With a composition of iron trioxides and iron trioxide-hydroxide, rusting is the resulting chemical reaction of oxygen and moisture that occurs on the surface of select metals. The metals affected include iron in their composition.
What is Magnesium?
This is an element with an atomic number of 12 and has a lustrous gray appearance. Naturally, you will find that magnesium has a reduced melting point and density but showcases increased reaction to chemicals. It is naturally found in an amalgamation of other elements.
Will Magnesium Rust?
No, this element is not susceptible to rusting. Rust affects specific metals which are mainly iron or steel or amalgamations that contain these two elements.
Magnesium is characterized by its increased chemical reactivity which prevents it from developing rust on its surface.
The element has reduced ionization energy which allows it to easily lose its electrons and form sulfides, oxides, and hydroxides. The formed compounds prevent rust from forming but begin the element’s corrosion process.
How Oxide Layer Affected Magnesium Rusting
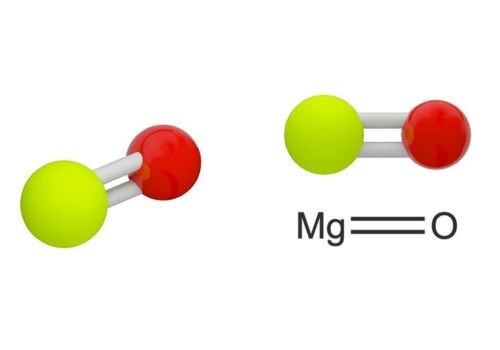
An oxide layer is formed on the surface of this element when exposed to oxygen which functions as a protective layer that prevents rusting from occurring on the surface of the element.
Subjecting magnesium to elevated reactivity to chemicals, you will realize it combines to form compounds such as oxide which is typically thin. The thin layer prevents the interaction between susceptible elements with oxygen and moisture and in so doing prevents the formation of rust.
A practical application of this oxide layer is presented in sacrificial protection where the element is used to coat susceptible metals. The element forms the oxide layer which is a form of corrosion but is effective in slowing down the formation of rust on the structure underneath.
Magnesium Rust Formula
The magnesium rust reaction involves an interaction between water, oxygen, and the element. This reaction results in the formation of magnesium hydroxide.
Here is what your formula for this reaction looks like:
Mg + O2 + H2O → Mg(OH)2
Comparing Magnesium Rusting to Magnesium Oxidation and Magnesium Corrosion
Magnesium Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical reaction that typically occurs when certain metallic elements are exposed to oxygen in the atmosphere.
This element similarly reacts with oxygen to create an oxide film on its surface that functions as a protective layer. It keeps the element from developing rust and prevents it from getting more corroded and potentially damaged from adverse environmental conditions.
Magnesium Corrosion
Given that the element had an elevated chemical reactivity with an external element, it is highly susceptible to corrosion.
The formation of compounds such as oxides, sulfides, and hydroxides are examples of corrosions occurring on the element as they involve degradation of the element during the formation of these compounds. Corrosion in this element is presented as a dull gray layer formed on the surface of the metal.
· Magnesium Rusting
This element does not undergo rusting which is a corrosive compound that typically forms on metals specifically iron or steel.
While magnesium experiences corrosion it typically results in the formation of oxide film that serves as protective layers that prevent rust from forming and also slows down further corrosion from occurring. This element can therefore be incorporated into steel or iron to help slow down rusting and corrosion.
Factors Affecting Rusting in Magnesium
This element has the advantage of being impervious to rusting thanks to its ability to quickly react with oxygen to create a protective oxide film.
The film prevents the metal from interacting with moisture and oxygen which are essential for the formation of rust. While it does form rust this metal is still susceptible to other forms of corrosion that differ in rate depending on several factors.
The factors that affect the rate of corrosion in magnesium include the following;
- Elements used to alloy the metal directly impact its ability to resist corrosion. Elements such as zinc or aluminum can be incorporated into its composition to reduce its rate of corrosion. While compounds such as iron or steel will decrease their resistance
- The element’s grain size also impacts its rate of corrosion. A decrease in the grain size increases its susceptibility to corrosive compounds because of the increased boundary area of the grain.
- The reinforcement variation present also influences the element’s resistance to corrosion. These reinforcements present as a composite matrix impact the rate of corrosion experienced by the element.
- An oxide layer formed on the surface acts as a preventative measure and you can also incorporate additional surface coating that will protect the metal from corrosion.

FAQs
1. Does Magnesium Rust in Water?
It does not. When exposed to water magnesium quickly forms a hydroxide compound which results in a protective film. This hydroxide film prevents the element from rusting.
2. Does Magnesium Rust in Salt Water?
The element is highly reactive in salt water which increases its rate of corrosion. Despite the increased level of reactivity, the element still forms a hydroxide layer which prevents it from rusting.
3. Is Magnesium Corrosion Resistant?
No, it is not. This element experiences varying levels of corrosion depending on various factors. Its low ionization levels lower its resistance to corrosion by allowing it to easily lose its ions.
4. Does Magnesium Rust in Air?
It is well known that magnesium and its alloys suffer rapid corrosion in the presence of sodium chloride in humid air.
Conclusion
This element can rapidly react with oxygen and other external factors to form protective films which make it resistant to rusting. The formation of the protective layers however can be viewed as a form of corrosion whose level varies depending on other factors. Therefore, while the element is resistant to rusting it is susceptible to corrosion.
More resources:
Is Magnesium Magnetic – Source: KDMFAB
Magnesium Properties – Source: BRITANNICA




