Melting point of metals is an important subject for metal fabricators. Today, you are going to learn everything about the melting temperature of tungsten.
From melting temperature to factors affecting the melting point. Besides, you will also learn how to melt tungsten.
Let’s dive right in.
What is Tungsten Melting Point?
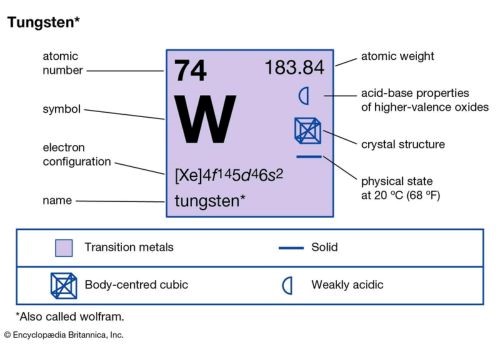
Tungsten has a melting point of 3422 °C, or 6192 °F. Due to its high melting point, it is widely used in high-temperature applications. Some of the most common applications include filaments of light bulbs, heating devices, and the nozzles of rocket engines among other uses.
| Melting Point of Tungsten in Kelvin | 3,695 K |
| Melting Point of Tungsten in Celsius | 3,422 °C |
| Melting Point of Tungsten in Fahrenheit | 6,152 °F |
Factors Affecting Melting Point of Tungsten
- Purity: The melting point of Tungsten may reduce through the impurities in it. Purity of the tungsten depends on the temperature; those that are impure, have lower melting points than high-purity tungsten.
- Pressure: Melting points of Tungsten are influenced by the pressure present in its environment. Commonly, the melting point increases with the increase of pressure.
- Alloying: The presence of other elements in the structure of tungsten also changes its characteristics such as its melting point when mixed with other materials in the creation of alloys. For instance, some of the elements present in an alloy could decrease the values of the melting point.
- Surface Condition: The oxide layers or any other surface treatment present on the tungsten surface can affect its melting pattern.
- Microstructure: Some properties of tungsten include grain size and crystalline structures that define the melting point of the material. Varying techniques used in production can lead to variations in the microstructure, which in turn may cause a slight variation in the melting point.
- Environmental Conditions: The type of environment in which the tungsten is heated can determine the temperature at which it melts. For instance, you can have some of the gaseous elements which on getting into a reaction can produce some compound which really changes the actual melting point.
Reasons for Tungsten High Melting Point
- Strong Metallic Bonds: Tungsten atoms have the ability to allow the formation of very strong covalent bonds since they transfer their electrons with each other.
- High Atomic Number and Density: This allows the formation of stronger metallic bonds.
- Stable Crystal Structure: It has the most stable body center arrangement, which is a body center cubic or BCC structure.
- D-orbital Electrons: Increase the covalent character by having a direct effect on the ‘d’-orbital electrons.
- Heaviness and Covalent Bonds: Regarding two in the increase of melting energy covalent bonding and high atomic mass are used.
- Low Thermal Expansion: Even at high temperatures it remains able to maintain the strength in the crystal lattice.
Tungsten Boiling Point vs Tungsten Melting Temperature
The Melting point for tungsten is 3,422 °C (6,152 °F) while the boiling point of tungsten stands at 5,555°C (10,031 °F).
A reason tungsten remains a popular choice for application requiring materials with high melting point. A good example is bulb filament and other high-temperature alloys.
This is because its atomic bonds are rather very strong to give such extremely high temperatures.
Comparing Tungsten Melting Point to Other Metals
Tungsten is credited for posting the highest melt point than any other metal with the temperature at 3422 °C or 6242°F. Here’s how it compares to other commonly known metals:
| Metal | Other Metals Melting Point in Degrees Celsius |
| Melting point of gold | 1,064°C |
| Titanium melting point | 1,668°C |
| Platinum melting point | 1,768°C |
| Copper melting point | 1,085°C |
| Steel melting point | 1,370°C to 1,540°C |
| Brass melting point | 900-940°C |
| Zinc melting point | 419.5°C |
| Melting point of iron | 1,538°C |
| Melting point of Rhenium | 3,180°C |
| Osmium melting point | 3,033°C |
| Molybdenum melting point | 2,623°C |
| Melting point of tantalum | 3,020°C |
| Niobium (Columbium) melting point | 2,468°C |
Melting Point of Tungsten Alloys
The melting point of tungsten alloys differs based on the specific components alloyed with tungsten and their proportions. They are as follows:
- Tungsten-Carbide: Tungsten carbide which is widely used in cutting tools and abrasives has a melting point of approximately 2,370°C (4,278°F).
- Cemented Carbide: This is where the tungsten carbide particles are bonded with a metal such as cobalt or nickel melts about 1400°C to1500°C (2,552°F to 2,732°F).
- Tungsten-Rhenium Alloys (W-Re): Such types of alloys might have the melting points between 3050°C and 3100°C (or between 5522°F and 5612°F) based on the content of rhenium.
- Alloyed Tungsten: This common category includes many tungsten alloys, including those that are alloyed with nickel, or with iron. Depending on the type of alloy, its level of the melting point may vastly differ, although most of the alloys will melt at a relatively lower temperature than the pure tungsten that has melting point of 3422 °C (6,192 °F)
How to Melt Tungsten Alloys
The steps are as follows:
- Preparation
- Material handling: When using materials wear protective wear, eye protection, gloves and ensure environment is well aired.
- Check of Equipment: Use a furnace that has the capability of reaching temperatures that are higher than 3422°C like the arc or the induction furnace.
- Setup of Equipment:
- Selecting a Crucible: Choose a crucible of a material that can withstand high temperatures it includes tungsten alloy or graphite.
- Furnace Adjustment: Make certain that the furnace has been properly set to gain the right temperature that would melt tungsten.
- Melting Process:
- Loading: Ensure you do not pollute the crucible by carefully putting the pieces of tungsten alloy into it.
- Heating: Turn up heat in the furnace then slowly increase the heat to melt the tungsten. In order to control the process and make sure that all layers will be heated evenly and will not be damaged by heat, closely keep an eye on the process has.
- Cast the Molten Alloy:
- Select a mold from a material with high heat resistance; therefore, your choice should be graphite or ceramic.
- Slowly pour the molten alloy into the mold to avoid the spilling of alloy that leads to formation of defects.
- Let the metal cool and solidify at a slow rate to eliminate formation of cracks and internal stresses.
- Perform post-processing:
- Temper the solidified alloy in order to reduce internal stresses which affects the properties of the alloy.
- Further process the alloy into the right shape and finish using the right tooling and processes.
Why is Tungsten the Hardest Metal to Melt?
Tungsten is the hardest metal to melt because of its melting point of 3422°C (6,152 °F).
This is alongside its strong metallic bonding, high atomic number and density, BCC stable structure, d-orbital interactions, heaviness and covalent bond characteristics.
Another significant factor to mention is tungsten low coefficient of thermal expansion.These characteristics lead to a very high melting point. Remember, a vast amount of heat is required to overcome the strength of the bond and cause the substance to change from solid to liquid.
Conclusion
As you can see, tungsten is among the few metals with extremely high melting point. At any given time, before choosing any metal for an application, knowing the melting point is important.
At KDM, we are the leading metal fabricators in China – contact us now for any inquiries.




