What Is Metal Spinning?
Metal spinning is also commonly referred to as metal turning, spin forming or spinning. A metal working procedure where different metals are taken through a high-speed rotation to form axially symmetric products.
Advantages Of Metal Spinning
Spun parts offer greater durability resisting pressures from the inside and forces from the outside.

Parts that need alterations after spinning can be altered easily especially when reducing the size.

Compared to other metal working processes, metal spinning produces smaller amounts of waste.

Metal spinning tooling system is made simple, cost-effective and easy to maintain compared to others.
Metal Spinning History
Metal spinning dates back before the 19th Century, being in use during the Egyptian error. During the Ancient Egyptian era, metal spinning was done with softer metals using hand driven lathes.
When hydro and steam sources of power were introduced in Europe and North America during the 19th Century, significant advances occurred. In early 20th Century, a high-speed spinning system was made possible through electric motors.
Many metal workers were now able to spin quality parts made of metals such as copper, aluminum and brass. Metal spinning was considered a low volume production process because it required highly skilled personnel.


Metal Spinning Design Considerations
Metal spinning can only be used to manufacture parts that are rotationally symmetrical. An example of such parts in one with a hemispherical shape. Another design consideration for metal spinning is that the parts internal diameters must be controlled from within.
Before the metal spinning process, ensure that tolerances are specified because the product doesn’t always have to be of uniform thickness. Dimensions considered earlier makes work easier and saves on time and prevents material wastage during the spinning process.
Knowing the types of materials to be used for a given part early enough also saves on money and reduces waste.
Types Of Metal Spinning Techniques


Conventional Spinning
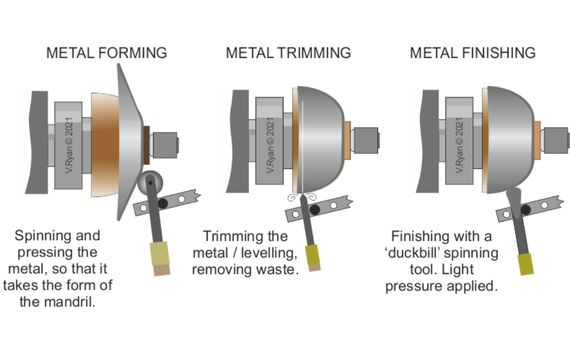
Conventional metal spinning is the simplest of all spinning techniques because it requires simple machinery and tooling. During the conventional spinning process, the metal is pushed over by the roller into the contour part of the mandrel.
The same level of material thickness is maintained throughout the spinning process. Parts that have different material thickness in different sections cannot be produced. In this process, material depth of the end product is increased while the diameter of the material is reduced.
Shear Spinning
Shear spinning uses rollers to push the metal downward and stretching at the same time over the mandrel’s contour. During shear spinning, material thickness is reduced compared to the original part.
However, the diameter of the end product remains the same as it was before being processed, increasing the depth. Mechanical properties of the metal part like hardness and strength are enhanced due to the high compressive forces applied.
In this technique more complex tooling system and a precise machine control system is needed. The process needs a coolant since the working of the machine creates heat.
Hot Spinning
Hot spinning is recommended for materials with low malleability and ductility properties or for those that cannot form at room temperature. Hot spinning technique uses a heating torch to raise the temperature of the workpiece to its forging temperature.
As the metal is pressed over the contour of the mandrel, it is heated using the heating torch. Hot spinning creates products with improved mechanical properties like strength but also oxidized. Controlling this process is a bit difficult and it is also more expensive.
Tube Spinning
Tube spinning works in the same manner as the shear spinning technique, however, tube spinning elongates the material. As it elongates the material, the material thickness reduces.
In this case, the material is clamped to the mandrel followed by drawing over the material using several rollers. Rollers move in the same direction as axial flow of tube. External tube spinning places the tube outside the mandrel while internal tube spinning places it on the inside of the mandrel.
Multiple-Pass Spinning
Multiple-pass spinning involves the use of rollers to apply force several times in the same direction of flow as the material. Most materials that are used with multiple-pass spinning techniques are those that are hard to deform. Different mandrels can be used for spinning parts with complex sections and shaper profiles.
Metal Spinning Process

Blank Loading
Blank is the metal that needs spinning and it can be loaded manually or automatically. A block which was previously formed, is to be loaded on to the lathe in the drive area. Usually, the material must be in a shape that can be spun through this machine.
Tailstock Clamping
Once the workpiece has been loaded it has to be clamped through a tailstock on to the contour of the mandrel. Clamping the workpiece ensures that it is stable enough to withstand the pressure exerted by the rollers. A pressure pad clamps the workpiece against the block that was loaded in the first step attaching it to the tailstock.
Multi-Rollers Ready
Rollers are cleaned and set ready before being loaded into the system for the spinning process. Rollers are used for smoothening and clearing the metal surface of any distortions caused by the previous metal working processes.
Multi-Rollers Feeding
Rollers are fed into the system and positioned equidistantly from the workpiece. Several rollers are used for the power spinning techniques because the technique can accommodate parts with unequal material thickness sections. However, for conventional spinning techniques, one roller is enough because the work piece has a constant material thickness.
Spinning Starts
Spinning begins when the workpiece receives a localized force that makes it move over the block. For conventional spinning, workpieces are simply removed from the block.
However, for power spinning techniques, the multiple rollers apply force to the various sections of the workpiece until it is ready. Highly complex designs are spun on ice forms but after spinning the ice melts away.
Other methods like necking or reducing can spin the workpiece in the air. This happens if surface finish or form are not necessary, eliminating the need for a mandrel.
Stop The Spinning
Once the spinning has been done and the required parameters have been achieved, the spinning process is stopped. A coolant is used to cool the system because spinning generates high heat.
Part Removal
Once the system has been cooled and it is safe to open the machine, the part is removed and it is ready for application.
Metal Spinning Tools And Equipment


Some of the most common tools include:
Mandrel
Mandrel is a die that is critical for the formation of shape and volume of a given metal part.
Roller
Rollers are used during spinning to apply a localized force on the workpiece to make it move over the die.
Tailstock
Tailstock is used to support and hold the metal in place during high-speed spinning on the mandrel.
Follower
Follower is a pressure pad used for clamping the metal in place on to the tailstock
Spindle
Spindle rotates the mandrel and the metal part during the spinning process.
Lathe Bed
Lathe bed has the responsibility of supporting the tailstock, headstock, and other machine components.
Suitable Materials For Metal Spinning

Carbon steel is a cost-effective type of steel with properties like high strength and formability making it suitable for spinning.

Brass is highly workable and malleable with high electrical and thermal conductivity and good resistance to corrosion, microbes and biofouling.

Bronze is highly weldable and formable making it suitable for spinning to form parts that are strong and durable.

Titanium is easily formable because of its ductile, soft and lightweight nature making it suitable for metal spinning top.

Stainless steel has high strength, rigidity and toughness which are all maintained at pressures or temperatures that are high.

Aluminum is suitable for metal craft spinning processes because it has properties like high ductility, malleability and strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effective.
Applications Of Metal Spinning

Parts with this kind of shape can be used for making mixing bowls, reflectors, tank heads, caps, domes and covers.
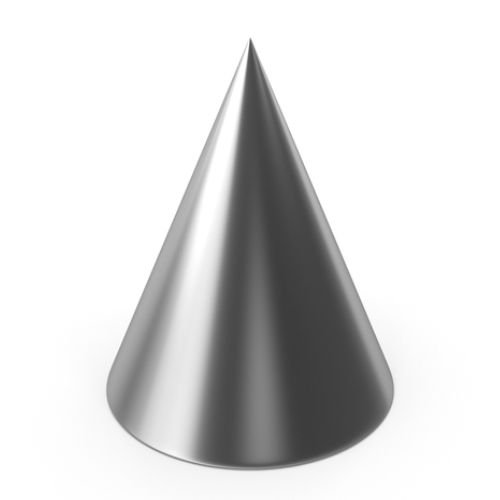

Cone-shaped spun parts can be used for making components such as pendants, funnels and hoppers.
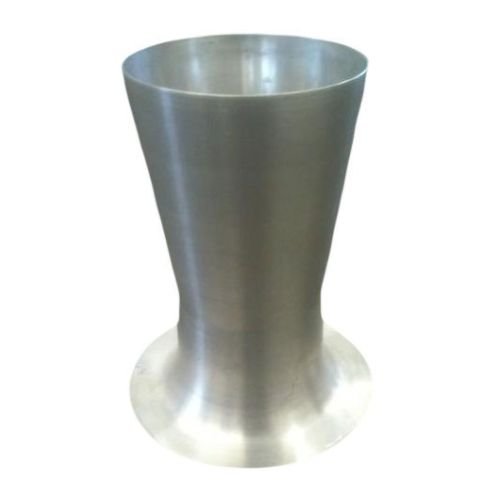

A venturi- shaped spun part can be a dust collector, fun, blower or scrubber.
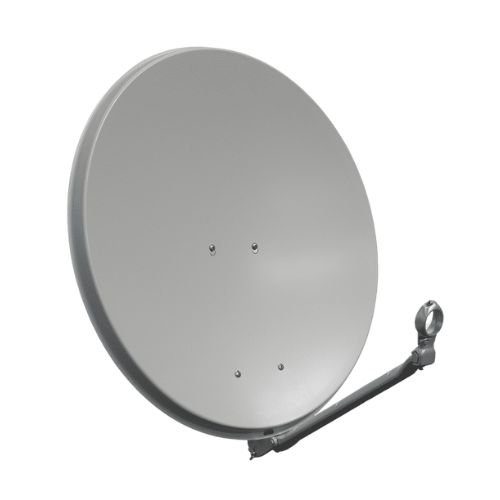

Bells, satellite dishes, lighting fixtures, bases for stands can all be made from parabola-shaped spun parts.

Products such as cans, vessels, tank shells, pipes, gas cylinders are made through spinning cylindrical parts.

Tank heads formed through spinning can take shapes like dished, flanged, high crown or tori spherical.
People Also Ask:
Metal spun parts done using CNC lathe for sale are more accurate and precise with tighter tolerances and quality surface finishes.
Metal spinning services is very affordable being that it is the cheapest compared to casting, tooling and stamping.
Metal screw spinning is slower compared to methods like casting and stamping.
Consistency is not assured when working with metal precision spinning method.
Metal sheet spinning has a limitation when it comes to shapes, it can work with axially symmetric parts.
- Low material waste
- Low tooling cost
- High speed process
- Stronger and stable parts
- Complex shapes can be done
- Performing various processes in one machine at ago is possible.
- Seamless components can be produced.
For parts that are below 1 foot in diameter the required tolerance would be +/- 0.005 inches.
2 to 4 feet needs tolerances of +/- 0.02 inches.
While 4 to 8 feet require a tolerance of approximately +/- 0.03 inches.
More Resources:



