Over the years, metal extrusion has undergone significant advancements and applications in manufacturing industries. This manual will provide insights regarding the field of metal extrusion, covering its procedures, benefits, disadvantages, and potential future developments.
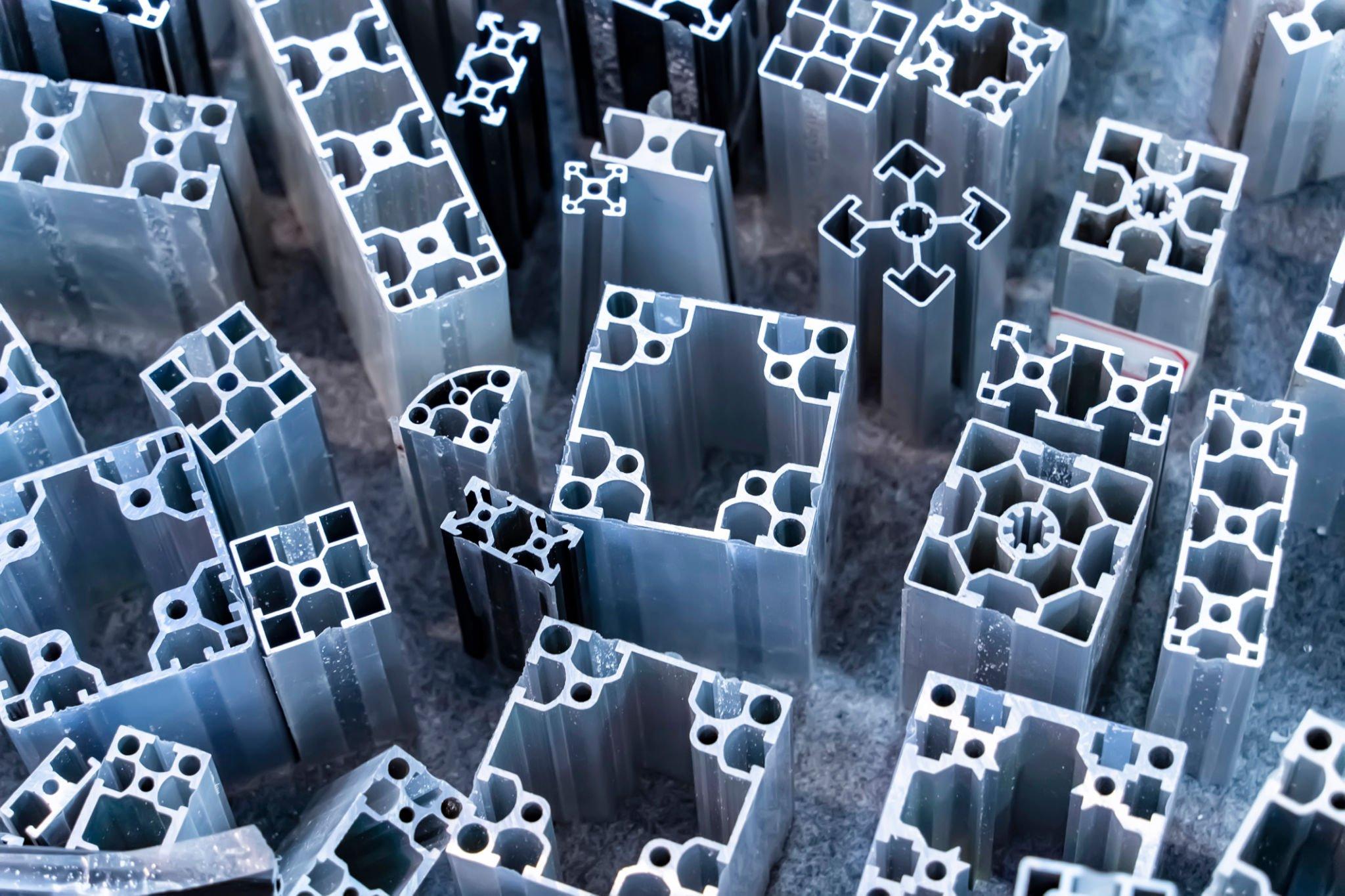
What is Metal Extrusion?
Metal extrusion is a manufacturing practice where a solid steel billet is forced through a specifically shaped die to produce a long object with a predetermined cross-sectional shape. This process is mostly applied to create objects like pipes and rods that need a consistent cross-section.
Materials for Metal Extrusion
The following material is frequently used for metal extrusion:
- Aluminum: Manufacturers use extruded aluminum in the construction, automotive, and aerospace industries
- Copper: Because of its exceptional conductivity, it’s frequently your first pick when it comes to electrical engineering.
- Steel: You primarily use this because of its effectiveness in the construction and automobile industries.
- Brass, Zinc, and Titanium: Extruded brass, zinc, and titanium can be used for a variety of applications by metal manufacturers, including aerospace parts and high-end architectural appliances.
Check Out The Application of Metal Extrusion on Different Materials:
Read: Applications of Aluminium Extrusion
- Aerospace/aircraft parts
- Automotive parts
- High-end machinery and appliances
- Architectural profiles
- Rail tracks
Read: Applications of Extruded Brass Parts
- Automotive parts
- Electrical components
- Architectural brass extrusions
- Extruded plumbing components
Let’s delve into various metal extrusion processes based on varying extrusion temperatures and the direction used for each.
Types of Metal Extrusion Based on Extrusion Temperature
Let’s examine several metal extrusion processes according to extrusion temperature:
Hot Extrusion:
This technique involves extruding metals at high temperatures. By facilitating material flow, this technique lessens the demand for unnecessary force. You should heat the metal until it becomes more malleable but not molten. You can precisely achieve the desired form by increasing the extrusion temperatures.

However, keep in mind that, due to the heating process, hot extrusion necessitates higher energy usage. In order to ensure that the final product satisfies your quality standards, post-processing may be necessary to prevent surface oxidation. In general, hot extrusion is preferred when formability and ease of shaping are priorities.
Advantages:
- It makes the material flow easier.
- The technique lessens the demand for strong force.
Disadvantages:
- High energy consumption
- Exposure to surface oxidation poses threats to your health.
Cold extrusion
You should apply this technique at optimum or close to room temperature in cold extrusion. After inserting the billet into the die, you exert pressure to mould it into the appropriate shape. This process results in enhanced material strength and great surface finishes.
However, keep in mind that cold extrusion requires more effort than hot extrusion and works better with ductile metals. Due to its ability to maintain high tolerances, it is commonly employed in industries that require accurate components, such as the automotive and electronics industries.
Advantages
- Work hardening increases material strength
- You get an elegant finish on the surface.
Disadvantages:
- Requires exerting additional pressure.
- Only more ductile metals are adaptable to this technique.

Warm extrusion
This technique uses temperatures halfway between hot and cold extrusion. Comparing this balance to hot extrusion will reduce energy consumption levels. Although it offers the advantages of both hot and cold extrusion, beware that it can be difficult to keep the process under precise control.
Advantages:
- Improves material ductility easily compared to hot extrusion
- Cuts on energy consumption rates
- Minimizes tool wear, thus maximizing durability
Disadvantage:
- The process is occasionally difficult to handle
- Demands intermediate/specific heating temperatures
- It might lead to scale formation on some materials
Types of Metal Extrusion Based on Extrusion Direction
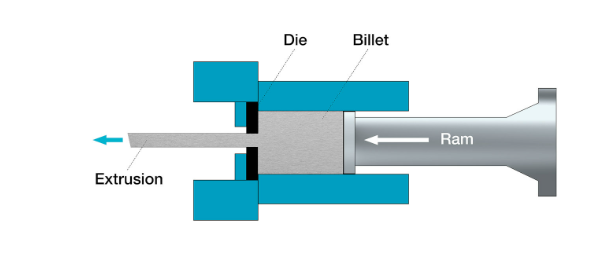
Direct extrusion
The most typical version involves forcing metal through a die. A ram is used to push a solid billet through the die, creating the required shape after you feed it into the container. It has a basic setup and a simple D-I-Y approach. You will need to exert greater force to accomplish the extrusion, so be ready for increased friction.
Advantages:
- It is more straightforward and easy to set up.
- It’s cost-effective since the extrusion machine requires minimal maintenance
Disadvantages:
- Demands excess force due to friction
- Shortens the lifespan of the die, thus increasing maintenance costs
Indirect extrusion
In this technique, the die advances toward the billet. By lowering friction, this technique makes the extrusion process more seamless. But in order to operate it, sophisticated equipment is needed.
When you want to reduce friction and obtain a certain form but want to make an investment in specialized equipment, indirect extrusion is the method of choice.
Advantage:
- It involves less friction
- A smooth material flow that enhances product quality
Disadvantages:
- Requires sophisticated extrusion equipment, which might be complex to use
- It limits billet size, thus restricting the dimensions of the end result needed
Impact Extrusion
This technique is primarily used for hollow parts. Although it only works with certain metals, this technique is quick. It is a useful option for production in large quantities in such applications since it is effective for generating goods such as metal cans or jars that require complex designs.
Advantages:
- This high-speed technique maximizes efficiency during bulk production
- Generates an elegant finish on the end product
- Strengthens metal surfaces, thus hardening the extrudates
Disadvantages:
- It’s limited to specific metals and material applications
- Complicates precision-machining levels, thus demanding post-extrusion

Lateral Extrusion
This involves extrusion from a billet’s side. This technique enhances distinctive product designs. However, because extra material is removed from the outside during extrusion, it may result in material waste.
Advantages:
- Generates intricate cross-sections.
- Can be used to achieve complex shapes easily
Disadvantages:
- Lateral extrusion may squander resources since it’s prone to tool wear
- It’s limited to particular materials which have certain characteristics
Hydrostatic Extrusion
In this technique, we use high-pressure fluid to force metal through a die. This procedure lessens material strain, thus resulting in an extrudate that is smoother and more distinct.
However, in order to deal with the hydraulic pressure adequately, it necessitates specialist equipment, making it suited for particular applications that require less material deformation.
Advantages:
- Fluid pressure is used to extrude metal, thus reducing friction.
- Lessens material strain.
- Achieves an eye-catching finish on the material surface
Disadvantages:
- Demands specific tools that are seemingly expensive.
- Requires complex maintenance measures
Qualities and Characteristics of Metal Extrudates
For their intended purposes, metal extrudates must have a number of specified characteristics and qualities to achieve ultimate efficiency. These qualities include accurate dimensional precision and making sure that parts fit precisely where you need them to.
Another important component that affects the extrudate’s appearance and performance is the quality of the surface finish. It’s important to meet particular functional requirements in your applications, which depend on mechanical qualities such as strength, hardness, and ductility.
Common Extrusion Defects
You can run into flaws in metal extrusion that might affect the caliber of your finished product. Surface cracking is a frequent problem that might result from high temperatures or poor die design.
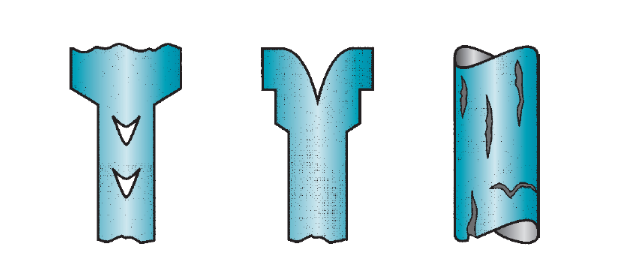
When the product doesn’t completely fill the cavity of the die, it is considered ‘incompletely filled’. This results in an incomplete extrude. Buckling, in which the extrudate forms unfavourable bends, is another flaw you should look out for.
The performance as well as integrity of your finished product could be jeopardized by these flaws.
Environmental Sustainability in Metal Extrusion
In metal extrusion, environmental sustainability has become increasingly important. Extrusion techniques like recycling cut down on waste and preserve production resources. Additionally, using greener manufacturing techniques reduces carbon emissions and energy use in the long run.
Environmentally friendly extrusion techniques depend on appropriate waste management and sustainable material supply.
For comprehensive details about operating an environmentally sustainable metal extrusion process amongst other additive manufacturing innovations, read the case study report below by SpringerLink.
“Environmental Sustainability in Extrusion” – Published: 19 April 2016.
Senior Author: Henrique A. Almeida.
Top Emerging Trends in Metal Extrusion
With various new trends emerging, the metal extrusion sector is evolving at a rapid rate. Integration of Industry 4.0 innovation is improving automation and data-driven judgement. Many industrial possibilities are expanding as a result of emerging extrusion technologies like additive manufacturing.

Sustainable practices, like using eco-friendly materials and cutting down on energy use, are also becoming more important. Metal extrusion will become more effective, inventive, and ecologically responsible as a result of these trends.
The metal extrusion sector is changing as a result of cutting-edge technological developments and modern manufacturing innovations like Industry 4.0.
Here’s an extensive PDF guide explaining the INDUSTRY 4.0 Tech, its current status, & future trends in the metal fabrication sector.
Metal Extrusion Process – Key Takeaways
Combining industrial adaptability and efficiency, the metal extrusion process has become a cornerstone in the ever-growing metal sheet fabrication industry. The most popular applications of metal extrusion are utilized in the automotive, aerospace, and high-end architectural industries.
In the modern manufacturing industry, most factories apply metal extrusion to aluminum products and other metal alloys such as zinc and brass. Remember, the ideal extrusion process should be compatible with your material’s components.
Our guide has covered the various extrusion processes, highlighting the requirements and steps you will need to achieve distinct and high-quality metal parts. We’ve provided a list of extrusion methods ranging from direct to hydrostatic extrusion to accommodate all your fabrication needs.
Apart from creating a custom cross-section for metal surfaces, the process achieves an impeccable finish on metal products. To achieve desirable extrusion forms and reduce defects during the process, die design is essential. In order to maintain material qualities and attributes during metal extrusion, proper material selection and temperature management is crucial.
Before starting the extrusion process, there are several factors you should consider. Keep in mind that these factors tend to differ from one extrusion process to another, depending on the operator’s desired end product.
What are the key factors affecting the metal extrusion process?
- Material composition properties
- Condition of your extrusion equipment
- Billet temperature
- The required extrusion speed and pressure
- The extrusion ratio
- Tongue ratio
- The metal’s cooling rates
- Post-extrusion heat treatment
For maximum efficiency during metal extrusion, make sure you observe quality control procedures consistently throughout the entire extrusion process.
CONCLUSION
Consider advice from professionals and capitalize on expert technical experience for safe and efficient metal extrusion operations. FYI, modern innovative solutions and better extrusion results demand market engagement with suppliers and consumers.
To make inquiries regarding the metal extrusion process, contact our technicians at KDM Fab, a renowned sheet metal fabrication company.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common challenges faced during the metal extrusion process?
Here’s a list of the common challenges most people face during metal extrusion:
- Improper system installation
- Improper system operation
- Resin defects
- Melt toughness or structure
- Moisture release
- Overheating
- Trapped air
How can I choose the right material for my metal extrusion project?
- To choose the right material for metal extrusion, consider the end product and its requirements.
- Determine the cost
- Consider the material’s machinability and its formability.
- Consider the finishing techniques applicable to the material surface
- Go for materials that are recyclable to sustain our environment and conserve our planet.
- Inquire from technicians in the metal extrusion industry for actionable insights and suggestions regarding the process.




