong magnet, only your iron bar will be attracted. However, when you put your thick aluminum sheet next to a strong magnet, it will be attracted, although subtly.
Despite aluminum’s subtle magnetic attributes, it boasts a higher magnetic affinity compared to diamagnetic metals like silver. These metals, which also include copper experience reverse attraction when placed within the vicinity of a magnetic field irrespective of its strength.
Aluminum Magnetic Properties
· Subtle Pull
Whenever you place a piece of aluminum within the confines of a strong magnetic field, it will be gently attracted to the source. This is because the magnetic moments of aluminum are naturally misaligned.
· Positive But Relatively Low Magnetic Susceptibility
Aluminum magnetic susceptibility to the attraction of a strong magnetic field is quite low but positive. This means that your aluminum piece gets magnetized although temporarily.
· Temporary Magnetism
As you pull your aluminum sheet further away from the magnetic field, it loses its magnetic capabilities. This is a consequence of the moments’ misalignment experienced.
· Thermal Stability
Subjecting your magnetized aluminum piece to heat results in the loss of its magnetic capabilities. Heat disorients the aluminum’s magnetic moments.
Factors Affecting Aluminum Magnetic Properties
A change in conditions such as temperature can boost or shrink the magnetic attributes of your aluminum piece. These conditions include;
· Magnetic Field Strength
Your aluminum sheet’s magnetization is only as strong as the external magnetic field you have exposed it to. As the field grows weaker, your sheet’s magnetization weakens in equal measure.
· Crystal Structure
The only reason behind your aluminum’s subtle magnetic capabilities is the partial alignment of its dipoles. A change in its crystal structure that may result in the misalignment of these dipoles further weakens its paramagnetic ability.
· Temperature
Heating your aluminum sheet disorients the harmonized dipoles resulting in the loss of its magnetic response.
· Presence of Impurities
Foreign elements can positively or negatively alter the magnetic response of your aluminum piece. Some impurities for instance iron elements can boost its magnetic properties while others may shrink it significantly.
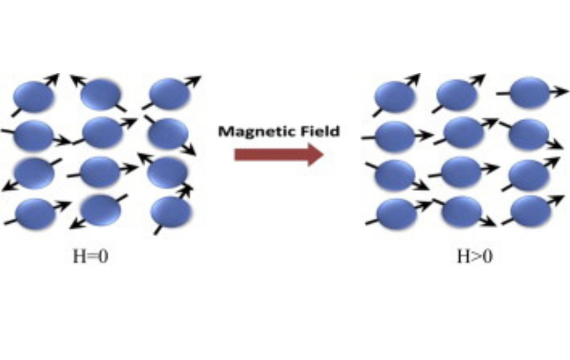
Aluminum as a Paramagnetic Material
Try placing a small aluminum sheet a few inches from a permanent magnet, then try the same with a small iron bar.
What do you notice?
The iron bar gets drawn to the magnet while the aluminum sheet most likely remains motionless. This phenomenon is the reason why aluminum is considered a paramagnetic material.
Paramagnetism captures the magnetic response of your aluminum piece in a nutshell. It categorizes materials with one or several unpaired electrons.
For instance, aluminum boasts of one unpaired electron and this explains its comparatively low magnetic susceptibility and response.
Other paramagnetic materials with more unpaired dipoles exhibit stronger magnetic responses, for example, titanium, which has two.
Magnetic Properties of Aluminum Alloys
At first glance, you might discard what aluminum has to offer when it comes to magnetism. In its natural form, this indispensable metal’s magnetic response is virtually imperceptible. However, once you spice it with other elements, its magnetic properties improve as illustrated below;
· Alnico
This aluminum alloy features iron and cobalt, which possess relatively impressive magnetic properties. As such, this alloy exhibits a higher magnetic response as well as coercivity hence it is classified as a ferromagnetic material. However, you cannot attribute this solely to aluminum magnetism.
· Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys
Despite the inclusion of magnesium, these alloys exhibit paramagnetic properties. This is because magnesium is also paramagnetic and does not possess any significant magnetic capabilities.
· Aluminum-Iron Alloys
Depending on the composition, your iron-aluminum alloy will demonstrate significantly impressive magnetic abilities. This is a result of the inclusion of iron, which is highly magnetic.
· Manganese-Aluminum Alloys
These alloys stand out when it comes to magnetic attributes due to their strength and corrosion resistance. You can also procure them at a relatively lower price point despite their comparatively superior magnetic susceptibility.
Applications of Non-magnetic Aluminum
Despite demonstrating inferior magnetic attributes, aluminum continues to find great usage in our daily lives. It is a revered material for:
- Magnetic shielding
- Alloy production
- Computer hard drives
- Aerospace components
- Electronic enclosures
- Food packaging
FAQs
1. Will a Magnet Stick on Aluminum?
Once you bring a magnet close to an aluminum piece, you are likely to experience little to no magnetic response. This is because aluminum in its purest form possesses weak magnetic properties.
2. Is Aluminum Magnetic or Non-magnetic?
Aluminum is paramagnetic. This means that it is largely non-magnetic but can respond to a magnetic field although very weakly. It is not as magnetic as iron nor is it as non-magnetic as silver.
3. How can you make a Magnet Stick on Aluminum?
Despite its low magnetic susceptibility, you can still strengthen aluminum’s magnetic response. Simply, combine it with ferromagnetic elements like cobalt and iron and it will become more responsive to magnetic fields.
4. How Does Aluminum Behave in a Magnetic Field?
Once you place a piece of aluminum at the center of a magnetic field, you will notice very weak attraction. In some instances, you might not even notice this pull. This explains the inferior magnetic response of aluminum.
5. Can Aluminum Become Magnetic?
Yes. Even in its purest form, aluminum exhibits positive receptivity to magnetization. And when you spice it up with magnetic elements, you improve its magnetic susceptibility tenfold.
Conclusion
Although its magnetic response can be so low to the point that you may not even notice it without a machine, aluminum still exhibits some magnetic properties. Its paramagnetic nature continues to drive its use in applications that necessitate magnetic shielding such as food packaging and electronic enclosures production.




