For starters, we can describe welding as the process of joining materials having a similar structural composition and melt temperature.
However, as you focus on more specific welding technique, it becomes a little challenging – but we will make that simple for you right here.
In this guide, we will explore every aspects of laser welding – from benefits, history, welding process, technique to application.
At the end, you will be an expert in this process.
What Is Laser Welding
Laser welding is an accurate and fast traditional technique of welding where we use a light beam to join materials, mostly metals. This laser beam induces a lot of heat energy into the joining materials and when the joint becomes molten, it cools down to give a firm weld.
You can benefit from achievable precision with this technology which allows you minimal distortion of the material you are welding. It also gives you excellent repeatability that is suitable for a wide range of applications in industries.

Benefits of Laser Welding
The applications of laser welding are cut across various industries largely because of the operational advantages it offers. Let us take a closer look at some of the gains of this welding technique:
Precision
The laser beam is normally very concentrated thus giving you maximum control over the whole welding process. You can find this precision very useful especially when dealing with fine welds or those having complex designs.
High Operational Speed
Due to the level of automation and accuracy, laser welding has a much faster operational speed. This rapid welding speed ensures that you achieve high production rates while working with the highest levels of efficiency.
Strength
Welds made by laser welding mostly possess a high tensile strength and are very durable. They are stronger than the base material being welded with the joints produced lasting for a very long time.
Small and Concentrated Heat Affected Zone (HAZ):
Since the laser beam is directly focused on the exact spot that requires welding, the HAZ is drastically reduced. This reduces the probability of thermal stress on the material or failure of its mechanical properties.
Versatility
The application of laser welding can be used on almost various types of material such as a wide range of metals or some form of plastics. Due to this flexibility, you can adopt it for various uses across many industries.
Advanced Technology and Automation
Laser welding systems are fully equipped with automation systems in addition to top-notch technology that ensures quality welds. The elimination of manpower also helps in minimizing labor expenses and improving the general efficiency of your operations.
Reduced Post Processing
Since you can easily control laser welding and with its precise operation, you end up forming very fine welds. Such welds may not require secondary operations such as grinding and polishing.
Background of Laser Welding Technology
The history of laser welding technology in general has a brief but significant background. The whole idea of focusing a light beam to weld material is a concept that came into existence in the 1960s just after the laser was invented.
Originally, it was used in the aerospace and defense sectors where the accuracy and rigidity of laser welding were very critical. However as the years progressed, there was an increase in the application areas that required the use of laser welding necessitated by laser technology upgrades.
The incorporation of computers for control systems made it suitable for the automotive, medical, and electronics industries. Presently, it is a standard and broader technique mastered and widely applied in different manufacturing sectors with progressive adaptations and improvements.
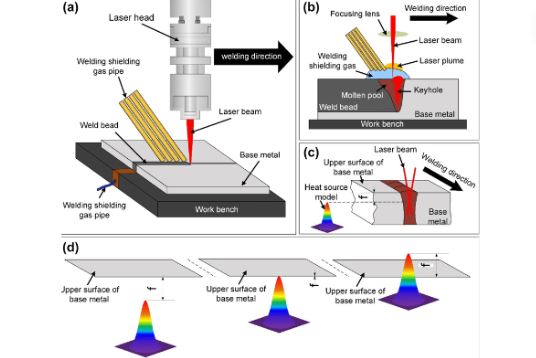
How Laser Welding Works
For laser welding to produce precise and strong welds, it has to go through several steps. Let us have a step-by-step analysis of the whole process:
- Laser Generation: the process starts by producing a laser beam from sources like fiber, and carbon dioxide laser among others. Each laser type is determined by the material that is being welded.
- Beam Focusing: usually, the laser beam is reflected by lenses or mirrors and aimed at a single spot on the material surface. This focused beam creates the necessary heat needed for the joint to weld.
- Heat Generation: after the laser beam has been focused on the material, it generates some heat that compounds at that spot to melt. The heat input is localized therefore restricting the heat-affected zone (HAZ) to a very small area.
- Material Fusion: the material of both pieces to be joined melts, then cools down to create a rigid joint that welds them together. This step is very important since it ensures the formation of a durable joint.
- control Systems: the whole procedure is generally managed through a computer system that regulates the beam intensity, focus, and direction. You can adjust them in real time to get correct welds of the highest quality.
Types of Lasers Used In Laser Welding
We have different types of lasers that can be generated to suit specific laser welding applications. Let’s explore in detail these lasers and how they differ:
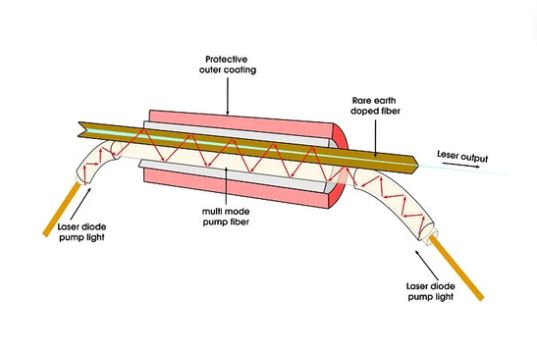
Fiber Lasers
Here, the beam is delivered with the help of an optical fiber. Fiber lasers are characterized by high efficiency, better beam quality, and the capacity to weld on any material. We majorly apply them in the automotive and aerospace industries and the manufacturing of medical devices.
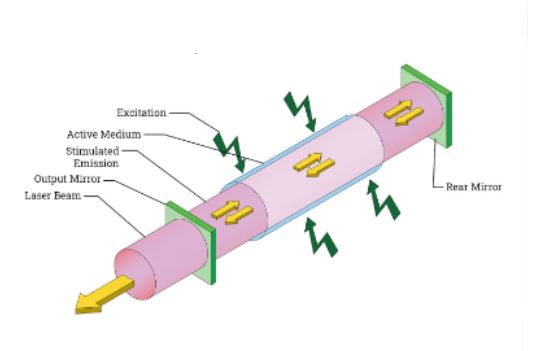
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Lasers
With carbon dioxide as the main gas, it is combined with other gases with the mixture forming the laser beam. We commonly apply it in welding materials that have a high reflectivity such as aluminum and copper. These applications require welding areas that demand a weld with deep penetration.
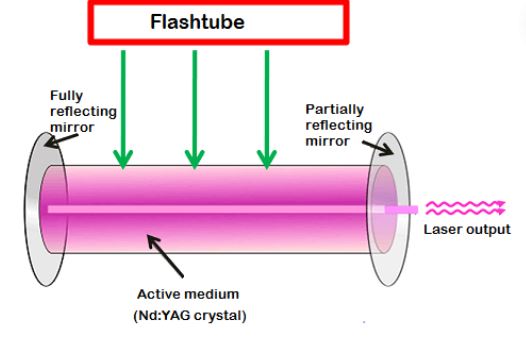
Nd Lasers
We refer to them as neodymium-doped Yttrium aluminum garnet lasers and are preferred for welding various materials including ceramics and metals. These lasers are well-known in many precision welding applications.
Diode Lasers
They are compact in nature and provide high-quality beams that you can use in the precise welding of electronics and medical devices. They are mainly applied in micro-welding and joining fragile components.
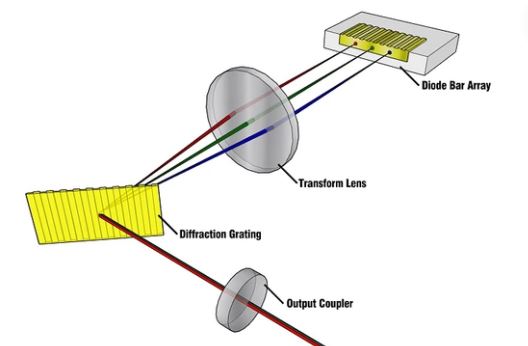
Types of Laser Welding Techniques
We have various laser welding techniques that you can apply depending on your material and application. We can go through some of them and what they entail:
Conduction Welding
This method exposes the material to the laser heat until it softens and fuses, ideal for welds that require visual appeal and slender materials. This technique works on the principle of heat conduction to pass the energy from the laser beam to the material.
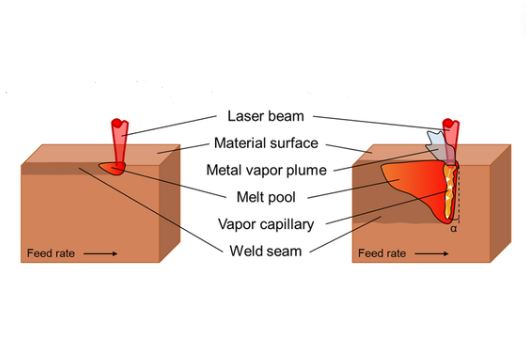
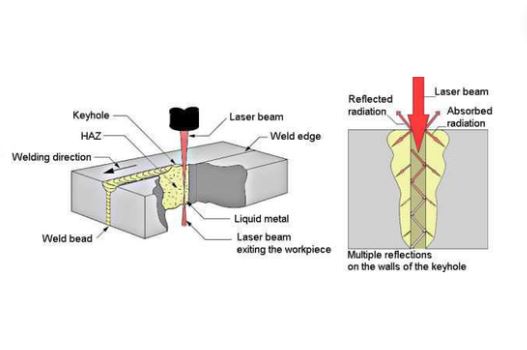
Keyhole Welding
This method forms a small hole that is buried in a pool of molten metal material that advances laser penetration and produces narrower joints. We use this welding on heavier gauges and is well known for its high durability and great accuracy.
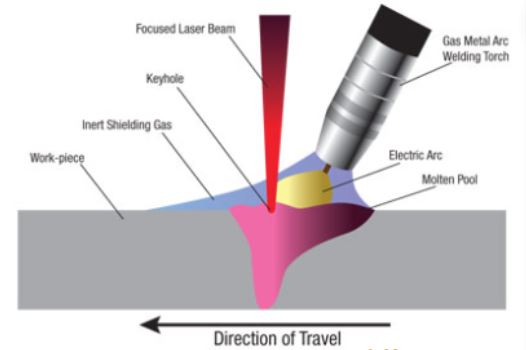
Hybrid Laser Welding
This is when you combine laser welding with another welding technique such as arc welding to improve the weld quality and increase the welding speed. This technique is highly recommended for materials having a heavy thickness and complex joint configurations.
Spot Welding
You can apply this technique by using a laser to produce very small and pin-pointed welded areas. We use this technique commonly in electronics and automotive applications which require light penetration and high accuracy.
Materials Compatible with Laser Welding
With the variety of lasers and the various techniques available for laser welding, the compatible materials are equally many. Let us dig deep into some of them:
Metals
Some of the common laser-welded metals include steel, aluminum, titanium, nickel, and copper alloys. The laser types and techniques you use will vary from one metal to another to achieve the best outcome.
Plastics
Some plastics, especially highly tensile ones can easily be laser welded. However, you will have to apply complex welding techniques to avoid damaging the material or creating poor welds.
Ceramics and Composites
Some applications require the use of advanced materials such as ceramics and composites which you can join using laser welding. The applications of such materials are mainly in high-tech industries that manufacture medical devices and airline components.
Laser Welding Vs. Traditional Welding
In as much as the principles and objectives are the same, you may find some variations between laser welding and traditional welding techniques. Let us analyze how they fair against each other:
Precision
Laser welding is usually a very precise process that you can easily control to produce high-quality standard welds. Traditional welding methods such as arc welding are much less accurate with lower-quality welds.
Welding Speed
The advanced technology and automation greatly increase the welding speed and efficiency of laser welding. Traditional welding processes involve multiple passes and use more material and time when carrying them out.
Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
In laser welding, HAZ is negligible meaning thermal distortion and material structural compromise are reduced. The size of HAZ is comparatively larger in traditional welding and can interfere with the quality of the material.
Level of Automation
With the incorporation of computer automation systems and assistive technology in laser welding, human interaction is very minimal. In traditional welding, you have to factor in a lot of physical human input and you cannot easily automate them.
Material Versatility
You can apply laser welding to various materials and cover those that you can’t easily weld using conventional techniques. As for traditional welding, you may face challenges while using certain materials.
Parameters Used In Laser Welding
While carrying out laser welding, some factors come into play that determine the quality and efficiency of the whole process. Let us take a closer look at some of them including:
- Laser Power: it dictates how much heat the laser produces therefore determining the weld depth and weld speed. You will require high power in the case of thick materials.
- Beam Focus: a narrow beam is ideal for producing precise and intense welds with minimal defects. A poorly focused beam will most likely result in poor-quality defective welds.
- Welding Speed: the laser speed is one of the major factors influencing the quality of the weld and heat produced. You have to optimize your laser speed if you want to avoid flaws such as porosity.
- Shielding Gas: the main purpose of this gas drastically reduce oxidation levels while welding and inhibiting weld contamination. The quality and appearance of the weld can be affected by your choice of gas such as helium, argon, or nitrogen.
- Pulse Frequency: when welding using pulsed lasers, the heat produced and weld penetration are determined by the laser pulse frequency. You can vary the pulse frequency rate to regulate your welding.
Precautions When Laser Welding
Safety is paramount any time you are carrying out laser welding due to the intensity and harmful nature of the laser beam. We can take a closer look at some of the practices that can safeguard you:
- To protect yourself from exposure to dangerous radiation, you must wear appropriate laser safety glasses. The reflected laser beams can affect your eyes and cause severe forms of injuries.
- Wear protective clothing that protects your skin from any form of burns and radiation. Laser welding produces rays of light and heat that can particularly cause skin burns.
- Laser welding requires adequate ventilation to clear out the fumes and gases that are produced. Breathing in such fumes may have a toxic impact on your body.
- Ensure that you undergo proper training to be knowledgeable enough to carry out laser welding. This eliminates the possible risks connected to the use of laser equipment.
Limitations of Laser Welding
Laser welding has proven itself worthy in industrial applications based on the advantages we get. However, it also comes with its fair share of imitations that we are going to briefly explore.
Cost
The initial acquisition of a laser welding system is quite expensive. This encompasses the cost of sourcing the laser, all its control systems, and any other related components.
Material Compatibility
You can apply laser welding to a variety of materials but not all of them. Sometimes you will need to manipulate the techniques or tools of welding when it comes to certain materials.
Thickness Limitations
You may have some limitations especially when welding very thick materials, although you can apply some hybrid methods. If you are dealing with materials having a significantly large thickness, then you are better off using the traditional welding methods.
Cost of Laser Welding Machine
If you want to acquire a laser welding machine, you will have to contend with a few factors that determine its actual price. Let’s discuss some of them and how they impact the price:
- Laser Type: the cost varies with the type of laser you need for your application such that can either be fiber, CO2, Nd, or others. Fiber lasers tend to be costlier due to their superior technology and they work more efficiently.
- Power and Specifications: lasers with a higher power and extra features can cost you more compared to regular lasers. Lasers that offer a higher tolerance or have a custom design will cost more.
- Brand and Quality: laser manufacturers with reputable brands and quality always quote a higher market price. There is always a risk of buying an unknown brand cheaply though you will not be certain about its reliability and performance.
- Automation and Integration: intelligent laser welding machines having more automated functions and systems are more expensive than the others. They may increase productivity and quality levels but that comes at a cost.
Applications of Laser Welding
Besides having very many benefits, we can use laser welding across a wide range of industries and applications. We can a brief look into some of these applications which include;
- Aerospace Industry: Applied when welding essential components such as blading for turbines, fuel containers, and precision structural components. Its accuracy and strong bond are vital in aerospace applications where safety and reliability are vital.
- Medical Devices: majorly used in welding diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments, and medical implants. This type of welding is clean and accurate, important traits needed in the medical field.
- Electronics: used to weld fragile electronic components such as sensors, connectors, and circuit boards. Their small heat-affected zone makes it suitable for welding sensitive electronic parts.
- Automotive: very useful when joining parts such as engine, transmission, and battery packs. It offers a very precise and fast welding option that’s widely applied in this industry.
- Jewelry: utilized in the manufacture and fine repair work of jewelry pieces. This welding technique masks the welds by giving them an aesthetic look with a neat finish.
- Manufacturing: it has its uses in a wide range of industries ranging from machining tools to different consumer products. The flexibility of laser welding allows it to be applied in many industries.
Conclusion
It is now clear that laser welding occupies a powerful and flexible position in the modern industry with its various uses and benefits. It is arguably the most effective method of joining materials with its fast and precise operations that produce high-quality welds.
Having a clear understanding of all that laser welding entails can ensure that you achieve the best welding results while practicing all safety precautions. The prospects of laser welding are rather bright with the possibility of further technological advancements.
Related Resources:
TIG and Heliarc Welding – Source: KDMSTEEL
Tack Welding – Source: KDMFAB
MIG vs TIG Welding – Source: KDMFAB
Welding Finishes – Source: KDMFAB
Sheet Metal Welding – Source: KDMFAB
Tube Welding – Source: KDMFAB




