
In this article you will learn all properties and applications of 3003 aluminium alloy. Further, it will compare the aluminum alloy with other grades to help you make the right decision.
Let’s dive right in:
What is 3003 Aluminium?
3003 aluminium is one of the general-purpose alloys that originates from the processed aluminium-manganese family. This type of alloy cannot be heat-treated but allows cold treating. However, when cold-treated, the product is of lower ductility.

Some of the properties that define 3003 aluminium are derived from manganese (1.25%) and copper (0.1%). These two give it the moderate strength it offers making it a better choice for manufacturers.
3003 Alloy Grade Aluminum Benefits
- Resistance to atmospheric corrosion – making the Alu grade perfect for most general applications
- Low weight to strength ratio – it is a good choice because it offers good weight to strength ratio and can be used for various applications.
- Easy to weld – it is easy to weld and form and can be transformed into any useful part.
- Improved mechanical properties – At high temperatures, this Alu offer good mechanical properties.
Limitations of Aluminum
Aluminium has various advantages. However, it also has its own set of limitations compared to other metals like steel. Some of these limitations include;
First, parts made of aluminium don’t perform well with applications that are involved is high temperatures.
Another disadvantage of aluminium is that it does not offer much fracture toughness when involved in applications that need strength.
Also, aluminium is costly and requires some good money to be able to purchase enough quantity for your applications.
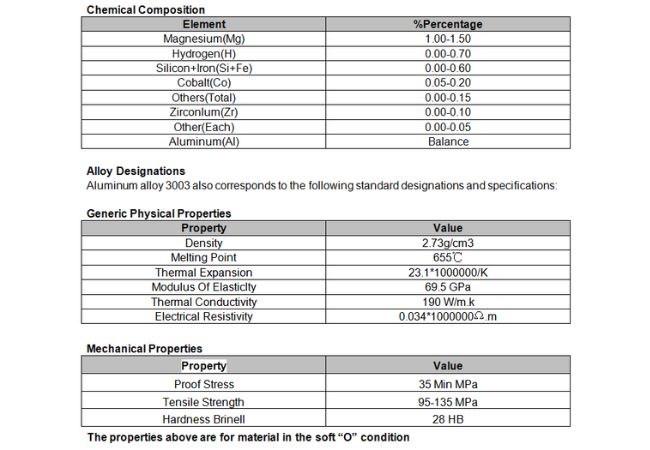
Chemical Elements in 3003 Alu Alloy
3003 aluminium alloys are made up of various chemical elements that contribute to its general chemical properties including;
| Element | Approximated percentage (%) |
| Aluminium | 96 – 99 |
| Copper | 0.05 – 0.20 |
| Iron | No more than 0.7 |
| Manganese | 1 – 1.5 |
| Silicon | Not more than 0.6 |
| Zinc | Not more than 0.1 |
| Residues | Not more than 0.15 |
3003 Aluminum Alloy Physical Properties
The table below will give you an overview of what physical properties an aluminium 3003 offers.
| Properties | Value |
| Melting point | 655°C |
| Modulus elasticity | 69.5 GPa |
| Electrical resistivity | 0.034 by 10−6Ω.m |
| Density | 2.73 g/cm3 |
| Thermal expansion | 23.1 by 10−6 /K |
| Thermal conductivity | 190 W/m.K |
Mechanical Properties of Alu 3003
Let’s look at the table below:
| Properties | Value |
| Tensile strength | 95 to 135 MPa |
| Proof stress | 115 (Min) MPa |
| Hardness Brinell | 40 |
| Elongation (50mm) | 8 Min % |
Note that the above mechanical properties can change depending on the type of 3003 aluminium alloy you are working with.
Difference between Aluminum 3003 and 5052 Aluminum
Aluminium 3003 and 5052 Aluminum Grade are basically two of the most supplied alloys within the manufacturing industry globally.
However, the differences between the two cannot be ignored. In order to choose between the two alloys, understand the differences in the various aspects as you can see below:

Alloying Elements
Find in the table below a summery of the different elements in percentage the two alloys are made of.
| Alloy | Ti | Zn | Cr | Mg | Mn | Cu | Fe | Si |
| 5052 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 45 |
| 3003 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0/1.5 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
Mechanical Properties
Secondly, find out the mechanical properties that make the two types of aluminium alloys unique from each other.
For instance, 3003 aluminium alloy offers tensile strength of20 to 26 KSI, hardness Brinell of 40 and proof strength of 21. 5052 aluminium on the other hand, has tensile strength of 31 to 38 KSI, Brinell hardness of 60, yield strength of 28.
Forming and Fabricating
3003 aluminium alloys are generally soft with good resistance to atmospheric and chemical corrosion, moderate strength and easy to weld.
On the other hand, 5052 aluminium alloy is strong, easy to form, draw and weld.
3003 Alu is corrosion resistant, and offers better welding properties and average strength. 5052 is chosen for its toughness, strength, workability and high resistance to corrosion.
Uses
3003 aluminium find most of its end uses in utensils, pressure vessels, hardware, food containers, cabinets, chemical equipment and tanks. 5052 aluminium alloy finds its end uses in food service, automotive, appliances, metal fabrication, medical equipment, marine and tanks.
Costs
Comparing the two aluminium alloys, their prices differ depending on the market availability and conditions. Generally, 3003 is cheaper compared to 5052 aluminium alloy.
How Aluminum 3003 Compares to Aluminum 6061
3003 and 6061 aluminium alloys have almost 98% similarities in chemical composition as illustrated in the table below.
| Elements | 3003 aluminium | 6061 aluminium |
| Aluminium | 96.8-99 | 959-98.6 |
| Copper | 0.050-0.2 | 0.15-0.4 |
| Chromium | 0.0 | 0.040-0.35 |
| Zinc | 0.1 | 0-0.25 |
| Manganese | 1.0-1.5 | 0-0.15 |
| Iron | 0-0.7 | 0-0.7 |
| Titanium | 0 | 0-0.15 |
| Silicon | 0-0.6 | 0.4-0.8 |
| Residue | 0-0.15 | 0-0.15 |
| Magnesium | 0 | 0.8-1.2 |
Besides, they both have good bendability properties. 3003 aluminium alloy for instance, can undergo a sharp bending without breaking.
Some of these differences include:
Strength
6061 Alu is stronger than 3003 after heat treatment.
Processing
3003 cannot undergo heat treatment and can only be made stronger through cold working. On the other hand, 6061 aluminium can undergo both aging and heat treatment.
Anodizing Effect
Between the two alloys, only 6061 aluminium alloy can be anodized and coloured. 3003 aluminium does not form a uniform colour after anodizing.

3003 Alu Alloy Fabrication
3003 aluminium alloy can accept all the fabrication processes except heat treatment. Find out from the table below.
| Fabrication Processes | Description |
| Forming | · 3003 aluminium is easy to form /its ductile and soft. |
| Welding | · 3003 aluminium alloy can be welded through conventional methods. |
| Heat treatment | · Not suitable for heat treatment. |
| Forging | · Forging does not take place with 3003 aluminium alloy. |
| Hot working | · Hot working with 3003 aluminium takes place at 260 – 510oC |
| Cold working | · Will produce high strength material properties with low ductility |
| Annealing | · Annealing is done at 4150C to soften the alloy. |
| Hardening | · Can be hardened through cold working. |
Forms Alu 3003 Exist
Some common options include:
Aluminum Sheet 3003 -An aluminium sheet 3003 has a thickness of between 0.15mm and 2000mm
Aluminum Coil 3003 -The most commonly supplied 3003 aluminium because of moderate strength and resistance to corrosion.
3003 Aluminum Alloy Tread Plate – It is an aluminum plate with various patterns on its surface. Alternatively, you may also get a super thick 3003 aluminium alloy measures more than 2000mm.
3003 Aluminum Alloy Rod – Aluminium 3003 alloy rod offers the following; corrosion resistance, accurate dimensions, sustain high pressure and temperature load, Rust proof finish.
3003 Aluminum Tube – 3003 aluminium tubing can be used for transporting water, oil, air among others.
Aluminum 3003 Uses
Common applications of this alloy include:
Building industry: Within the building industry, 3003 aluminium is required for sidings and roofing, corrugated sheets and acoustic ceilings.
Food industry: The food industry uses 3003 aluminium to make pipes, storage tanks and metal work
Chemical industry: 3003 aluminium alloy can also be applicable in making chemical equipment and other products within the chemical industry.
Heating and cooling industry: Here the alloy is mostly used in making heat exchangers, evaporators, air conditioners, freezer linings and vehicle radiators.
Home appliances: Other manufacturers also use aluminium 3003 for producing cooking utensils and bakery moulds
Packaging industry: 3003 aluminium alloy can also make good containers and closures.
3003 Aluminum Alloy Specification
Aluminum alloy 3003 contains about 1.25% manganese and 0.1% copper.
Conclusion
From this guide, you are now in a better position to decide whether you will need 3003 aluminium for your applications or not.
As you can see, this material plays an integral role in various aluminum fabrication applications.
More Resources:
Aluminum Alloy – Source: Wikipedia
3003 Aluminum Alloy – Source: Wikipedia




