What Is Laser Etching?
The technique of laser etching involves melting the surface of parts and products to leave imprints on them. It belongs to the broader area of laser marking, including engraving. It works with most metals and is incredibly versatile.
Advantages of Laser Etching
Numerous materials with different degrees of thickness can be etched by using a laser. Some of them are stainless steel, aluminum lead, and zinc.

The method of laser etching and branding is precious. It can be quickly transitioned between drugs and a range of depths by giving its users a choice of several outcomes.
The speed of the process with laser etching is impressive. The material vaporizes after each laser etch. Thus the process doesn’t take very long to complete.

Laser etching has excellent precision and can etch complicated images into small objects like rings or necklaces.
When Lase Etching Was Invented?
- 1917 – Quantum Theory of Radiation; it is a theory put out by Einstein Albert that particular wavelengths of light can be produced by manipulating electrons.
- The first continuous laser etching was developed in 1960, and then the Q-switching technique for creating pulsed laser beams was built in 1962.
- 1978 – Despite being basic, the first laser etching was bought; it was employed to produce works of art.
- 1996 – the development of the first laser-specific software appeared. Eventually, laser etching equipment was equipped with direct computer integration.


Laser Etching Materials
Some of the main materials you can easily laser etch include:
- Aluminum
- Magnesium
- Lead
- Steel
- Zinc
- Stainless steel
Laser Etching Process
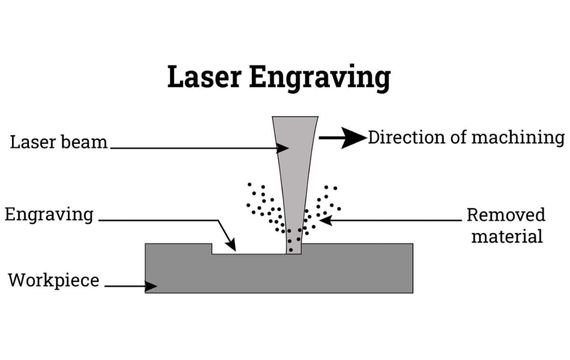
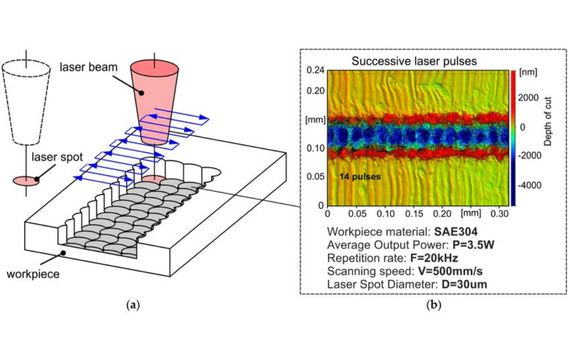
Step one: Creating Design
The image that will be etched onto the metal must first be created. Whether a photo or a vector graphic, it should be black and white or grayscale. You can see how it will seem after etching, thanks to this stage. As a general rule, if something looks bad on the screen, it will also appear bad on metal.
Resize the image to the required dimensions. Be aware that some picture stretching may be necessary if you’re etching on a non-planar surface. Save your work in a format so that the software for your laser can accept.
Step Two: Clean
Utilizing a soft cloth and rubbing alcohol, thoroughly clean your metal item. Clean the surface of any grease and dust. Apply some fine-grit sandpaper to the metal surface to remove any corrosion or rust that has developed.
Wearing gloves when cleaning and preparing the metal would be a good idea to prevent contamination from your hands’ oils and grease.
Step Three: Applying The Spray
Before spraying, let your metal object a few minutes to dry. Once more, make sure the surface is spotless before applying. Make a mark on the edges of the surface you intend to etch with some masking tape.
On the metal surface, uniformly apply the etching spray. Spray two or three applications of dry lube, allowing each one to dry completely before applying the next.
Step Four: Adjusting The Focus
Turn on your device and get it ready for etching. Remember to wear the appropriate safety eyewear. Place your metal component inside the apparatus and check that the laser’s height is set correctly.
Step Five: Etching
Put the file you downloaded in Step 1 into the laser’s control program. You should start with the highest power and the slowest pace for the best results.
Step Six: Finishing Up
Take your metal item out of the laser after it is finished, then clean it. New spray and other remnants can be cleaned off the metal piece using a soft cloth and rubbing alcohol from previously.
Laser Etching VS Laser Engraving
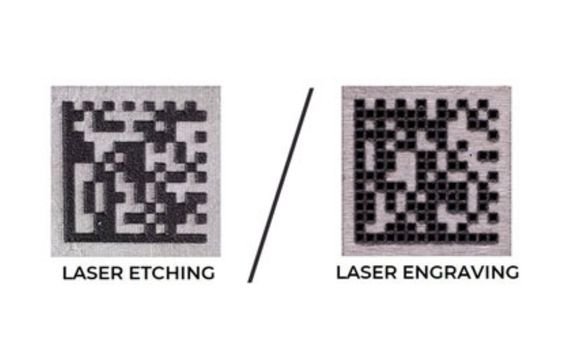
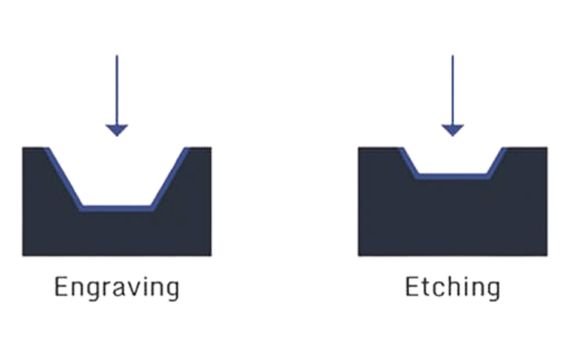
Although laser engraving is more powerful, laser etching is faster. It’s because it takes more energy to vaporize a substance than it does to use a laser to etch it to its melting point. More laser passes and time may be required for deep laser engraving. On the contrary hand, elevated marks left by etching are less durable than holes that have been engraved.
The depth of the laser engraving can go up to 500 microns, whereas the laser’s etching depth can go as deep as 80 microns. Due to its ease of usage, speed, and accuracy, laser etching is applied to a wide range of materials.
But metal surfaces can also benefit from laser engraving, which is applied regularly. Stainless steel, brass, cold rolled steel, and aluminum are among the metals that are frequently laser etched.
Choosing Equipment For Laser Etching Process


Only fiber lasers will work for laser etching.
It makes it possible to etch metals that respond better to fiber lasers. The laser you require depends on the material you want to etch, not how you plan to mark it. Metals regularly etched include steel, aluminum, magnesium, lead, zinc, lead anodized aluminum, and lead. A laser emits laser beams with predetermined wavelengths to release energy.
Most of the beam’s energy is reflected by the surface when it collides. Heat is created by absorbing excess energy. To be etched by a laser, a substance merely has to absorb heat sufficient to melt it. Different materials absorb and reflect these wavelengths since the Carbon dioxide, and fiber laser frequencies are separate. You need the proper wavelength to enhance energy transmission from the laser beam to the substance.
People Also Ask:
Yes
Laser etching leaves no traces and is permanent.
Compared to other direct part marking technologies, a laser etched mark will be easier to read throughout the component’s useful life. Non-abrasive processes like laser etching, powder coating, and heat treating may withstand one another.
Yes
Laser etching is faster than laser engraving and annealing. Laser etching is twice as quick. To expedite the etching process, use laser systems with higher laser strengths. The powerful laser needed for the majority of marking applications is 100W.
If one system has better optical components and optimal laser parameters, it can etch faster than another system of equivalent power.
Only black, white, and several shades of grey can be produced via laser etching. Black and white provide the finest contract out of the three. As a result, they are the color used more frequently for high-quality markings. Try laser annealing, another method that discolors the work piece’s surface with a laser beam, for multiple-color marking.
A lower-powered laser is used in laser marking to produce high-contrast markings on a substance’s surface without damaging the material itself. In contrast, a high-heat laser beam melts the laser, etching the surface of the target material. The intended picture may be seen because the melted material expands and creates a slightly elevated mark.
The only outcomes a fiber laser can produce are: The only machine that can be used for the process is a fiber laser marking machine. It is because metals, the most common supporting material, may more effectively absorb the wavelength of the fiber laser marker than other laser markers. This limitation impacts how small-scale metal fabrication businesses employ the technique.
When working on materials, the laser engraving machine’s lens focal length is reduced to provide a finer spot size. When engraving goods like photographic photos, this improves the quality. The greater focal length lens used by laser cutting machines is more forgiving of fluctuations in focus height and results in less taper in the cut edge.
More Resources:



