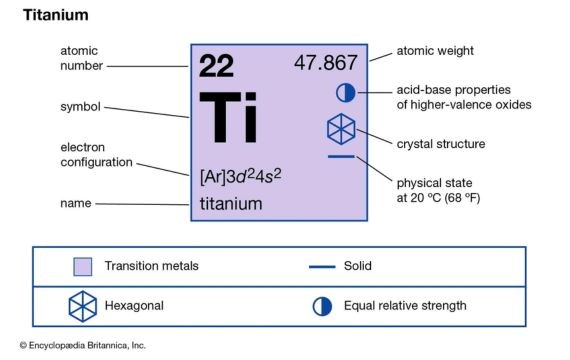
Titanium is a type of metal that has an element symbol of Ti and an atomic number of 22.
In this article, we will explore the fundamental aspects of titanium magnetism.
Is Titanium Magnetic?
Pure titanium is non-magnetic. However, there is an argument that titanium experiences weak magnetism. The truth is, this magnetism is not significant to the point that it is visibly noticeable.
Non-magnetic Properties of Titanium
· Diamagnetic
Generally, titanium features a crystalline structure with no unpaired electrons.
Although there are instances where titanium develops a weak magnetic field, usually this is so negligible.
· Weak Magnetic Moments
Magnetic moments due to titanium are very weak. Besides, they are not permanent to make titanium a magnetic material. Furthermore, even the net magnetic moment when titanium is in the magnetic field is quite low.
· Cannot be attracted by Magnets
When you put titanium in a magnetic field, it is not attracted by the magnet. This is usually due to a lack of ferromagnetic properties or elements.
What makes Titanium Non-Magnetic?
This is because titanium has no unpaired electrons and a crystalline structure. For a metal to exhibit magnetic properties, it must have a magnetic moment.
For metal to be considered magnetic, it must have unpaired electrons that can align their spin in the presence of the magnetic field. It is this property that will make a magnet attract a metal (that is if the metal is magnetic).
The outer electron shell of the titanium configuration makes the electrons pair, thus displaying weak magnetic properties.
Factors Affecting Non-Magnetic Properties of Titanium
Temperature
At room temperature, titanium is considered non-magnetic and its magnetic susceptibility can increase at lower temperatures.
Purity
The purity of titanium affects its non-magnetic properties. This is one variable you can use to determine whether titanium is pure or not.
For example, titanium with impurities that include ferromagnetic material will exhibit some magnetic properties. In such circumstances, you may assume titanium is magnetic.
Alloying Elements
When an alloy element is added to titanium, it affects its non-magnetic properties. That is, alloying titanium with ferromagnetic material will make the material exhibit magnetic properties.
Application of Titanium
· Power Generation
The non-magnetic properties of titanium can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion.
These features make it applicable in the use of power generation industry for manufacturing turbine blades and heat exchangers.
· Medical Applications
In the medical industry, titanium is used in the manufacture of implants due to its biocompatibility, non-magnetic properties, and resistance to corrosion in the human body.
Conclusion
In short, titanium in its pure form is non-magnetic. However, the existence of ferromagnetic properties may make titanium exhibit some magnetic properties. This is quite critical when testing the purity of titanium.
More resources:
Titanium Magnetism – Source: BEMAGNET
Magnetic Properties of Titanium – Source: TERP CONNECT
Titanium Melting Point – Source: KDMFAB




