Calcium is a silvery white Group alkali metal with a variety of industrial uses with its unique characteristics. It needs proper handling because they have a strong tendency to oxidize readily in the air.
It is highly reactive, readily soluble in air, and has a melting point of 842°C (1548°F).
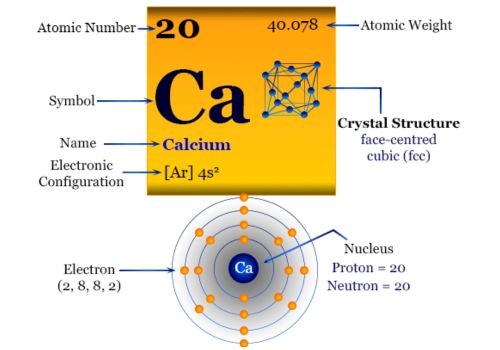
Properties of Calcium Metal
| Property | Value/Symbol |
| Melting Point | 842 °C (1548 °F) |
| Appearance | Dull gray, silver; with a pale yellow tint |
| Ductility and Malleability | Soft and malleable |
| Density | 1.55 g/cm³ (at 20°C) |
| Atomic number | 20 |
| Symbol | Ca |
| Boiling Point | 1484 °C (2703 °F) |
Factors Influencing Calcium Melting Point
The melting point of calcium is affected by the strength of the metallic bond, which holds the atoms together. Meanwhile, when comparatively strong metallic bonds between calcium atoms need a certain amount of energy to break down, the melting point is shown.
Additionally, when there are different impurities, such as oxygen or nitrogen, they can destroy the crystal lattice structure of calcium metal. In short, when you make the metallic bond weak, that’s when you can lower the melting point.
The M.P. of Calcium metal is affected by several factors. Under normal circumstances, the melting point of calcium metal is 842°C or 1548°F, which is higher than that of magnesium or strontium.
As you know, the Mg and Sr belong to the 2nd Metal Group. Likewise, their melting points are higher in most of the 2 Metal Groups. This because it has 4s electrons in the metallic bond.
Recent Advances in Understanding Calcium Melting Behavior
The recent advancements in calcium melting behavior studies include levitation techniques and computational modeling.
Levitation melting techniques use electromagnetic forces to break down the calcium droplets into a highly pure inert gas environment. Likewise, this gas minimizes contamination and lets you find the perfect melting point.
On the other hand, computational modeling changes the behavior of calcium at high temperatures. Also, it gives proper information on the melting process at an atomic level. However, all these modern innovations have helped you to understand the melting point of calcium more clearly.
Applications of Calcium in Industry and Science
There are many different uses of calcium in many industries. From producing perfect steel to being used as an alloying element in aluminum.
However during the process, it is important to remove oxygen impurities. This ensures you get high quality steel.
Also, calcium is very important in reducing air pollution when its compounds catch the sulfur oxides in flue gas cleaning.
Likewise, researchers are continuously experimenting with calcium metal. They believe it will be used in future as batteries for better and cleaner energy production. Also, it works best for bone production and muscle function, making it a lifesaver as well.
Conclusion
Due to its high melting point of 842°C, calcium is essential in industries ranging from steelmaking to medical applications. Such novel properties will hopefully ensure a great future for the material in science and technology.
Related resources:
Bronze Melting – Source: KDM
Aluminum Melting Point – Source: KDM
Copper Melting Point – Source: KDM
Melting Point of Zinc – Source: KDM
Melting Point of Magnesium – Source: KDM
Melting Point of Graphite – Source: KDM




