Finding an ordinary metal with excellent resistance to heat and corrosion is not the easiest of tasks.
This has prompted the generation of a superalloy that thrives even in the toughest environments. This alloy is Inconel, which we will discuss in detail below.
What is Inconel Metal?

Inconel is a distinct alloy that stands out for its immense strength and unrivaled ability to resist rusting and remain stable even under unfavorable heat conditions.
The impressive features of this robust nickel-chromium alloy have seen it gain tremendous reverence in the aerospace and nuclear energy industries.
History of Inconel

The world’s search for an extremely robust material capable of enduring the heat of rocket engines bore fruits in the 1930s when Inconel was invented.
This historic invention was spearheaded by the International Nickel Company (INCO), who experimented by manipulating the composition of nickel-based alloys.
Although the first grade of Inconel invented was used to manufacture milk cans, this changed rapidly thanks to its impressive properties. This superalloy quickly found its way into nuclear reactors and rocket components due to its strength and distinct mechanical properties.
At present, Inconel is a household name reigning supreme in distinct applications ranging from the oil and gas industry to the nuclear energy industries. Newer variations of the alloy have popped up, furthering its application beyond your imagination.
Chemical Composition of Inconel
Components deployed in the marine industry must exhibit tremendous tolerance to pressure while those deployed in the aerospace industry must demonstrate strong heat resistance.
This means that they must be manufactured from a super-strong material and Inconel is one distinct material that demonstrates these attributes. This is often a consequence of its makeup, which includes;

- Nickel: This is essentially the captain of the Inconel ship. The majority of Inconel alloys you come across are likely to depict a 50%-76% nickel composition. Nickel ensures that your alloy remains stable irrespective of the fluctuations in the respective thermal conditions. This element equips your Inconel alloy with;
- Corrosion resistance.
- Heat resistance
- Thermal stability.
- Excellent oxidation.
- Chromium: Typical Inconel alloys boast of a chromium composition ranging from 15%-30%. This makes it the second in command only inferior to nickel. It is primarily responsible for the impressive endurance your Inconel alloy demonstrates against corrosion and oxidation. It is also responsible for;
- Forming a protective layer.
- Improving its oxidation resistance.
- Enhancing its corrosion resistance.
- Titanium: Although titanium is not featured in all Inconel alloys, its presence in certain alloys helps enhance their mechanical strength. It features mainly in Inconel 718 at a composition range of 0.6-2.5%. Inconel alloys endowed with titanium exhibit the following attributes;
- They are comparatively harder.
- They have better oxidation resistance.
- They remain stable even under extreme heat.
- Molybdenum: This element features consistently in multiple Inconel alloys at a concentration ranging from 3%-10%. Its inclusion is designed to make your material impervious to crevice corrosion. It also makes your Inconel material impervious to pitting. Inconel grades with a high molybdenum concentration boast of;
- Pitting resistance in chloride environments.
- Crevice corrosion resistance.
- Enhanced strength even under high temperatures.
- Niobium: Niobium is only present in a myriad of Inconel alloys and its addition is primarily responsible for steadying the material’s structure. One reputable Inconel grade that features niobium is Inconel 718 at approximately 5%. Niobium helps your Inconel alloy by enhancing its;
- Age hardening.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Structure irrespective of the thermal conditions.
- Iron: Iron is a consistent feature in most Inconel alloys and it primarily equips your alloy with better tensile strength. In most alloys, it is added at a concentration ranging from approximately 5-10%. Its inclusion is also designed to lower Inconel’s price. It is also responsible for;
- Strengthening mechanical properties.
- Making your Inconel alloy tougher.
- Enhancing tensile strength.
- Cobalt: Cobalt is primarily added to Inconel alloys meant to be subjected to high temperatures. Its composition is often approximately 1-3% and this helps Inconel materials retain their integrity irrespective of the extremity of the operational conditions. It contributes to;
- Mechanical strength even at high temperatures.
- Stability during thermal cycling.
Types of Inconel Metal
Inconel remains a consistent feature in most high-temperature components but are you aware that it comes in different grades?
The uniqueness of each application demands a tailored Inconel grade. Here are the main Inconel metal grades and their respective properties.
· Inconel 600:

This grade has been in use for decades and is revered for its ability to endure tough thermal conditions without suffering oxidation or corrosion. It has found great usage in applications synonymous with high temperatures including furnace components and nuclear reactors. Inconel 600 is characterized by the following composition;
- Nickel: 72-76%.
- Chromium: 14%-17%.
- Iron: 6-10%.
· Inconel 601

This grade is largely similar to its Inconel 600 counterpart. It is, however, characterized by a higher carbon concentration, making it resistant to thermal shock. It thrives in high-temperature applications and this explains its extensive use in heating elements and gas turbines. Its specific composition is;
- Nickel:58-63%.
- Chromium: 21-25%.
- Aluminum:1-1.7%.
- Iron: 8%.
· Inconel Alloy 617

This Inconel grade boasts a high endurance to oxidizing media making it perfect for turbine blades, heat exchangers, and reforming furnaces, among others. It is also endowed with a high-temperature resistance, meaning it can endure temperatures exceeding 980°C. You can weld it easily using conventional means and tools. Here is its composition:
- Nickel: A minimum of 44.5%.
- Chromium: 20-24%.
- Molybdenum: 8-10%.
- Cobalt: 10-15%.
- Iron: A maximum of 3%.
- Carbon: 0.005-0.15%.
· Inconel 625
This Inconel metal type is synonymous with excellent fabricability, which makes it easier to weld. Its endurance of fatigue, pitting, and crevice corrosion has seen it broadly utilized in chemical processing plants, aerospace, and offshore structures.
It contains a comparatively higher concentration of molybdenum thus making it more resistant to pitting than other grades. Here is its composition:
- Nickel: A minimum of 58%.
- Chromium: 20-23%.
- Iron: A maximum of 5%.
- Molybdenum: 8-10%.
- Carbon: A maximum of 0.10%.
- Niobium: 3-4%.
· Inconel Alloy 686

This is an advanced single-phase alloy renowned for its resistance to rusting. This has seen it thrive in environments synonymous with corrosive elements like acids and other aggressive chemicals.
It boasts a comparatively superior nickel and manganese concentration, which contribute greatly to its high pitting resistance. Its composition is as follows:
- Nickel: 57%
- Chromium: 19-23%
- Molybdenum: 15-17%
- Tungsten: 3-4.4%
- Iron: A maximum of 2%
- Manganese: A maximum of 0.75%
· Inconel 690
Inconel 690 is mainly utilized in applications that demand a high resistance to aqueous media and strong metallurgical stability. This explains its broad usage in acid production, particularly nitric and sulfuric acid. It features a considerable amount of chromium making it oxidation resistant while its high nickel concentration enhances its corrosion resistance. Here is its composition:
- Nickel: A minimum of 58%.
- Chromium: 27-31%.
- Iron: 7-11%.
- Silicon: A maximum of 0.50%.
- Carbon: A maximum of 0.05%.
· Inconel 700
This Inconel metal type is typically manufactured using the Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD), which endows it with superior age-hardenability. It is exceptionally resistant to stress rupture and its thermal stability is as high as that of other Inconel alloys. Inconel 700 boasts an exceptional tensile strength and its composition is as follows;
- Nickel: 46%.
- Chromium: 15%.
- Cobalt 28.5%.
- Titanium: 2.2%.
- Molybdenum: 3.37%.
· Inconel Alloy 706
The Inconel 706 has stood out for years thanks to its impeccable mechanical strength coupled with superior machinability. It is also revered for its precipitation hardenability, which can be attributed to the substantial concentrations of titanium and niobium. This alloy is a household name in the aerospace industry, particularly in manufacturing turbine discs and engine mounts. Its composition is as follows;
- Nickel and Cobalt: 39-44%.
- Chromium: 14-17%.
- Titanium: 1.5-2%.
- Niobium: 2.5-3.3%.
· Inconel 718
This is an age-hardenable Inconel alloy suitable for applications that operate at temperatures ranging from -252.78°C to 704.44°C. It is highly resistant to post-weld cracking meaning you can machine it into unique and complex components of your choice. It is commonly utilized to manufacture parts and machinery used in liquid-fueled rockets and aircraft components. It features the following elements:
- Nickel: 50-55%.
- Chromium: 17-21%.
- Niobium: 4.75-5.5%.
- Molybdenum: 2.80-3.30%.
- Cobalt: A maximum of 1%.
· Inconel 713C
This alloy has proven its worth across multiple industries due to its impressive structural integrity and outstanding castability. Components made of Inconel alloy 713C demonstrate unrivaled durability even under tough conditions like extreme temperatures. However, when welding this alloy, you should pay special care to avert cracking. Inconel 713C comprises of;
- Nickel: 70-75%.
- Chromium: 12-14%.
- Molybdenum: 4-5%.
- Aluminum: 5.5-6%.
- Titanium: 0.5-1%.
- Carbon: 0.12%.
· Inconel 722
If you are looking for the perfect material for components that will be exposed to harsh conditions like high temperatures (over 704°C), Inconel 722 is your pick. It demonstrates great resistance to creep distortion as well as corrosion and oxidation. It also leaves you with room to elevate its hardness. This can, however, be a challenge during machining. It consists of;
- Nickel: 55-60%.
- Cobalt: 10-15%.
- Chromium: 14-16%.
- Niobium: 2-3%.
- Molybdenum: 3-4%.
- Aluminum: 1-2%.
- Titanium: 2.5-3.25%.
- Carbon: 0.02-0.08%.
· Inconel 725
This alloy remains revered because of its hardness, which is ordinarily imparted using heat treatment. This means that you are less likely to experience cracking during machining. It is also quite resistant to reducing media thanks to the inclusion of molybdenum in its composition. Inconel 725 finds extensive usage in the oil and gas industry since it can withstand the aggressive nature of hydrogen sulfide. Its makeup comprises;
- Nickel: 55-59%.
- Chromium: 19-23%.
- Molybdenum: 7-9.5%.
- Niobium: 2.75-4%.
- Titanium: 1-1.7%.
- Aluminum: A maximum of 0.35%.
- Carbon: A maximum of 0.03%.
· Inconel Alloy 740H
This top-tier Inconel alloy reigns supreme in steam power plants and turbine systems among other harsh environments. This is a consequence of its stable microstructure and exceptional oxidation resistance. Its thermal stability permits its use in high-temperature environments even higher than 760°C. Its makeup comprises of;
- Nickel: 42-50%.
- Chromium: 24-26%.
- Titanium: 1.8-2%.
- Cobalt: 19-21%.
- Molybdenum: 1.5-2%.
- Niobium: 1.5-2%.
- Aluminum: 0.5-1.2%.
- Carbon: 0.03-0.08%.
· Inconel X-750
This Inconel metal type features traces of titanium, hence it often exhibits superior hardness and mechanical strength. It is easily found and commands a comparatively lesser fee. Its usage transcends airframe applications, forming tools, and gas turbines. The Inconel X-750, however, necessitates specialized tooling and know-how due to its rigidity. Its composition comprises;
- Nickel: 70%.
- Chromium: 15-17%.
- Iron: 5-9%.
- Titanium: 2.25-2.75%.
- Aluminum: 0.4-1%.
- Niobium: 0.7-1.2%.
- Molybdenum: 0.5-1%.
- Carbon: A maximum of 0.08%.
· Inconel 783
This alloy has not been in the market for long but it continues to draw great demand from multiple industries thanks to its oxidation resistance. It is characterized by niobium and aluminum additions. However, its thermal expansion is comparatively lower than that of its 718 counterparts.
The Inconel alloy 783 is quite prominent amongst material engineers who utilize it to manufacture casings, exhaust systems, and casings. It can, however, have you digging deeper into your pockets due to its sophisticated makeup. It consists of;
- Nickel: 26-30%.
- Chromium: 2.5-3.5%.
- Iron: 24-27%.
- Cobalt: 25-30%.
- Aluminum: 5-6%.
- Titanium: 0.1-0.4%.
· Inconel 825

This is a distinct Inconel alloy that favors corrosive conditions or environments. Its structure and makeup are uniquely designed to endure corrosion and cracking. It is specially injected with titanium and copper making it quite durable and robust. It is a mainstay in marine engineering, particularly the construction of components that come into contact with salt water. Its makeup comprises;
- Nickel: 38-46%.
- Chromium: 19.5-23.5%.
- Iron: A minimum of 22%.
- Molybdenum: 2.5-3.5%.
- Titanium: 0.6-1.2%.
- Copper: 1.5-3.0%.
· Inconel Alloy 903
This high-strength Inconel metal type thrives in the production of ordnance hardware and rocket-engine thrust chambers. It has the unique ability to preserve its dimensional stability, which is a result of its low CTE. Its toughness coupled with its comparatively higher price point has however limited its usage. The Inconel 903 features the following elements;
- Nickel: 36-40%.
- Niobium: 2.4-3.5%.
- Cobalt: 13-17%.
- Titanium: 1-1.85%.
- Aluminum: 0.3-1.15%.
· Inconel Alloy HX

This matrix-stiffened alloy is known for resisting oxidation and its ability to sustain its strength even at temperatures as high as 1200°C. Components made from Inconel alloy HX demonstrate a high level of stability making this alloy grade one of the most sought-after grades. It is perfectly suited for combustion chambers and gas turbine engines. It is easy to fabricate and its composition includes;
- Nickel: 47-52%.
- Carbon: 0.05-0.15%.
- Iron: 17-20%.
- Silicon: A maximum of 1%.
- Molybdenum: 8-10%.
- Cobalt: 0.5-2.5%.
Inconel Material Manufacturing
Quite often, the stand-out quality and performance of Inconel components are attributed to the unique makeup of this superalloy. However, their distinct production techniques are equally responsible. These methods include;
Forging
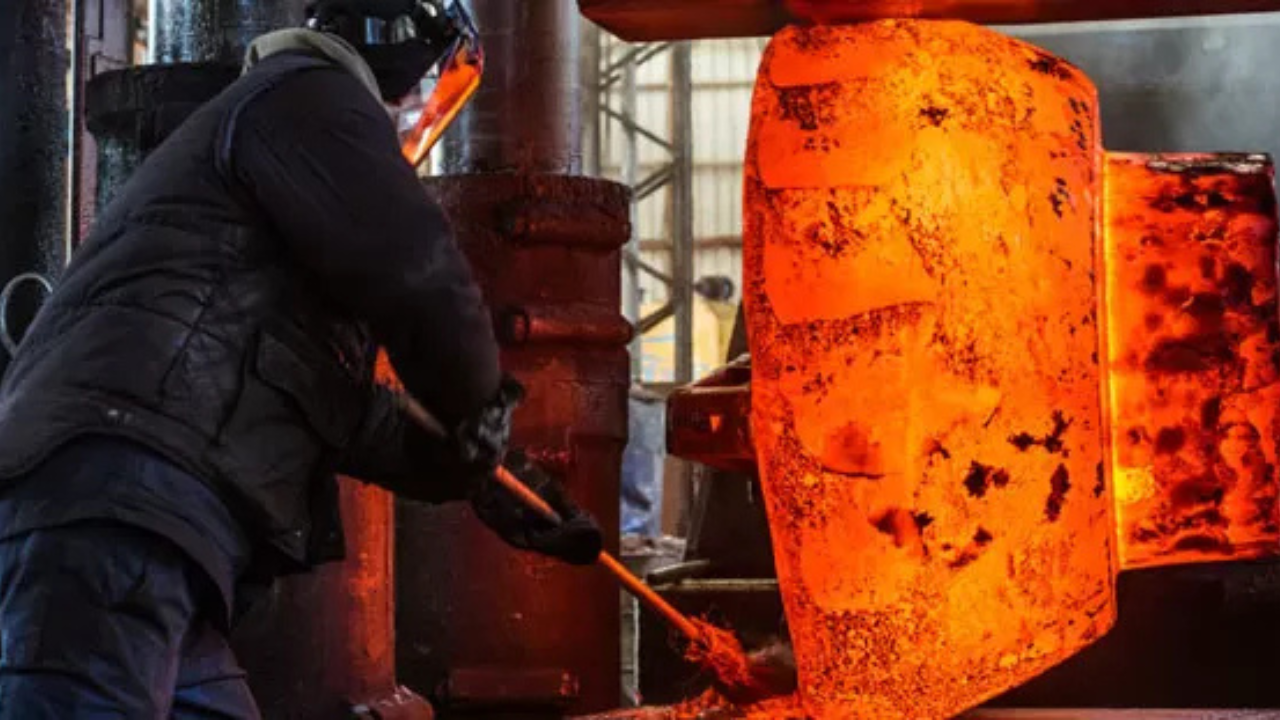

This Inconel manufacturing technique promises to deliver Inconel components with minimal defects. It relies on heat and mechanical pressure, which ensures that your components are perfectly formed. Additionally, it strengthens your component’s structure thus making them suitable for use in demanding environments.
Powder Metallurgy
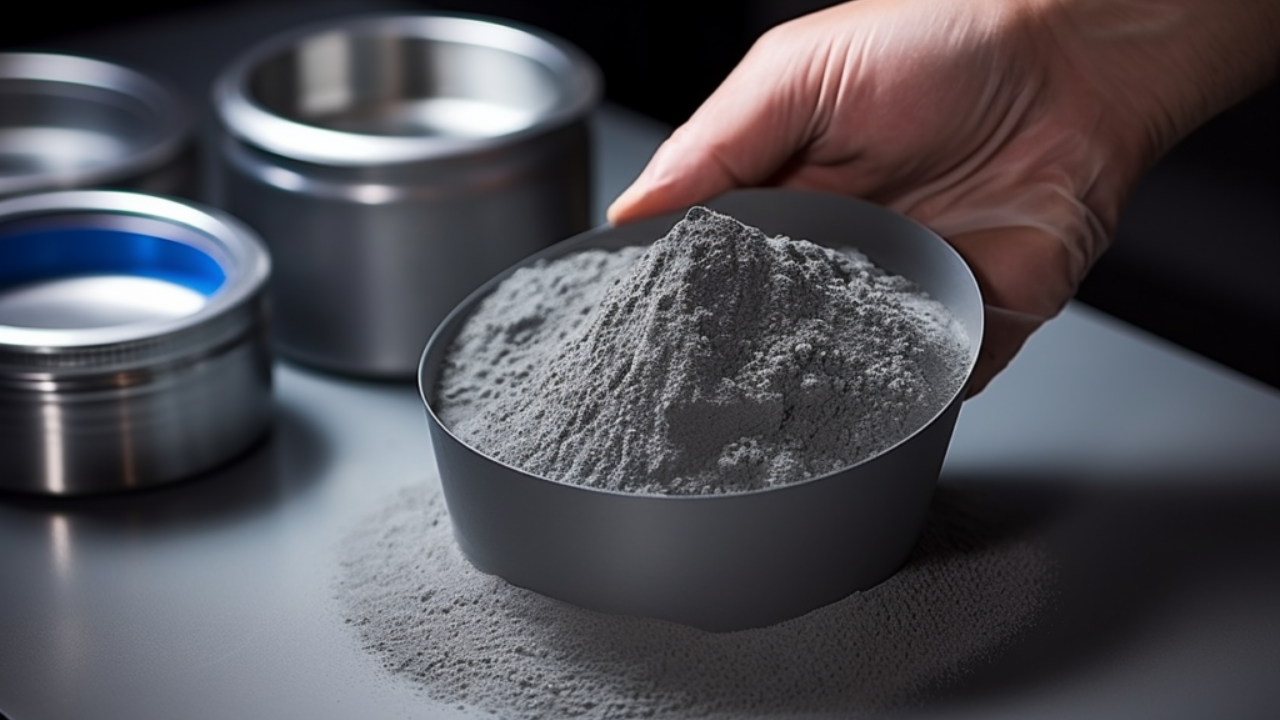

This is a prominent method and it involves bonding Inconel powder using heat. It generates Inconel components characterized by toughness and a strong microstructure. These components boast a near-perfect but it may necessitate a complementary manufacturing process like hot isostatic pressing.
Machining Processes
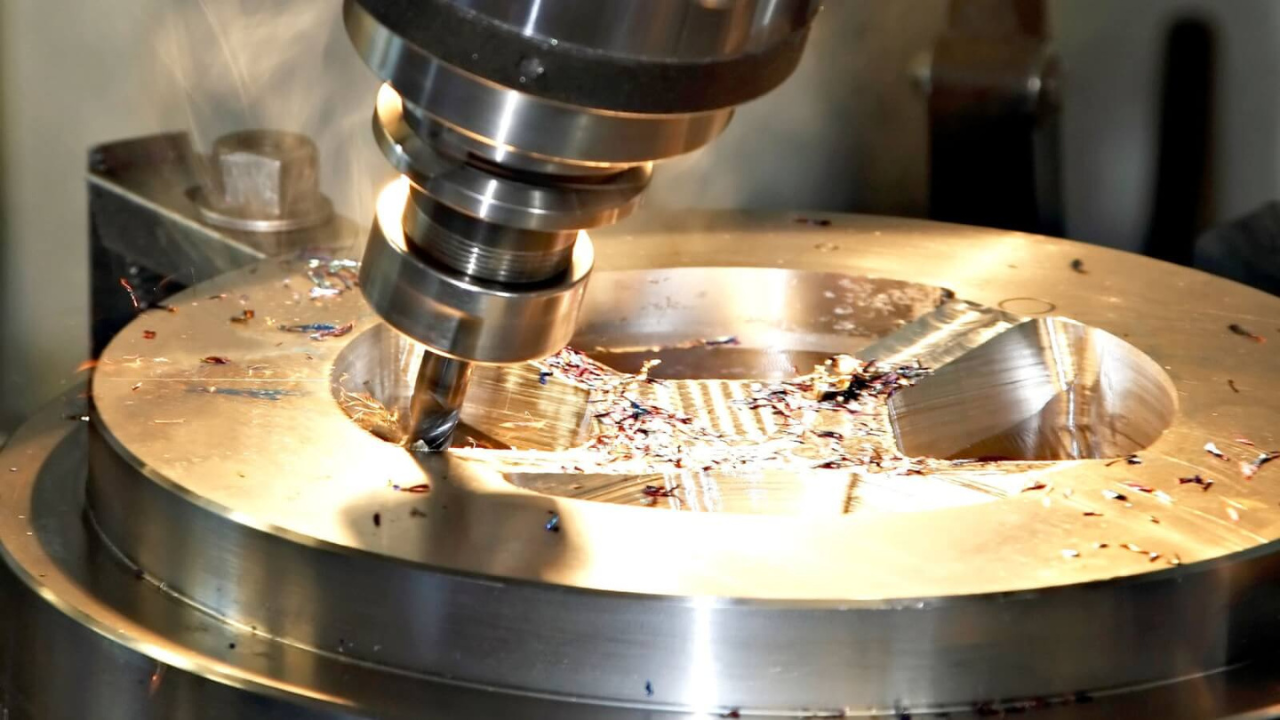

This Inconel manufacturing process has been greatly exploited over the years courtesy of the smooth surfaces it attains. It simply involves shedding off unwanted material from an Inconel raw material. The only downside associated with this method however is the frequent wearing off of the used machining tools.
Welding

This process permits you to fabricate sophisticated Inconel components with impressive properties such as high toughness. However, the toughness of this alloy means that you can only utilize specialized welding techniques. They include;
- Gas Metal Inert Gas Welding: This welding technique prospers when fabricating thick sheets of Inconel workpieces. It relies on an electric arc and you must be extremely cautious to avert cracking.
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding: This welding method relies on a distinct shielding gas such as helium coupled with a non-consumable electrode, which generates an electric arc. This allows for the production of exceptional Inconel components in a quiet environment.
Properties of Inconel
The ability to endure corrosive elements and scorching heat are just some of the primary attributes engineers and manufacturers look for in raw materials.
Inconel possesses these attributes as well as other desirable attributes making it an in-demand commodity. These features are:
Inconel Hardness
Inconel is naturally a very hard and tough metal alloy although its hardness is dependent on its constituents and their respective concentrations.
For instance, Inconel grades with traces of titanium will demonstrate higher hardness levels. You can make your Inconel workpiece or component harder by further subjecting it to additional heat treatment processes.
Inconel Thermal Conductivity
This alloy usurps a myriad of other materials when it comes to thermal conductivity and heat dissipation. Its configuration allows heat movement making it possible for you to produce heat exchangers and furnace components.
Inconel Heat Resistance
Some of the primary components that make up Inconel are nickel, iron, and chromium. These elements are renowned for their impeccable heat resistance and this is often exhibited in the resulting components.
This property explains the extensive use of Inconel in aerospace components as well as exhaust manifolds.
Inconel Tensile Strength
Inconel components boast of robustness that allows you to utilize them in applications where they will be subjected to extreme pulling forces. This is thanks to their impeccable tensile strength, which can be as high as 180 Ksi.
Usually, this is significantly higher than that of other materials explaining the use of Inconel in pressure vessels.
Inconel Wear Resistance
The fine-grained structure of Inconel coupled with its hardened surfaces contributes to the exceptional wear resistance of this alloy. This explains the unrivaled durability of Inconel components even when frequently exposed to harsh conditions. This permits you to use Inconel to manufacture valves and cutting tools among others.
Inconel Corrosion Resistance
Inconel, specifically Inconel alloy 718 and 625 are not only resistant to acidity-linked corrosion but are also resistant to stress corrosion cracking. This means that you can still use your component even in corrosive environments. Thanks to this property, Inconel is broadly exploited in the marine field and the petrochemical industry.
Testing the Key Properties of Inconel
To ascertain the quality of Inconel, you must examine some of its essential features. Simply employ either of the following tests.
- Chemical Composition Test: This analysis should give you a glimpse of the distinct elements contained in the Inconel as well as their respective concentrations.
- Welding Test: This test attempts to establish certain qualities including hardness and tensile strength by examining the welded joints of your Inconel component.
- Metallographic Test: This test necessitates the use of a microscope to determine the Inconel’s grain size and structure.
- Mechanical Test: Mechanical tests encompass a myriad of tests including hardness testing and tensile strength testing. They help you establish essential mechanical qualities possessed by your workpiece.
Inconel Welding Process
Inconel’s reinforced strength and resilience are responsible for the tremendous upsurge in its demand. However, these same qualities have raised issues regarding its weldability. To bypass the trickiness of welding Inconel alloys, follow the underlying steps.
- Prepare Your Inconel: Begin by dislodging the dirt on your Inconel workpieces and focus more on the surfaces or ends you intend to weld. Furthermore, grind both ends to create a rough and consistent surface, which will facilitate seamless welding.
- Select Your Ideal Welding Process: Subsequently, assess your Inconel material and consider your desired end results before choosing your perfect Inconel welding technique. You may choose from;
- Plasma arc welding.
- Tungsten inert gas Welding.
- Metal inert gas welding.

Kindly note that most welders prefer TIG welding.
- Set Your Welding Parameters: To accomplish seamless Inconel welding, you must set your welding parameters accordingly. For instance, if you are utilizing TIG welding, make certain you set your voltage and current as per your recommendations. You will also need to adjust the gas flow rate as well as your electrode travel speed.
- Weld Your Inconel Workpiece: Begin welding your constituent by making a rough cut known as the root pass. This will allow you to achieve deeper penetration in the subsequent passes. Then, using a bigger electrode, widen or deepen your root pass until you achieve your desired weld finish.
- Post-Treat Your Weld: Once you are done, subject the welding area to a consistent and controlled amount of heat for a while. This will alleviate stress imposed on the respective surfaces during welding.
Steps in the Inconel Machining Process
Assertions have been made that machining Inconel is a notoriously daunting task. Although there is some truth to that, you will find machining Inconel easier once you equip yourself with the right expertise and machinery.

- Get the Right Machining Tool: Inconel is not your typical metal material hence it demands specialized machining tools. You will need a tool capable of enduring the material’s toughness and abrasiveness. Good examples of these tools are;
- Carbide tools.
- Ceramic inserts.
- Coated tools.
- Prepare Your Workpiece: First, settle on an Inconel metal type or grade that best suits your intended application. Then, examine your Inconel metal to ascertain it is not defective before clamping it onto your machining tool.
- Set Up Your Machine: Now, proceed to adjust the machining settings on your machine. Begin by configuring the settings of the following parameters;
- Cutting Speed: Avoid setting high cutting speeds since this can lead to defective machining in addition to destroying your cutting tool.
- Feed Rate: Try to set your feed rate relatively high to avert work hardening.
- Cutting Depth: Be very specific about your intended depth of cut to ensure you achieve your desired machining results.
- Machine Your Inconel Workpiece: With your machining parameters set, set about machining your mounted Inconel piece. You can undertake the following machining operations;
- Drilling
- Tapping
- Roughing
- Reaming
- Finishing
- Apply a Coolant: As you machine your Inconel piece, you will notice excessive heat generation on the contact surface. Apply your carefully selected coolant on this surface to safeguard your cutter’s integrity.
- Extract the Resulting Chips: Undertake this step continually to prevent the excessive accumulation of tough and stringy Inconel shavings. You can utilize a high-pressure cooling system to flash out these chips.
Advantages
Under extremely harsh conditions, most materials crumble but Inconel thrives in these situations. This explains their extensive exploitation in high-risk and highly demanding settings like jet engines. Utilizing this superalloy promises a myriad of rewards.
- Exceptional strength.
- Unrivaled temperature resistance.
- Fatigue resistance.
- Low thermal expansion.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Heat resistance.
Uses of Inconel

- Power Generation: Its high endurance for heat and corrosion has seen it become a staple in nuclear reactors and steam turbines among other power generation components.
- Marine Industry: The marine industry relies on Inconel to produce propellers, heat exchangers, and other essential equipment due to its corrosion resistance.
- Aerospace Industry: A myriad of aerospace components are manufactured using Inconel including jet engines and turbine blades.
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry also benefits greatly from Inconel’s heat resistance and toughness. It is used to produce turbochargers and exhaust systems.
- Chemical Processing: In chemical processing plants, Inconel reigns supreme when it comes to manufacturing storage tanks, pipes, and heat exchangers.
FAQs
1. What is the Difference Between Hastelloy and Inconel?
These superalloys are both remarkable and they share multiple resemblances such as superior strength and toughness. However, they differ slightly when it comes to the harsh conditions they can endure. Whereas Inconel reigns supreme in high-heat environments susceptible to oxidation, Hastelloy thrives in acidic and corrosive conditions.
2. Which is the Hardest Inconel Material?
Whereas all Inconel grades are hard, Inconel 718 trashes all other grades when it comes to hardness. This is a consequence of precipitation hardening combined with its superior tensile strength.
3. What is Inconel Tubing?
This is an incredibly strong pipe characterized by heat resistance and impressive mechanical attributes thanks to its parent material (Inconel).
4. What is Inconel Cladding?
This is a material reinforcing process that sees your base material encrusted with an Inconel layer resulting in a composite component with better attributes.
5. What is the Difference BetweenMonel and Inconel?
Despite sharing the same base element (Nickel), these alloys differ greatly as demonstrated in the table below.
| Feature | Monel | Inconel |
| Composition | Nickel -Copper | Nickel-Chromium |
| Strength | Relatively less strong | Relatively stronger |
| Weldability | Excellent | Good |
| Copper Content | Higher | Lower |
6. What is Inconel Welding Filler used for?
Welding Inconel demands comes with extra demands such as the use of a befitting welding filler. This filler plays several essential roles including;
- Matching the properties of the welded joint to those of the parent workpieces.
- Strengthening the bond.
7. What is the Composition of Inconel in Welding Rod?
Welding rods must demonstrate great strength and exceptional heat resistance, which are rare attributes only synonymous with Inconel. Typical Inconel welding rods are made up of;
- Nickel: 70-80%.
- Chromium: 15-20%.
- Iron: 0-5%.
- Molybdenum: 0-5%.
- Titanium: 0-2%.
8. What is the Melting Point of Inconel?
When it comes to high-temperature environments, there are minimal materials that can tramp Inconel. This material boasts of a superior melting point whose range falls between 1300-1400°C. The range is a reflection of the difference in material composition.
9. What is the Mass of Inconel?
To determine the precise mass of your Inconel metal, you will need to first establish its density and factor in your volume. Typical Inconel bears a density ranging from 8-8.4g/cm³ and with the following formula, you can calculate its specific mass;
Mass = Density × Volume
10. What is the Scrap Price of Inconel?
The price of Inconel is broadly dependent on the Inconel grade. And as of today, the average scrap price of Inconel ranges from $2 to $ 2.75/lb. Kindly note these prices may fluctuate slightly depending on market conditions and your locality.
11. What is the Sintering Temperature of Inconel?
Inconel comes in distinct grades and each grade has a designated sintering temperature, which is often dependent on the sintering technique you exploit. However, the typical range covering all grades falls between 1200°C and 1350°C.
12. Is Inconel Stronger than Steel?
Yes. The makeup of Inconel encompasses several base elements that form a strong bond resulting in a far superior material. Inconel boasts superior tensile strength, heat resistance, and wear resistance.
13. Why is Inconel so Expensive?
Although procuring Inconel will have you digging deeper into your pockets, its rewards over time guarantee you sufficient returns on your investment. Its higher price is attributed to its rarity, and demanding production process.
Conclusion
Inconel has been the backbone of engineering for ages as evidenced by its extensive usage in industries spanning from chemical processing to aerospace. The invention of newer grades such as the X-750 further underlines the value of this remarkable superalloy in modern engineering. You can trust Inconel to produce resilient components guaranteed to endure the toughest conditions.
More resources:
What is Stainless Steel – Source: KDMFAB
Aluminum Alloys – Source: KDMFAB
What is Alloy Steel – Source; KDMFAB




