The press brake is one specific type of tool used to bend sheet metal. The total bending length and the metal-bending capacity of the machines are two important indicators of their capabilities.
Sheet metal is bent by a press brake by lowering a punch into the metal that is placed over a die. Moreover, a press brake also allows the metal to be bent repeatedly into the required shape.
Types of Press Brake

- Uses a mechanical flywheel to provide power.
- Utilized a clutch system to function.
- Ideal for smaller production quantities and straightforward bending jobs.

- Relies on hydraulic systems to produce the necessary bending force.
- Gives the bending process more control.
- Ideal for a variety of bending activities, including those requiring a lot of force.

- Ensures precise and equal bending along the whole length of the machine by using a set of synchronized hydraulic cylinders.
- Perfect for high-volume, precise bending applications.

- Uses electromagnetic force rather than mechanical or hydraulic systems.
- Ideal for thin and fragile materials and offers fine control over the bending process.

- Creates force for bending by using compressed air.
- Less frequent than mechanical or hydraulic press brakes, and usually utilized for smaller bending jobs.

- Combines the automated and accurate bending capabilities of computer numerical control (CNC).
- Permits intricate turns and precise repetition of operations.
- Possibly servo-electric or hydraulic.

- For accurate control and energy economy, makes use of servo motors.
- Ideal for uses where a high degree of precision and flexibility are needed.
- Superior to hydraulic press brakes in terms of energy efficiency.

- Involves the simultaneous operation of two or more press brakes.
- Applied to large or lengthy pieces to enable multiple bending operations to be completed at the same time.
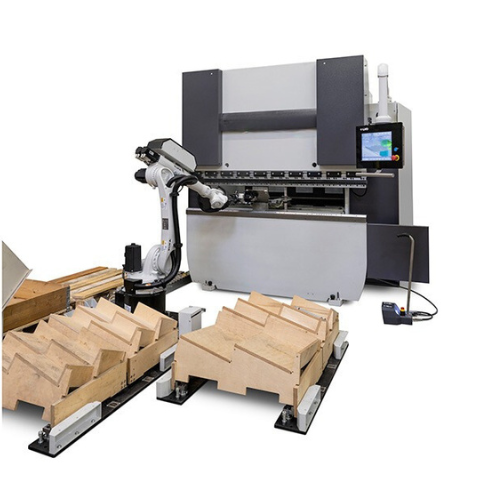

- Automates bending and loading/unloading processes by integrating robotic systems.
- Increases productivity and can manage challenging jobs.
Press Brake Features














Press Brake Benefits in the Fabrication of Metal
Reduced wasting of materials – The press brake is recognized to generate less material waste than other production techniques.
Increased productivity – In every production process, defects are inevitable. Instead of trying to get rid of them, lessen their frequency until it has no impact on daily activities and output.
Internal production capacities – Businesses can bring part or all of their production in-house with the help of a press brake machine.
Versatile programming – Press brakes are the perfect complement to fundamental production methods, even though they are still useful. Press brakes feature various programming possibilities.
Automation – Depending on the situation, press brakes might be fully automated, semi-automated, or handled manually.
Intricate designs – Almost every industry has used sheet metal fabrication at some stage. For example, fabrication is used by construction companies to create the beams, rafters, and other structural components needed to construct high-rise buildings.

Typical Applications for Press Brakes
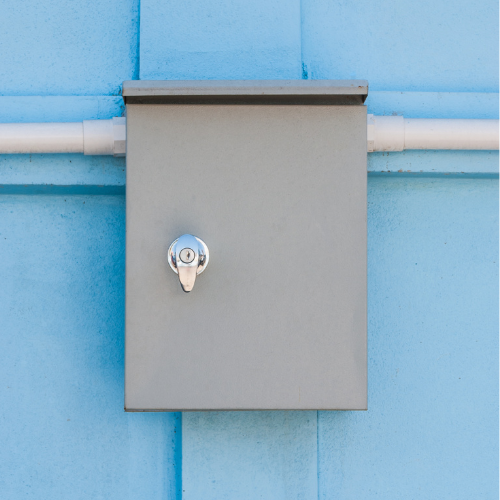

- Electrical cabinets
- Control panels
- And various equipment housings.



- Refrigerators
- Ovens
- Washing machines
- And other household appliances.



- Metal signs
- Displays
- And other advertising materials



What is the initial reason for calling a press brake a “press brake”? The definition of a “brake” in the fourteenth century was a device for pounding and crushing; over time, the phrase developed to mean a machine.
The word “press” is derived from the verb “pressed,” which originally meant “to crush or to crowd.” Over time, the word came to refer to a device or tool that exerts force by squeezing.
Press brakes operate by applying pressure to a sheet of metal, pressing it up against a die to generate bends or folds, utilizing hydraulic or mechanical force.
The ultimate form of the metal is determined by the combination of the punch and die.
The kind and thickness of the material, the required bending precision, the volume of production, and the available space are a few things to consider.
While servo-electric press brakes provide precision for lightweight materials, hydraulic press brakes are typically chosen for heavy-duty applications.
Accurate control and reproducibility are made possible by the automated and programmable features of a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) press brake.
With manual press brakes, operators must manually modify the settings. For intricate and highly accurate bending jobs, CNC press brakes are perfect.
Using a press brake requires extreme caution. Consistently adhere to the manufacturer’s safety instructions.
Make that operators have received the appropriate training, put PPE to use, and install safety measures like guardrails and emergency stop buttons.
Press brake dies and punches are referred to as tooling. To achieve specified bend angles and prevent errors, proper tool selection is essential. Various press brake bending machine applications call for different tooling configurations.
Yes, a variety of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and more, can be handled by press brakes.
The capacity and tooling of the machine need to be suitable for the particular material and thickness that it is processing.
Frequent maintenance entails calibrating the equipment accurately, examining hydraulic systems, and lubricating and inspecting moving parts.
Observe the maintenance recommendations provided by the manufacturer for the particular press brake for sale model.



