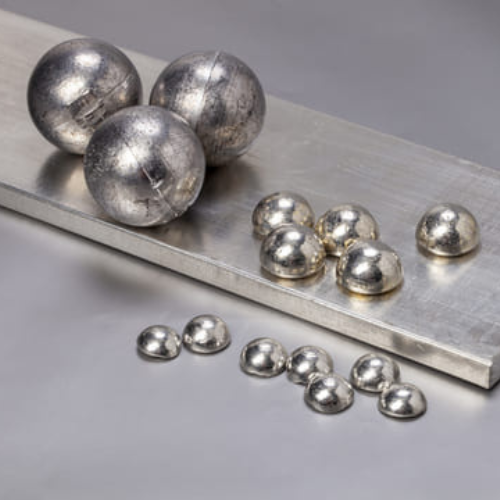
A common method of manufacturing that produces precise goods with exceptional dimensional accuracy and consistency is permanent mold casting. It is a well-liked option for sectors that need large quantities of intricate small-to-medium-sized metal parts.
Process of Permanent Mold Casting
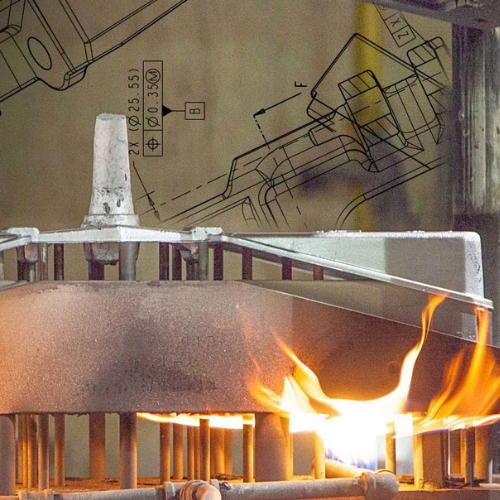
The ideal temperature to heat the mold to enhance metal flow and reduce defects is between 300 and 500°F (150 and 260°C). Subsequently, the surfaces of the mold chamber are coated with ceramic material to facilitate the removal of parts and increase the mold’s longevity.

The mold is made up of at least two parts, regardless of whether exact features are created utilizing cores. Despite being frequently composed of steel or iron, these cores may contain disposable sand cores.
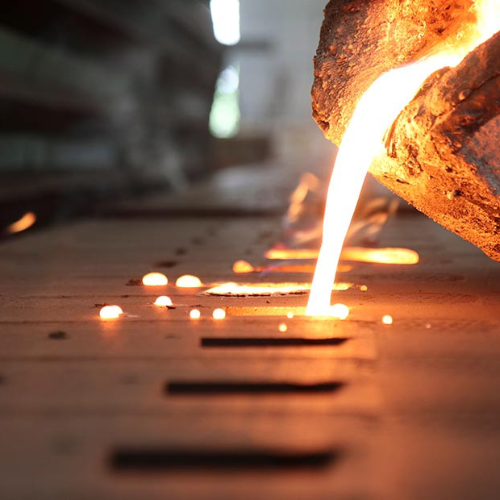

Using a ladle, melted metal is gently poured into the mold through a sprue located at the top of the mold. Before entering the mold chamber, the metal passes via a runner system.

It’s acceptable for the molten metal inside the mold to cool and solidify.
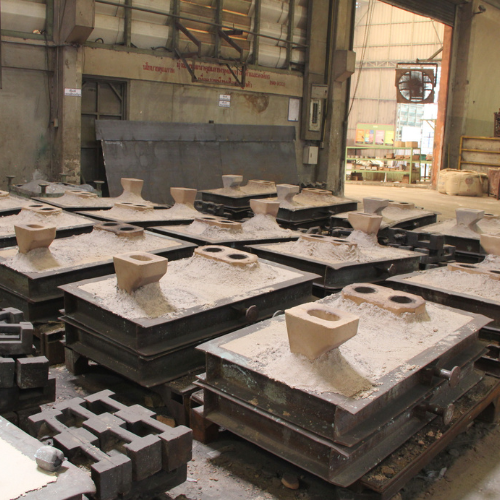

After the metal has set, the casting can be removed from the mold by splitting the two pieces.
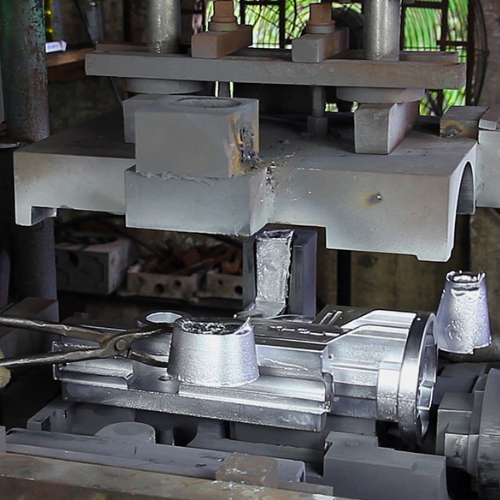

The metal in the sprue and runner system solidifies and joins with the casting when it cools. At this stage, the extra material is removed.
The Metals Used in Permanent Mold Casting
Permanent Mold Casting's Benefits
Superior Surface Finish: When compared to sand casting, permanent molds offer a smoother surface finish.
Tighter Tolerances: This method makes it possible to produce products with greater dimensional accuracy and precision.
Higher Production Rates: Through multiple casting cycles, the robustness of permanent molds enables more efficient manufacture.

Difference Between Different Casting Techniques and Permanent Mold Casting

Sand casting is less precise than permanent mold casting, which often produces goods with a smoother surface.

Although die casting is a fast process, it may require more expensive equipment. The cost-precision trade-off is provided via permanent mold casting.
Permanent Mold Casting: Applications

- The automotive sector regularly uses permanent mold casting to create parts like gearbox housings, cylinder heads, and engine blocks.

- Impellers, casings, and housings are a few of the items that are commonly made in the pump and valve sector employing permanent mold casting.

- Turbine blades, impellers, and other aerospace components, as well as jet engines, are made by permanent mold casting.

- The manufacturing of gears, pulleys, and other parts for machinery and equipment is another application for permanent mold casting in the industrial equipment sector.

- Turbine blades, casings, and other pieces are cast in a permanent mold for use in power-generating applications.
Initial Cost: Compared to the disposable molds used in other casting techniques, the manufacturing of permanent molds can be costly.
Limited Complexity: When it comes to simpler, less complex components, permanent mold casting performs better than some other casting process techniques.
Permanent mold casting can produce intricate designs, however for more intricate and detailed objects, it might not be as suitable as other methods like investment casting.
For large-scale manufacturing, long-term mold casting makes sense. Large part quantities may be produced at a reasonable cost due to the reusable molds and quick cycle times.









