Have you ever wondered how those fundamental parts that facilitate fluid and gas flow are designed and made?
The magic behind all this is in valve casting that produces such reliable and robust valves we can rely on.
What Is Valve Casting?
We commonly use this casting process to manufacture valve parts by pouring molten material. The process makes it possible for us to easily shape complex pieces that are essential in constructing valves.

You know these valves must operate under extreme conditions such as high temperatures and pressure or even corrosive medium. The flexibility and accuracy of valve casting ensure that such parts are reliable and can be used in industries such as oil and gas, power plants, and water utilities.
Benefits of Valve Casting
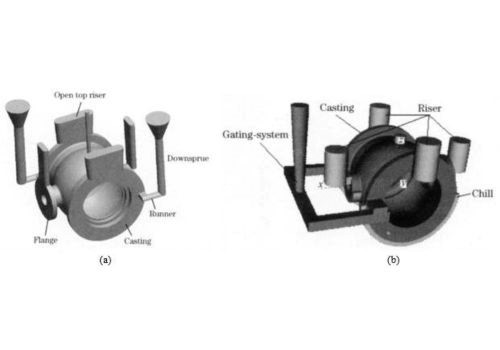
We can rely on valve casting as a viable technique when we are producing various valves and their components. Some of the key advantages that we can benefit from this process include:
· Achieve Complex Geometries
One of the major advantages of this process is that it allows you to create intricate and complex valve shapes. Such complex valve designs are difficult to achieve using other techniques. The flexibility of this technique is critical when making such designs.
· Material Versatility
You have the freedom to choose the kind of material that you will cast your valves with that can withstand their operating environmental conditions. There are several metal options and various alloys that can withstand various parameters such as corrosion, or high strength.
· Strength and Durability
Since we create cast valves from durable materials, they can handle demanding conditions well and last for quite a long time. Such resilience is very crucial to the reliability of the systems that the given valves are a part of.
Materials Used In Valve Casting
We can create valves by casting a variety of materials during their production. Selecting the right valve material for valve casting is a vital aspect that you should give all your attention.
This material must be able to meet all the required application operational standards be it corrosion, high pressure, or high temperatures. Some of the common materials we can apply in valve casting include:
· Cast Iron
This metal is easily machinable with excellent castability properties and is widely used in its pure form or as gray or ductile iron. It is a choice of many because of its strength and high resistance to wear.
· Carbon Steel
It is good for valve casting because it is strong and tough enough to withstand pressure therefore suitable for high-pressure equipment. It has a robust material structure that copes well with very demanding applications.
· Stainless Steel
When you are dealing with applications where high corrosion resistance is a requirement, then stainless steel is your best option. You can find the valves cast with this material commonly in use in processing industries and marine applications.
· Alloy Steels
When an application requires a mix of engineered properties such as hardness, strength, or resistance to heat and corrosion, alloy steels can satisfy such. Specific alloy steels such as chromium-molybdenum and nickel-based alloys can create valves that offer high performance in such extreme applications.
· Bronze and Brass
These materials possess excellent corrosion and machinability properties. Both bronze and brass are ideal for casting valves that are applied in water industries and any other industry dealing with non-corrosive fluids.
Types of Valve Casting Methods
Based on the definition we gave of valve casting before; we can see that this valve manufacturing involves various casting techniques. We can have a look at some of the important casting methods and their significance.
· Sand Casting
In this sand casting process, you have to first create a mold using a sand mixture where the pattern of the required valve has to be put. You can then use this sand mold in casting where you pour molten metal inside and then separate the sand mold from the metal after some time.
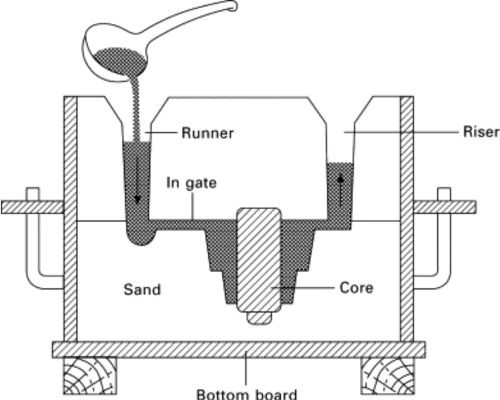
Advantage: you can cheaply create large and complex valve designs if you’re operating on a small to medium production scale. It is fairly liberal in terms of the dimensions and mass of the valve you want to cast.
Limitation: it does not provide a precise dimensional accuracy compared to other methods. You will also be required to carry out further fine-tuning due to a poor surface finish.
· Investment Casting
Also called lost wax casting, this method entails the production of a wax pattern that is then covered by a layer of ceramic.
Once the ceramic becomes hard, you can remove the wax creating a cavity where you pour the molten metal. After the metal hardens, you can break the ceramic shell and remain with the valve.
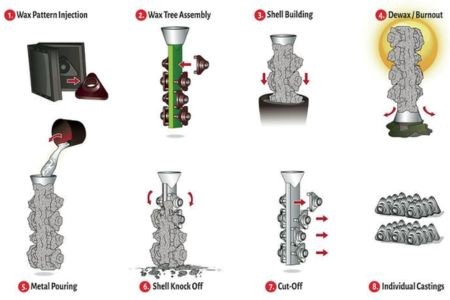
Advantage: you can achieve some of the best surface finish surface finish and tolerance compared to other valve casting processes. It is ideal when you’re creating intricate and large-based valves and may take almost any metal and alloy.
Limitation: it is a bit pricey compared to sand casting and takes longer. Works well if you are dealing with casting small valves.
· Die Casting
This metallurgical process uses high pressure to force molten metal into a reusable mold cavity that we refer to as a die. The strong and tight structure of the die ensures that molten metal cools and solidifies rapidly to form the valve component.
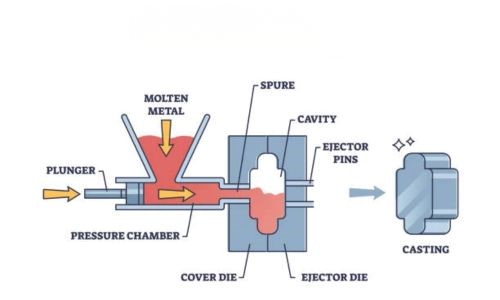
Advantage: gives a fine finish coupled with a high dimensional accuracy of the finished valve. It is ideal for large production of intricate valves that are fairly sized.
Limitations: the initial costs of tooling are relatively high. Additionally, you can apply it strictly on non-ferrous materials such as aluminum, zinc, etc.
· Shell Molding
In this valve casting technique, you initially create a thin shell mold from a mixture of silica sand and resin. The valve is created after you pour molten metal into the thin shell mold and allow it to dry.
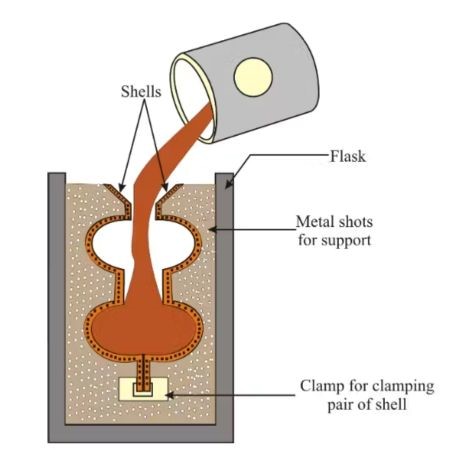
Advantages: best option for precision valves that have a complex geometrical configuration. It works well with a production line that has medium production runs.
Limitations: it may be more affordable compared to investment casting but it is slightly more expensive than sand casting.
· Centrifugal Casting
This casting process takes place when molten metal is placed inside a spinning mold which makes contact with the mold through the centrifugal force. This method is ideal for creating cylindrical-shaped valves.
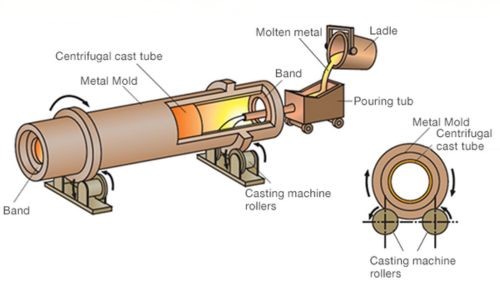
Advantages: this method results in high-strength and high-density valve parts. They produce well-crafted cylindrical components such as valve bodies and liners.
Limitations: you can only cast symmetrically shaped valves with the process incurring higher equipment expenses.
Valve Casting Process
The valve-casting process generally contains a complex flow from the design to the finishing stage. We can dive into the step-by-step analysis of a typical valve casting process and what it entails.
- Design And Pattern Making
The process starts with the production of the valve component which in most cases we do using computer-aided design (CAD) applications. We create a pattern that is identical to the required valve component that we in turn use to generate the mold cavity.
- Mold Making
This is the step that, depending on the chosen casting method, we create a mold around the pattern. For instance, if you opt for sand casting, then a sand mixture is packed around the pattern while a ceramic shell is built around a wax pattern in investment casting.
- Melting And Pouring
Your choice of metal or an alloy is heated to its liquid state and then poured into the mold cavity. The only difference with all other processes is that in investment casting, you have to pre-heat the ceramic shell to prevent thermal shock when pouring is done.
- Cooling And Solidification
The molten metal inside the molds rapidly cools down and solidifies. The rate at which the cooling takes place has a direct impact on the structure and properties of the cast valve component.
- Mold Removal
Immediately the molten metal cools and solidifies, you can get rid of the mold. We destroy the mold cavities in sand casting and mechanically shed off the ceramic shell in investment casting just to mention a few.
- Cleaning And Finishing
You can finally flush and dry the cast valve component to get rid of any mold material, scales, or any other impurities on its surface. Other finishing operations such as grinding and polishing are carried out here for the dimensional accuracy of the final valve component.
- Inspection And Testing
The finished valve is examined for compliance and testing to conform with the industry requirements and specifications. Common tests include dimensional checks, structural analysis, pressure testing, and non-destructive testing (NDT)
Challenges When Valve Casting
Just like any other manufacturing method, you are bound to face some challenges when carrying out valve casting. Understanding these challenges is crucial for improving the process and ensuring high-quality outcomes.
Let us have a look at some of these defects and the mitigations you can put in place to avert them:
- Defect Management
The quality of your finished valve part can be noticeably affected by casting defects such as porosity, shrinkage, and inclusions. This requires that you carry out strict quality assurance checks to monitor and prevent them in the initial development stages.
- High Initial Costs
The cost of valve casting largely depends on the number of patterns you are going to use and the total number of tools needed to shape the pattern. This initial cost may go even higher if you are dealing with intricate shapes or having small production runs.
- Material Limitations
You will come to the sad realization that some valve casting methods cannot be done using all types of materials therefore limiting some of the best alloys. A perfect example is die casting where you can only use non-ferrous materials since ferrous metals form excess oxides in that process.
- Environmental Concerns
The valve casting process ends up generating waste materials and fumes that may negatively impact the environment. You need to follow the appropriate environmental regulations and measures concerning the management of harmful emissions.
Applications of Valve Casting

Due to its ability to develop very strong and reliable valves, you will find the applications of valve casting stretching across various industries. We can list down some of the notable applications that include:
- Oil And Gas Industry
The valves used in this industry have to cope with high pressure, temperature, and corrosive conditions during drilling, production, and transportation. Cast valves offer the required physical characteristics to operate in such challenging environments.
- Petrochemical Industry
Cast stainless steel and alloy valves have strong anti-corrosive qualities and strength. This makes them most suitable for operating in chemical processing plants where they are exposed to aggressive chemicals and high-temperature conditions.
- Water Treatment
Cast valves made specifically from iron and bronze materials have cemented their active use in water treatment plants. They are preferred due to their corrosion resistance and their long-lasting service life.
- Power Generation
The steam turbines and boilers in power plants expose the various valves to extremely high temperatures and pressure and subject them to wear and tear. This requires cast alloy valves due to their strength and heat resistance.
- Marine
Valves used in marine applications are in constant exposure to corrosive sea water and a lot of mechanical stress. For such purposes, you should go for cast bronze and stainless steel valves since they are comparatively durable and adequately safe.
Conclusion
In summary, we have seen how important the valve casting process is in producing robust and reliable valves which are very important in various industries. By understanding the whole valve casting process, you now have a clear grasp of how intricate this process of creating this vital component is.




