Copper and brass have distinctive features which makes them useful in different situations. Differentiating them is a prerequisite for choosing the type of material fit for both technical, architectural, and many other uses.
What is Copper?
Copper with the chemical symbol Cu has an atomic number of 29. Copper belongs to group 11 elements and has a very high heat and electrical conductivity. For thousands of years, copper has been a material known for being malleable, resistant to corrosion, and conducting heat and electricity. You will find different copper alloys in electrical and heating systems.
Copper is commonly used in different sectors, such as power cabling, household plumbing, electronics, construction, and transportation.
It is also an essential trace element for living organisms and is implicated in different biological functions.
What is Brass?
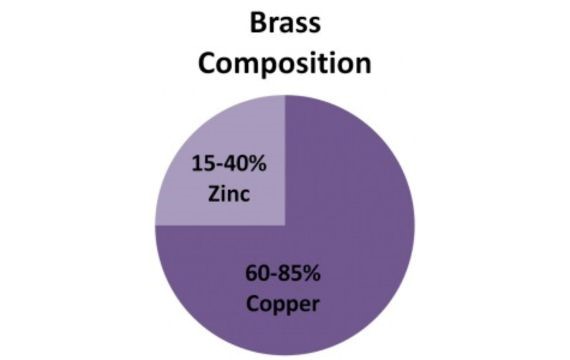
Brass is an alloy that is made up mainly of copper and zinc. Usually, it has 60–90% copper, and the rest is zinc, yet this composition may also vary from one purpose to another or according to the needed properties.
Brass’s yellowish color is a blend of copper and zinc, hence its brownish-reddish shade or gold-like brightness at different proportions of the elements. Brass is popular for the combination of properties it possesses, such as malleability, corrosion resistance, and acoustic features.
Differences between Brass and Copper
Composition
Copper as Base Metal
Copper is made of atoms that are arranged in crystalline structure. It is flexible with excellent electrical and heat conductivity. One of copper’s different features is its reddish color. It is also abundantly available in nature.
Brass an Alloy of Copper and Zinc
Brass is an element that is made of a combination of copper and zinc. Copper usually makes up 60 to 90% of the brass, while zinc takes up the rest.
Zinc reacting with copper alters the characteristics of brass as it becomes tougher and stronger while maintaining copper’s malleability and corrosion resistance. The range of brass colors, from reddish-brown to yellow, is determined by the proportions of copper and zinc.
Physical Properties
Color
Copper has a characteristic orange-reddish color, which is often described as “copper-red.” This color arises from the metal’s electronic structure, which is its absorption and reflection of light wavelengths.
The surface of the new copper will rather have a shiny metallic look. However, with time, there is a possibility that it will gradually develop a greenish tarnishing due to the oxidation process.
Different from that of copper, brass is diverse in color, ranging from reddish-brown to golden yellow, depending on its composition. The special color of brass is subjected to the fractions of copper and zinc in the alloy. Therefore, it is useful in applying to the aesthetic fields.
Density
Copper, being very dense, has a density of 8.96 g/cm2 at room temperature. Due to its high density, it can be used in structural and engineering applications, which makes it useful for both of them.
Copper density maintains a relatively low consistency regardless of its transformation between the pure copper metal and the copper alloys.
In contrast, the density of brass varies, assuming that its composition changes, which depends on the relative amounts of copper and zinc. On the whole, copper is larger than brass as a result of its heavier weight than zinc.
Melting Point
Copper has a quite high melting point, which is about 1984 degrees Fahrenheit (1,085 degrees Celsius) on average. Usually, copper melting point is attributed to the metallic bonds that exist in the Cu crystalline lattice structure.
Copper can withstand high temperatures, making it useful in applications that require heat resistance, like electrical wiring, plumbing, and processing metals.
As far as brass goes, it has a lower melting point compared to pure copper because of the zinc that is present in the material, which reduces the cohesive forces between copper atoms. The melting point of brass is influenced by its composition and usually varies from 900° to 940°C.
Conductivity
Copper has a unique ability to conduct electricity and heat faster than many other metals. It has great electrical conductivity, second only to silver, and shows superior thermal conductivity, which is just after diamond and silver.
These characteristics are the reason that copper is indispensable in wiring for electricity, electronic components, heat exchangers, and areas that require the transfer of heat and power to be done efficiently.
Brass has relatively lower conductivity than copper in electrical and thermal conductivities, but it’s still a good conductor because of its metal characteristics. On the other hand, the purity of zinc is less than that of copper, which in turn makes zinc less of a conductor.

Sound
Copper and brass have appealing acoustic properties, although with differences. Copper is applied to many of the musical instruments, such as bells, where its tone and resonation bring about rich sound.
Sound waves are transmitted very well on the material, making it a good one to use in acoustic applications.
Brass being a mixture of copper and zinc, inherits some of the acoustic properties but may show some variations depending on its composition. The brass-metal combination is key to its resonance, tone, and timbre, making it fit for different musical applications, like trumpets to cymbals.
Durability
Copper is well-known for its durability, as it has excellent resistance to corrosion, rust, and degradation over time. Its intrinsic stability and resistance to the environment make it the number one option for outdoor uses like roofing, plumbing, and electrical.
Furthermore, copper’s malleability enables it to accommodate bending and shaping without cracking, which is beneficial in many structural and engineering projects.
Brass has the durability of copper since it has some strains of copper in it. However, because it also has zinc it has a higher corrosion resistance as compared to copper which makes it perfect for marine and high humid areas.
This property makes it stand out from copper and is better for marine use, decoration, and outdoor items.
Applications
The application of copper is ubiquitous and extensive, ranging from multiple industries to various applications. Conductivity is the aspect that makes it so vital in electrical wiring and electronics; it helps to transmit electricity most efficiently.
Its corrosion resistance and ductility, make it an excellent choice for plumbing systems, roofing materials, and architectural components. Besides, copper is prominent in heat exchangers, machine parts, and coinage in virtue of this metal’s thermal conductivity and antibacterial properties.
Brass, with a unique mix of properties, finds deployment across a wide variety of industries. With its aesthetic look and rustlessness, it is used for decorative purposes such as ornamental items, jewelry, and musical instruments.
Brass is likewise used for tubing fittings, valves, and hardware because of its durability and machinability.
Additionally, its antimicrobial properties manifest themselves in healthcare contexts where it is utilized on doorknobs and fixtures. In electronics, brass parts are used as connectors and terminal pins because they are conductive and resistant to corrosion.
Conclusion
Although copper and brass, share some attributes, there are significant differences between them in terms of their composition, physical properties, and applications. Awareness of such entity formation enhances sensible choice-making in different industries and spheres.
More Resources:
Bronze vs. Brass – Source: KDM
Brass Fabrication – Source: KDM
Copper Fabrication – Source: KDM
Does Copper Rust – Source: KDM
Does Brass Rust – Source: KDM
Is Brass Magnetic? – Source: KDM




