
Powder coating is a popular brass finishing process. You can choose either electrostatic deposition or fluidized bed powder coating.
Let’s learn what brass powder coating process entails.
What is Brass Powder Coating
Brass powder coating is applying a layer of dry, thermoset or thermoplastic powder directly on the brass surface. Later the powder melts and hardens into a uniform coating.
Methods of Brass Powder Coating
There are two main ways that you can utilize to powder coat your brass. Wondering what are they? Find out right now!
1. Electrostatic Deposition (ESD)
ESD or electrostatic deposition refers to the material deposition phenomenon. In this phenomenon, electric charges play a main role in depositing a layer of powder over another surface.

2. Fluidized Bed Powder Coating (FBPC)
The FBPC refers to a coating process in which powdered particles remain in the air. A preheated brass product passes in this powder bath, resulting in a uniform coating.

Preparing Brass Material for powder Coating Process
It is essential to first prepare material before beginning the coating stage. Without putting the material through the preparation stage.
You will experience a bad quality and end finish. Find out which ways you can employ to process material preparation effectively.
· Cleaning
The first step in material preparation for powder coating is cleaning. It involves the removal of surface soil, grease, dirt, etc. If the soil/ dirt is tough, you can use pressure cleaning.

Options exist to make use of deionized water or reverse osmosis to experience even better results. When simple cleaning or deionized water does not assist, you can use mechanical cleaning.
· Rinsing
The term rinsing refers to wet stripping. You can use it to get rid of chemicals or solution that is on your brass product. Most people use well or ordinary water for dirt removal in this phase.
· Etching
Etching is when you place the brass product in a chemical referred to as the etchant. You can use iron phosphate as an etchant. It plays a great role in effectively removing oxidants, contaminants, etc.

This adds up an inert layer to facilitate high corrosion resistance. Besides this, it also forms pits on the surface which are invisible to the naked eye. These pits allow you to achieve a seamless coating finish with higher longevity.
· Blasting
Blasting is another surface preparation method you can use before powder coating. This process makes use of small steel balls or steel scrap. The brass product you want to clean is placed inside the booth where the blasting of steel balls takes place.

Doing so can further make a surface rough or smooth out the uneven surface. With this step, you can eliminate the previous powder coating layer, contaminants, and rust. The abrasive blasting feature is in your control, depending on the hardness of your material.
· Drying
When you have finished cleaning the surface entirely. Now you need to proceed with drying. Suppose you place the brass material having a wet surface directly for coating. Then this will not be fruitful. This will disturb the end quality, durability as well as finish. Therefore, drying is essential.
Brass Powder Coating Process
As discussed above, there are two main techniques for copper brass powder coating. Let’s examine each in detail one down below:
Through ESD Process
Electrostatic Deposition, or ESD, takes place by following these steps:
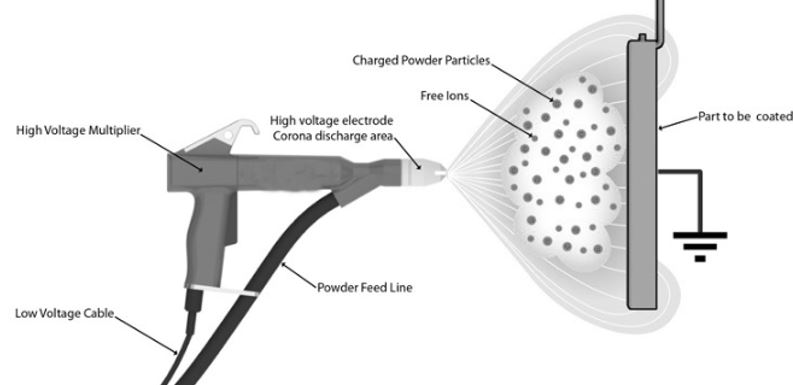
Step 1: Powder Charging
An electric spraying gun (e-gun) is the main component that charges the powder particle. Compressed air transfers the powder particles from storage to the e-gun. The e-gun contains an electrode on its tip. This electrode contains a very high voltage.
The high voltage develops an electric field between the tip and the uncharged brass material/product.
When the strength of the electric field in the electrode vicinity reaches up to 30 KV/cm. The release of free ions begins. As soon as the powder particles pass through these free ions, they receive a negative charge.
Step 2: Transport
The electric field lines in the electrode vicinity play a role in transferring the powder particle to the brass product. Free ions that remain suspended in the air. Or those that don’t attach to powder particles also reach the brass product. Pneumatic forces present around also play the same role.
Step 4: Deposition
When the negative charge powder particles reach the brass material/ product. They get deposited on it and form an even layer of coating. When the brass product/material completely covers with the charged powder particles. They begin to repel the other incoming powder particles. Thus, you can experience a uniformly thick layer coating on the entire surface.
Through FBPC
Discover steps you need to follow to achieve qualitative fluidized bed powder coating right down.
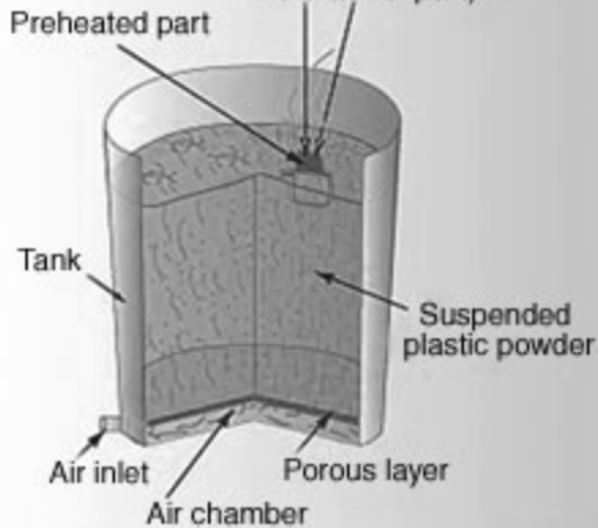
Step 1: Pre-heating
The brass product you want to powder coat first passes through the pre-heating process. In this step, keep the temperature between 1760C to 2320C. Please note the temperature range depends on the melting point of the powder particles. Keep the temperature above the melting point of the powder particles. The convection oven serves the purpose best in this regard.
Step 2: Powder Bath
Then you must pass the preheated brass product from the powder bath. It is a bath where the powder particles remain suspended in the air. The particles then stick to the metal surface and melt. It would help if you kept it in the bath, depending on the coating layer thickness you want to achieve.
Curing of Brass Powder-Coated Surface
For ESD Powder Coating Process
After the charged particles depose over the brass material or surface. There comes curing in the end stage. In this stage, you must put the brass material containing the charged powder particles in an oven.
You must keep it there for 20 minutes, from 300 to 400 degrees Fahrenheit. After completing this step, the ESD process ends.
For Fluidized Bed Powder Coating
Curing refers to the post-heating or heating of the brass product you obtain after a powder bath. This step ensures every leftover powder particle remains intact on the surface effectively. This is why most heating done at a lower temperature than pre-heating. It further provides a uniform coating layer over the entire surface of the brass product.
Factors Affecting Brass Powder Coating
There are certain things in the polished brass powder coating for which, if you don’t pay heed. They can contribute to effective and faulty layers. Here are these factors for both methods ESD as well as FBPC.
ESD Method
Take into account these aspects:
1. Powder Conductivity
As in the ESD method, you need to charge the powder particles. Before choosing the powder, material, make sure it is highly conductive and thermally stable. If it does not offer higher conductivity, you will not get a proper coating layer. The powder particles have zero attraction towards the material surface and fall below.
2. Particle Size
The particle size matters, and it greatly affects the final coating layer. Finer particles have great surface tension, higher electrostatic forces, and poor flow properties. At the same time, fine powder has not had better flow properties.
On the other hand, the large particle will lead you to face better flow. They can lead you to experience non-uniform coating. So, choose the particle size considering these facts. In general, the recommended particle size is 10µm to 90µm. This is not too large and not too fine but the optimum particle size.
3. Spray Voltage
The higher the voltage, the better it is, but not true for all cases. If the voltage is taller, the transfer efficiency of the powder particles increases. This means sticking more powder material on the brass product. In this case, you can increase the distance between the spray gun and the brass product. Keep the voltage level between 60 to 80 KV.
4. Air Supply Pressure
Keep the pressure of air within permissible optimum limits. The main reason is that it affects powder delivery, kinetic energy, and coating quality. On the other hand, it also affects the powder and fluidization air pressure.
5. Spraying Distance
The spray distance you cannot ignore it. It is responsible for the electric field strength. Keep the distance between the spray gun and material in the range of 200 up to 300mm. If the distance is small, it can produce fire and break down the end quality. At the same time, a large space means weaker electric field strength. It also decreases the powder particle’s deposition efficiency.
Fluidized Bed Powder Coating Method
Following factors need your attention:
1. Preheating Temperature of Heat Subject
The preheating stage, as already discussed, requires an optimum temperature. If the brass product or object has not been preheated properly, particles will not stick and melt. This will affect the powder coating phenomenon. The size and thickness of the subject also affect the temperature range. The object’s temperature is generally slightly greater than the powder melting temperature.
2. Immersion Duration
How long you keep the brass product in the suspended powder bath does matter. Keeping it above the optimum time will result in a thick coat. On the other hand, you are holding it for fewer time results in thinner skin. The optimum coating is beneficial, which is neither thick nor thin.
3. Heat Capacity of Subject
The material you are going to powder coat through the FBPC should have higher heat conductivity. Doing so will offer you to experience uniform surface temperature throughout. This will also lead you to observe uniform and even layers of coating.
4. Particle Size
The particle size affects the end coating result. For more information, refer to the “the impact of particle size on the coating in the ESD phenomenon” section. (above)
What Colors are Available in Powder Coating?
- Antique pink
- Anthracite gray
- Bottle green
- Chocolate brown
- Chrome
- Carmine red
- Heather violet
- etc.
How to remove powder coating from brass?
- Heat
- Chemical Stripping
- Abrasive Blasting
Can you clear powder coat brass?
Yes, brass has been successfully powder coated for many years.
Conclusion
Now you have in-detail insights and familiarity with the powder coating process. You can choose anyone depending on your product requirement and needs. If there are any questions in your mind, seek our assistance.
You can contact us at any time. If you find the above information helpful and guiding, please share it with others.
More Resources:
Powder Coating – Source: Wikipedia
How to Remove Powder Coat on Electrical Enclosure – Source: KDM
Stainless Steel Powder Coating – Source: KDM




