You may already know what lead is as a metal and what in can do or not do. However, how well do understand lead with regards to rusting? Here is what you need to know about lead and rust.
Does Lead Rust or Corrode?
Lead does not rust. Usually rusting is a term specifically reserved for the corrosion of iron and its alloys, such as steel. Nevertheless, lead does erode, but the process and product of it do differ with those regarding iron.

How Rusting Lead Looks Like
Even though lead doesn’t “rust” in the way iron does, it does corrode, which can result in chemical changes. Lead corrodes to form this cover of many different lead compounds. This color of corroded lead depends on the environmental conditions and compounds formed.
Visual Markers of Lead Corrosion
Color Changes: The transition from the first, metallic, bluish-white to dull gray, white, or off-white as different compounds develop.
Texture
The surface becomes less smooth until it becomes powdery or crusty through the accumulation of corrosion products.
Pattern
Depending on the exposure conditions, corrosion may appear evenly across the surface or as separate spots.

Causes of Rusting in Lead
While lead doesn’t seem to rust in the same way as iron does it is still corroded. The lead matter corrosion is attributed to different environmental factors and chemical reactions.
1. Oxygen Exposure
Oxidation: When lead interacts with oxygen, it forms a thin superficial layer of lead oxide. It is usually the first step of oxidation that works a positive effect on the protection of the metals, making the process slower.
2. CO2 and Relative Humidity.
Formation of Lead Carbonate: With the exposure of moisture and carbon dioxide inside, lead is capable of forming lead carbonate, also called cerussite.
3. Sulfur Compounds
Formation of Lead Sulfate: The reaction of lead and sulfur compounds that are frequently seen in polluted air or industrial places produces lead sulfate.
4. Chloride Ions
Formation of Lead Chloride: In areas near oceans or seas, chloride ions (Cl⁻) taken from saltwater can be produced to lead chloride (PbCl₂).
5. Acidic Conditions
Acid Rain: Lead may oxidize rapidly due of acidic rain that is characterized by sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and nitric acid (HNO₃).
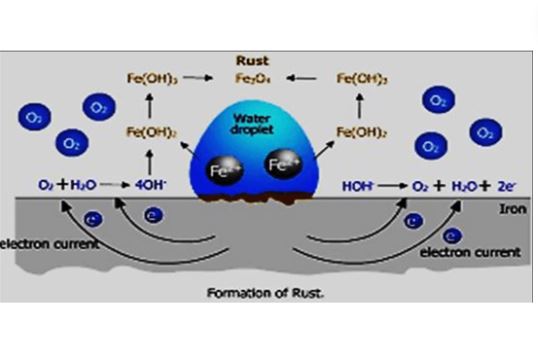
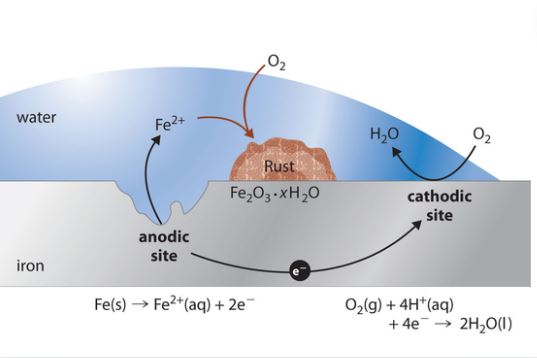
Lead Corrosion vs. Lead Rusting
Lead Corrosion
Corrosion is a wider term, which is defined as a slower and destructive chemical consequence. It is caused by the reaction of a material (usually metal) with its surrounding environment. For example, in lead it comes to a formation of different lead compounds on the surface of the material.
Lead Rusting
The term “rusting” is very closely related to “corrosion,” which certainly refers to the metal oxides that result from iron corrosion. The term “oxidizing” is used instead of “rusting” since lead does not participate in the process of oxidation.
Lead Rusting and Corrosion in Water Treatment
Corrosion Control:
PH Monitoring and Adjustment: Keep the water pH within neutral to slightly before it is made even more alkaline to diminish lead pipe corrosion and fittings.
Corrosion Inhibitors: Suffuse the water treatment processes with corrosion inhibitors that gives rise to the protective coatings of lead surfaces and prohibit erosion.
Protective Coatings:
Epoxy Linings: Introduce the epoxy coatings by lining the lead water pipes interior surfaces so that the two will not be in direct contact with each other. It reduces the corrosion incidence and lead leaching.
External Coatings: Coat the exteriors of lead pipes with environmental protection coatings. The main aim is to minimize the extent of the environment’s contact with the pipes and to reduce the problem of corrosion.
Corrosion Control Devices:
Cathodic Protection: Substitute the cathodic protection systems to the pipes that are usually made of lead. So as to protect them from corrosion by giving the pipes the lowest voltage electrical currents.
Regular Maintenance:
Cleaning: Use a soft tool to clean up lead parts often, and this way remove any dirt buildup and corrosive components.
Prompt Repairs: Provide immediately maintenance upon any leak, crack, or damaged component in order to stall the corrosion and contamination.
FAQs
Does Lead Rust in Water?
Lead won’t rust in water; instead, it might be corroded. The kind and the level of corrosion relates to the water’s pH, hardness, and the dissolved gases and ions present in it such as chlorides and sulfates.
Does Lead Rust in Salt Water?
While lead does not rust in salt water, it on the other hand corrodes. The addition of salt in water is the factor that speeds up the corrosion rate of most metals, including lead alloy.
Does Lead Pipe Rust?
Lead pipes don’t rust in the way the iron and steel pipes do. Rust is distinctly related to the creation of iron oxides which is a characteristic that iron and its alloys only possess. Yet, leads pipes may corrode.
Does Lead Tarnish?
There is no doubt that lead oxidizes due to the surrounding air. Tarnishing is a kind of surface discoloration, stemming from the exposure of metal to the surrounding environment.
Conclusion
Lead is a metal that can corrode easily when exposed to environments or conditions that lead to this process. Like other metals such as, copper, tungsten, gold, and titanium, lead does not rust easily.
However, from the information given above, you now consider taking the necessary steps into protecting lead from corrosion.
More resources:
Does Copper Rust – Source: KDM
Does Gold Rust – Source: KDM
Does Tungsten Rust – Source: KDM
Does Nickel Rust – Source: KDM
Does Titanium Rust – Source: KDM




