Glass is an amorphous silicon form but not a metal. Meanwhile, it can be solid or liquid and made from silicon dioxide. However, Glass is a mixture of silicon and metallic and non-metallic oxygen compounds.
So, the melting point of Glass is variable, such as:
- 1400 / 1600 degrees Celsius
- 2,552–2,912 F degrees Fahrenheit

Composition of Soda-Lime Glass
Glass is a complex material with a non-crystalline structure consisting of randomly arranged atoms of amorphous silicon.
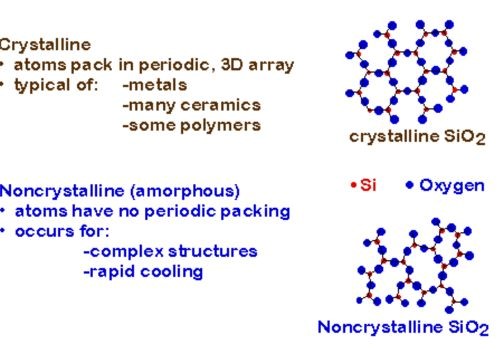
| Component | Percentage |
| Calcium Oxide (CaO) | 5-10% |
| Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) | 70-75% |
| Other Oxides (MgO, Al2O3) | trace amounts |
| Sodium Oxide (Na2O) | 12-15% |
Factors Determining Glass Melting Temperature
Firstly, you need to know that glass does not give some certain melting point. It shows the glass transition temperature represented as Tg; when it’s under Tg, the Glass is considered solid.
On the other hand, when it goes over Tg, the viscosity decreases, and it becomes soft. As viscosity means resistance to flow, it can become moldable. Many factors can impact the melting point of Glass.
Likewise, when you use different types of Glass or various proportions for melting, it directly influences the Tg. Meanwhile, the silicon (SiO2) normally shows a high melting point, and when you add diodes like sodium oxide (Na2O) to this process, the Tg decreases.
Also, when you add this kind of dioxide, it can help the glass melt more easily. Meanwhile, there are some elements like aluminum (Al2O3) that increase the glass transition temperature.
Innovations in Glass Melting Technology

Electric furnaces provide cleaner and perfect efficiency and sustainability, which replace traditional fuel-fired furnaces.
The induction melting uses electromagnetic fields to give good heat to Glass. Meanwhile, it nicely reduces the environmental impact and controls the melting process by minimizing the waste of energy.
Additionally, manufacturers use continuous technology to streamline the large-scale manufacturing of Glass for uninterrupted glass production.
All these modern advancements in melting techniques work smoothly, and they are environmentally friendly as well.
Applications of Glass in Various Industries
Glass is famous for its unique qualities of transparency, strength, and formability.
Like other metals, it also has many uses in various kinds of industries, construction, and both inside and outside of your house. Take for instance, in construction, it is used as window doors, architectural panels, and filter optic cables.
Many food industries need glassless for their products, such as jars, bottles, and containers.
Glass is everywhere, from use in pharmaceuticals to beverages. It might be possible that you are reading this article through a glass in your eyes. All the science labs are classless for different kinds of experimentation.
Typical Glass Transition Temperature Ranges
| Glass Type | Glass Transition Temperature (°C) | Glass Transition Temperature (°F) |
| Soda-Lime Glass | 500-550 °C | 932-1022 °F |
| Borosilicate Glass | 510-560 °C | 950-1040 °F |
| Lead Crystal Glass | 500-570 °C | 932-1058 °F |
Conclusion
Glass has a variable temperature, which is not specific. Meanwhile, with so many applications in various kinds of industries all over the world, you have to understand there are still some factors that can affect the melting point of glass.
More Resources:
Melting Point of Zinc – Source: KDM
Melting Point of Magnesium – Source: KDM
Melting Point of Graphite – Source: KDM
Aluminum Melting Point – Source: KDM
Copper Melting Point – Source: KDM




