This is a very important step taken in many production industries converting steel tubes from one form to another shape or size.
We will explore all this process entails and the aspects of fabricated steel.
What is Steel Tube Fabrication?

Steel tube fabrication refers to various processes that transform steel metal into a tubular form such as welding or bending.
Alternatively, it may also refer to processes of transforming steel tubes into other suitable forms and designs.
The type of metal fabrication technique you apply will determine the type of steel tube and custom dimensions needed for your application. To sum it up, steel tube fabrication is an indispensable part of contemporary engineering across many industries.
Steel Tube Fabrication Processes
Any steel tube fabrication services provides should handle a wide range of processes or techniques.
The method that you will settle for will be determined by your dimensional requirements and the intended purpose of your application.
Let us dive deep into the primary fabrication methods and the processes involved:
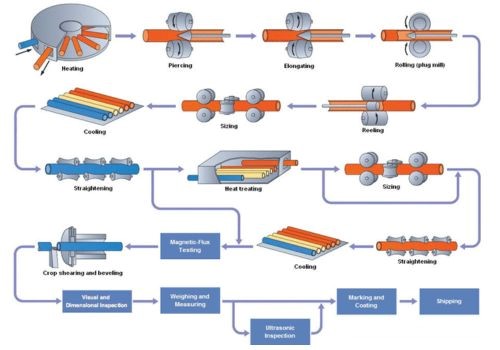
a) Seamless Steel Tube Fabrication
- Extrusion: this is one of the most common fabrication methods where a billet of steel is heated and forced through a die to create hollow tubing. Your final product has no welds or joints thus enhancing its strength and reliability.
- Pilgering: this cold-working process involves altering the diameter and wall thickness of a seamless tube. By passing it through a cavity die and mandrel, you greatly improve the tube’s mechanical characteristics.
b) Welded Steel Tube Fabrication
- Electric Resistance Welding (ERW): you can merge two or more steel tubes by welding their edges together using this method. You can fabricate a large number of tubes of similar sizes.
- High Induction Frequency Welding (HFIW): Just like ERW, you have to heat to reheat the edges for joining but using HFIW instead of a flame. You can achieve high-quality steel tubes having uniform weld cross-sections.
- Spiral Welding: it involves laying several steel metal sheets side by side to create a long strip of steel that you can coil into a spiral and weld on its edge. This is the best fabrication method when you want large-diameter pipes in large quantities.
c) Steel Tube Bending
There are several tube bending techniques you can apply including;
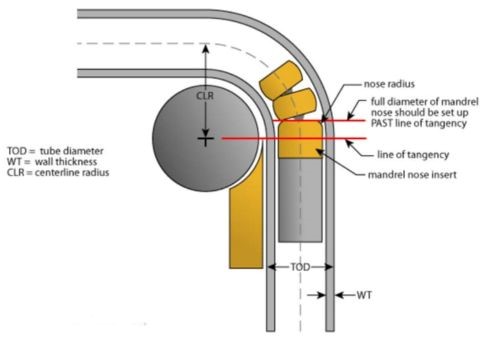
- Mandrel bending
- Rotary draw bending
- Press bending
- Compression bending
- Roll bending
- Heat induction bending
- Rotary compression bending.
If you want to create intricate designs that cannot be achieved through these, you can opt for custom steel tube bending to develop your desired form.
a) Cutting Steel Tube
Some of the most common cutting techniques you can apply when fabricating steel tube pipes include:
- Band Sawing: you can use a looped and toothed metal blade structured continuously to cut through steel tubes with precision and unmatched functionality
- Abrasive Cutting: involves grinding through a steel tube using an abrasive material attached to a disc
- Laser Cutting: uses a very powerful CO2 laser beam to cut through the steel tubing with utmost precision
- Oxy-Acetylene Cutting: you can melt through the steel tube using this flame that consists of a combination of oxygen and acetylene. This can either be done manually or through automated flame-cutting
- Rotary Steel Tube Cutting: if you are handling thin-walled tubes, this method is the best since the tube rotates while the cutter slices it.
b) Sandblasting Steel Tubes
It is a process whereby you expel a blast of abrasive sand particles from a container at extremely high velocities to improve surface readiness. It creates a good bonding environment for any additional coating.
Properties of Steel to Consider for Tube Fabrication
Steel tubes have several characteristics that enhance their fabrication ability. We can take a swipe at some of them and their benefits in fabrication:
- Strong And Durable: when fabricating them for applications that are not weight-sensitive, they are very strong and sturdy
- Corrosion Resistant: their impressive rust resistance ensures that your fabricated parts are highly durable even in harsh environments
- Versatile: you can find them in a variety of thicknesses and sizes to suit your various application designs.
- Thermal Conductivity: steel tubes can conduct both heat and electricity well making them suitable for heat exchangers and electrical applications.
Types of Steel Tubes for Fabrication
Steel is normally an alloy that consists of iron and a small portion of carbon which can be altered by adjusting the carbon or adding other elements to enhance properties. Let us have a look at some of these variations briefly and how fabrication impacts them:
- Carbon Steel Tubing: the most frequently utilized steel in fabricating tubes. It is very cost-efficient and best for high-strength applications with minimum cost
- Alloy Steel Tubing: it has a high concentration of elements that enhance attributes such as strength, hardness, wear, and corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel Tubing: the high chromium content gives it excellent corrosion resistance and works well in moisture-prone applications
- Galvanized Steel Tubing: they are zinc plated to protect them from corrosion in industrial applications having ambient climate
- Structural Steel Tubing: we recommend this for your construction and automotive fabrication due to its robust and versatile properties that allow precise shaping and welding.
Fabricating Steel Tube Part Examples
Due to their strong and durable properties, we use steel tubes to fabricate various parts used across various industries such as:
- Construction: building frames, support frames and scaffolding
- Automotive: strong and rigid frames, exhaust systems, drive shafts, hydraulic and fuel systems
- Aerospace: landing gears, engine mountings, and hydraulic systems that require light steel tubes with a high tensile strength
- Energy And Utilities: pipelines used for conveying oil, water and gas, heat exchangers, and condensers in power plants
- Medical: medical instruments, surgical equipment, and hospital furniture.
Conclusion
The fabrication of steel tubes has necessitated the creation of operation-critical components applied across various industries. Its possibilities are further cemented by the advancements in fabrication technology that will enable you to fabricate even more complex designs and parts.
More resources:
How to Custom Steel Tube – Source: KDM
Here’s Everything to know about Stainless Steel Pipe Fabrication – Source: KDM




