
Brass extrusion is a manufacturing process in which a brass alloy is heated and forced through a die to create a specific shape or profile.
In this basic knowledge guide, we will answer some of the questions you have about this process. You will get to know types of brass extrusion, surface finishes, and applications, among others.
Advantages of Extruding Brass
Extruding brass is a popular manufacturing method for creating a wide range of products. This is because it offers several advantages over other forms of manufacturing.
Here are some benefits you stand to enjoy from extruding brass:
- The process is efficient since you can conduct mass production within a short time cycle
- Extruding brass can make products that come in a wide range of cross-sectional areas
- Also, it will produce structures that are resistant to corrosion and machinable compared to casting
- Compression during extrusion results in parts whose grain structure is dense and with suitable mechanical traits
- The extrusion process offers high dimensional accuracy thus can produce complex parts which are accurate and precise
Limitations of Extruding Brass

Extruded Brass Profiles
While extruding brass offers many advantages, there are also certain limitations to this manufacturing method. However, this should not deter you from using this manufacturing process.
Here are some disadvantages you need to be aware of:
- High cost to set up and start the extruding brass process
- Extruding brass needs a large amount of force to squeeze
- It is not suitable for small productions
- The final cross-section is the same across the entire product length
Types of Brass Extrusion Machine Processes
There is no one way to make extrusions from brass. Here, we are going to discuss the various methods you can use. These include:
· Direct Extrusion of Brass

Direct Extrusion
It is also referred to as forward extrusion. Here, you will have the billet, ram, and punch move in a similar direction. Since the billet will slide against the stationary wall, friction between the billet and container will increase.
Some of its benefits include:
- Simple and efficient process
- Low-cost for each component
- Allows for large production volumes
- Good for manufacturing simple shapes
- Can produce longer brass components
- The surface finish is good
The limitations include:
- Need for high extrusion pressures than that of indirect extrusion
- Dummy blocks with smaller diameters are necessary to inhibit oxidation
- Lubricants are vital for reducing friction
· Indirect Extrusion of Brass
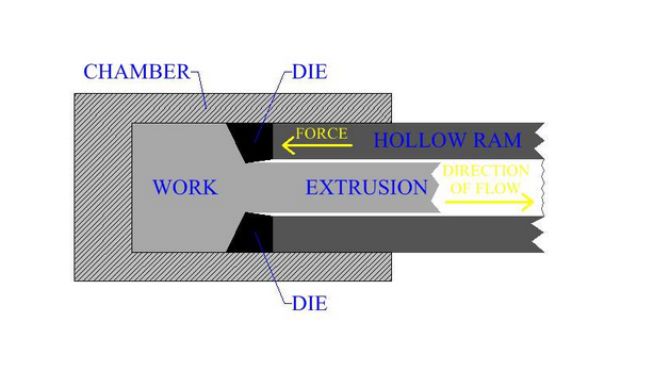
Indirect Extrusion
It is also called backward extrusion. In this process, the punch and billet move in opposing directions. The container and billet will not experience relative motion, this means minimal friction is generated.
Advantages include:
- Requires less force compared to direct extrusion of brass
- Produces minimal friction than direct extrusion
- Suitable for large production operations
- The container is durable since is experiences minimal wear
Disadvantages include:
- Not suitable for manufacturing long extrusions of brass
- The size of the stem dictates the cross section of the brass product
· Impact Brass Extrusion
This method is suitable for making hollow brass items like cups.
Advantages include:
- It is suitable for producing brass tubes whose walls are thin
- The process is simple to perform
- The tooling cost is relatively low
· Hydrostatic brass extrusion
In this method, you will employ liquids when extruding brass. The fluid is the medium through which pressure moves.
Advantages include:
- No friction is generated as the billet and container are not in contact
- Suitable for brittle products due to limited pressure and that it happens at room temperature
More Resources:
Metal Extrusion Process – Source: Wikipedia
Metal Extrusion – Source: Fractory
Brass Casting – Source: KDM
Brass Stamping – Source: KDM
Extruding Metal – Source: The Library of Manufacturing
Extruded Brass Surface Finishes
Surface finishes play an important role in the appearance and functionality of brass extrusion products. These finishes can be applied to the surface of the extruded brass to improve its appearance, increase its resistance to corrosion, or improve its overall durability.
Let’s have a look at some of the common surface finishes you can apply on extruded brass products:

Extruded Brass Channel Profile
Anodizing Brass Parts
This is a surface treatment that forms a protective layer on the surface of the brass parts. It entails passing an electrical current through an electrolyte bath. This finish is often used to increase the corrosion resistance of the brass product.
Polishing Brass Parts
When you conduct polishing, you are simply smoothing and shining the surface of the brass parts. This finish is often used to enhance the aesthetic appearance of the product and make it more visually appealing.
Electroplating Brass Parts
In this process, you will deposit a thin metallic layer on the surface of different extruded brass products. Electroplating will help increase the corrosion resistance as well as enhance appearance of the final product.
Powder Coating Brass Parts
This is a process that involves applying a fine powder to the surface of the extruded brass parts. Thereafter, you will heat it to fuse the powder to the surface. Powder coating will improve durability and corrosion resistant of the extruded brass.
More Resources:
Brass Finishing – Source: KDM
Anodizing Brass – Source: KDM
Polishing Brass – Source: KDM
Best Brass Grades for Extrusion
The best brass alloys to use for extrusion process are those that have good extrudability, good strength, corrosion resistance, and good machinability.
Some examples of alloys that are commonly extruded are:
- C26000
- C27000
- 28000
- C35300
- C38000
- C48200
- C48500
- Alloys 260, 272, 330, 353, 360, 385, 464
More Resources:
Brass – Source: Wikipedia
Brass Alloys – Source: Azo Materials
Applications of Extruded Brass Parts
If you look around your environment, you probably will see a product made from brass extrusion. The versatility of brass extrusion allows you to make products that are used in different areas.
These include:

Extruded Brass Profiles
· Brass Profile Extrusions
These extrusions can be in the form of a simple shapes such as a rod, tube, or flat bar. It also allows for a more complex shape such as a gear, screw, or other mechanical part.
Brass profile extrusions are used in a wide variety of applications. These include electrical components, plumbing fixtures, automotive parts, and more.
· Extruded Brass Channels
These refer to the process of creating a specific shape or cross-sectional profile, similar to the letter “U” or “C” that is used as a structural support, guide or barrier.
They are often used in the construction industry, particularly in architectural applications such as window and door frames, curtain walls, and more.
· Architectural Brass Extrusions
In this process you will create a specific shape or cross-sectional profile from a brass alloy that is used in architectural applications.
Applications include window and door frames, curtain walls, handrails, door handles and other decorative elements. Architectural brass extrusions are known for their durability, corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
· Extruded Electrical Parts
These are commonly used in the electrical industry due to their good conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability.
Examples include electrical connectors, terminals, and other electrical components used in wiring and electrical systems.
· Extruded Plumbing Components
These are used in the plumbing industry and include fittings, valves, etc.
· Extruded Automotive Parts
These apply to the automotive industry and entail gears, valves, and other mechanical parts used in automotive systems.
How Brass Extrusion Compares to Brass Drawing
Extruding brass and brass drawing are both manufacturing processes used to create brass parts, but they have some key differences. These differences include the process itself, the final product, and the applications for which they are best suited.
| Extruding brass | Brass drawing | |
| Process | Entails pushing brass in dies to produce shapes | Entails pulling brass via dies to produce shaped |
| Cross-section | Produces brass products with uniform cross-sections | The brass product may have varying cross-sectional area |
| Time | Faster than brass drawing | Takes more time than extrusion |
| Cost | Relatively cheap | Expensive |
| Speed | Done at higher speeds than brass drawing | Done at slower speeds than extrusion |
| Force | Requires less force to extrude | Requires more force to draw |
Factors Determining Quality of Custom Brass Extrusion
Custom brass extruding is a versatile manufacturing process that can produce a wide variety of parts and components with precise shapes and dimensional accuracy. However, the quality of the final product is determined by a number of factors.
These factors must be carefully considered and controlled to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
Material Quality
Brass should be ductile enough pass through the die and form shapes. The crystals within brass should glide against each other as opposed to locking together.
Temperature
Heating brass increases the ductility and movement of the grain. High ductility means you need less force to extrude.
Speed of Extrusion
It is important to have suitable speed and temperature when extruding brass. This allows you to attain a stable extrusion process. Besides, the speed affects the surface finish, grain size and the grain direction of the brass.
Pressure
Here, you will press the brass metal in the profiles to make an extrusion. By heating the brass, you enable it attain the recrystallization temperature. This means it needs minimal force to extrude.
Recommended Tolerance in Extruded Brass Parts
Tolerance refers to the degree of variation that is allowed in the dimensions and shape of a product. The tolerance for brass extrusion rods can vary depending on the specific application and the desired level of precision.
In general, extruded brass tolerance ranges from +/- 0.120” to +/- 0.120” mm, but this can vary depending on the specific application and the extrusion process being used. For example, tighter tolerances will be required for precise and delicate parts while looser tolerances may be acceptable for larger, more robust parts.
Factors that affect tolerance levels include:
- Temperature of billet
- Extrusion speed
- Size of press
- Time to cool
- Shape and the type of the die
Conclusion
Extruding brass may sound complex. But as you can see, it will offer you a myriad of benefits since the process is efficient. We hope this guide had given you important information when it comes to extruding brass.
For all your brass fabrication process, contact KDM now.




