Using laser technology to cut titanium sheets or components with remarkable accuracy, titanium laser cutting is a precise and effective metal fabrication technique.
This technique is a common option in companies because of its capacity to create precise edges, reduce material waste, and accept intricate designs.
Titanium Laser Cutting Applications

A variety of structural components, including panels, frames, brackets, and ribs, are made using laser cutting

Important parts like turbine blades, compressor disks, casings, and exhaust components are made by laser cutting.

When creating elaborately designed fuel tank constructions, laser cutting guarantees accurate dimensions and leak-free operation.
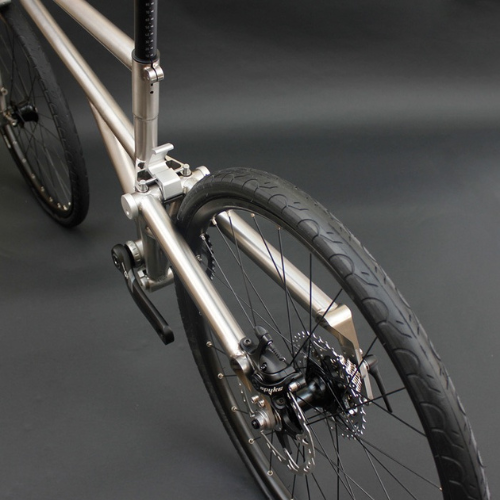

Tennis rackets, golf club heads, bicycle frames, and diving equipment are among the sporting goods made of titanium.

Architectural applications can employ titanium to make screens, dividers, ornate panels, as well as complex patterns.

Tanks, pipes, valves, and fittings are among the components of chemical processing systems that are made via laser cutting.

Parts for military vehicles, weaponry, armor plating, and ballistic protection are made via laser cutting.

Titanium is a favored material for electronic device cases, such as those for watches, computers, and cell phones, due to its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal.

For accurate duct forms, such as bends, branches, and connections, that guarantee structural integrity and optimal airflow, laser cutting is a dependable technique.

Intricate items like washers, bolts, and screws are made with laser cutting, which guarantees exact dimensions and close tolerances.

Titanium is the perfect material for surgical instruments, prosthetics, implants, and other medical equipment because of its biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion.
Titanium Laser Cutting: Advantages



The Titanium Laser Cutting Process
Getting the Materials Ready – Before being cut, the titanium sheet or plate must be cleaned to get rid of any grease and dirt.
Putting the Laser System Together – The correct focusing lens, cutting parameters, and laser power are set up on the laser cutter.
Positioning – The perfect cutting is ensured by precisely positioning the titanium sheet on the laser machine’s cutting bed.
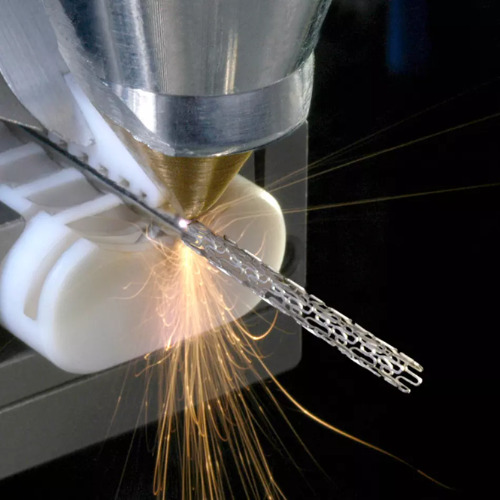
Cutting Using a Laser – When the selected cutting route is crossed by the laser beam, the titanium surface melts and vaporizes.
Fuel Assistance – An auxiliary gas like nitrogen or argon is occasionally used to evacuate the molten titanium.
Ensuring Quality – The titanium components are examined for correctness, smoothness, and flaws.

Other Options for Titanium Laser Cutting

Slices through surfaces with a waterjet cutting device using a high-pressure water stream containing abrasive particles.
Cutting titanium and other materials, such as thick or heat-sensitive materials, is possible with this versatile technology.

In plasma cutting, metal is melted and sliced through using a high-temperature plasma arc.
Thick titanium sheets are commonly cut using it due to their rapid cutting rates.
- Things Take Into Consideration
- Ensuring Precision and Accuracy
| Maximum force | A powerful enough laser cutter is needed for this. |
| Grade and Thickness Compliance | The laser cutter you choose is suitable for the specific titanium grades and thicknesses. |
| Beam size | The quality of the laser’s beam is very important. |
| Fuel Assistance | argon or nitrogen gas assistance is widely utilized. |
| CAD/CAM Programs | Ascertain whether it works with CAD/CAM software environments. |
| Material Handling Caution | Guard against contamination and surface deterioration. |
| Laser Settings Adjustment | Select the appropriate laser settings according on the titanium’s quality and thickness. |
| Detailed Quality Control | Establish an exhaustive protocol for quality control. |
| Normal Maintenance | Laser cutting apparatus undergoes routine cleaning, inspections, and calibrations. |
| Precise CAD Design | Invest the necessary effort in producing a thorough and accurate CAD drawing. |
When laser cutting titanium, extreme delicacy is achievable, but optimal performance services requires precise apparatus setup.
Laser cutting allows for accurate shape and cutting while maintaining the strength and durability of titanium parts.
Titanium is produced by laser cutting, which involves striking a titanium surface with a strong laser beam and melting or vaporizing the material at the point of contact.
From thin sheets (about 0.1 mm) to thicker materials (several millimeters), titanium can be cut with a laser in a wide variety of thicknesses.
Although titanium laser cutting has several advantages, the maximum thickness that may be effectively cut may have restrictions.
Ti-6Al-4V and other economically pure grades (Grades 1 through 4) are among the many titanium alloys that can be treated with titanium laser cutting.
Because titanium laser cutting frequently yields perfectly cut edges, no additional post-processing is required.
Yes, the accuracy with which titanium laser cutting can create complicated, complex designs is one of its main advantages. This can be made for sale at an affordable price and with cost-effectiveness.



