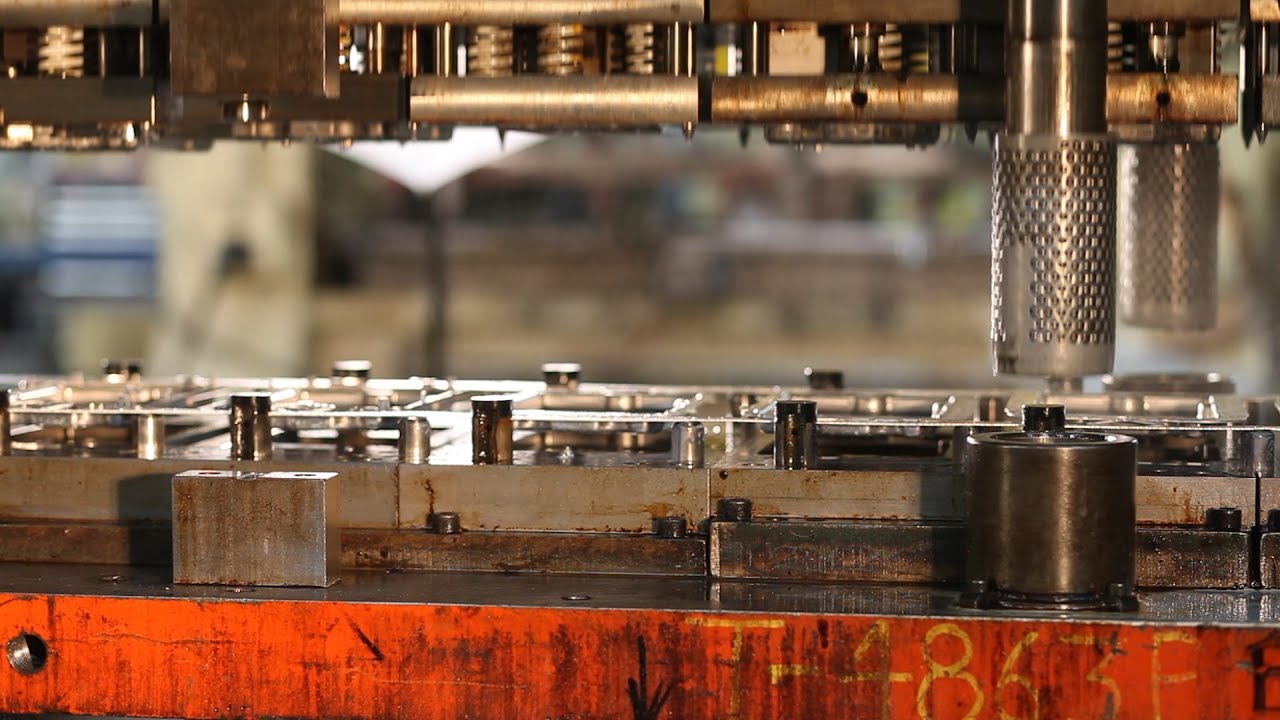

The process of fabricating intricate and complex parts can be daunting. In most cases, manufacturers and metallurgists have to go through a litany of fabrication options just to make sure they get the right, most functional one.
Among the many options available is progressive die stamping – a process known for its overall efficiency and speed. In this article, we’ll look into the progressive stamping die design as well as how manufacturers can take advantage of stamping molds to operate.
Introduction to Progressive Die Stamping
What is Progressive Die Stamping?
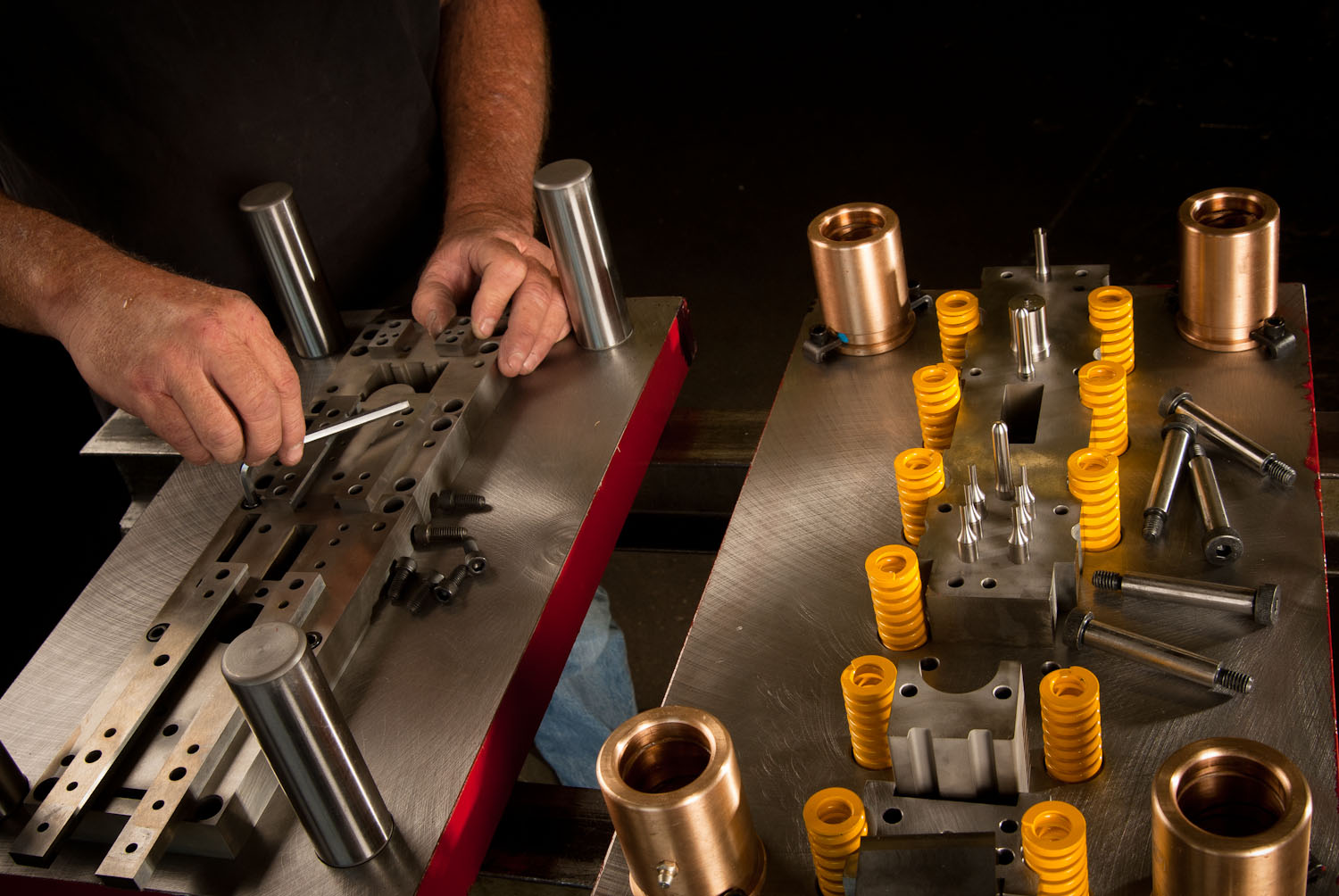

In progressive die stamping, you have a metalworking process that is used to efficiently and quickly produce several parts. The progressive die design is a variation of a general metal and die stamping process, which is especially suitable for high-volume production of components with intricate shapes.
The long-run progressive stamping process is used to cut and form sheets of metal thanks to the use of a stamping die. The process comprises several standalone workstations, which specialize in performing one or more operations on their part. A regular progressive die press should be able to perform functions such as coining, cutting, bending, punching, shaving, and much more.
As its name suggests, the use of progressive scrap metal encompasses different progressive steps where a raw material is passed sequentially and at the same time in an automated feeding system. Each step works with the previous one serving as a background, operating until you get the desired material shape. Once the process is completed, you can cut the part from the stock strip to get your final product.
With its ability to produce metal components of different sizes and shapes, progressive die stamping leads to shorter lead times and can cut production costs significantly.
Materials Used In Progressive Die Stamping
Depending on the specific requirements of the parts you’re looking to make, progressive stamping and fabrication can be used with a bevy of materials. Of course, factors such as the part’s durability, function, corrosion resistance, and more will play a role in determining which is perfect for you.
However, some of the most common materials being used in this process include:
Steel Alloys
With progressive steel alloys, you have different variations available. There’s cold-rolled steel, which is known for its durability and broad availability. Stainless steel also comes in handy, offering corrosion resistance to help make parts that can easily withstand harsh environments.
Then, there’s high-strength, low-alloy steel. Also known for its durability, this material works especially when you need to ensure optimal structural integrity.
Aluminum Alloys
A progressive die company can make use of aluminum, taking advantage of its corrosion resistance and lightweight build to create different progressive parts.
Alloys made of aluminum can offer different levels of strength and other mechanical properties, so you want to be sure what you’re applying and why.
Copper and Copper Alloys
Known for its impressive electrical conductivity, copper works in producing different electrical components. Then, you have bronze and brass – its most popular alloys, which offer both functionality and optimal aesthetic properties.
Exotic Alloys
Access to exotic alloys could also be the key to success with progressive die stamping. Titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it perfect for applications ranging from medical to aerospace, and you can also take advantage of inconel’s high temperature and corrosion resistance.
If you’re creating a progress tool & die for marine operations, then Monel just might be what you need.
Plastics
Materials such as thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics are suitable for optimizing progressive die stamping operations – especially when it comes to producing lightweight parts, insulators, and other components that can be used in making electronics.
Other Materials
If none of these does it for you, then you might want to consider rubbers, precious metals, and more. At the end of the day, your choice should be informed by your requirements and the ease with which the progressive stamping press works.
How Are Parts Made Using Progressive Die Stamping?
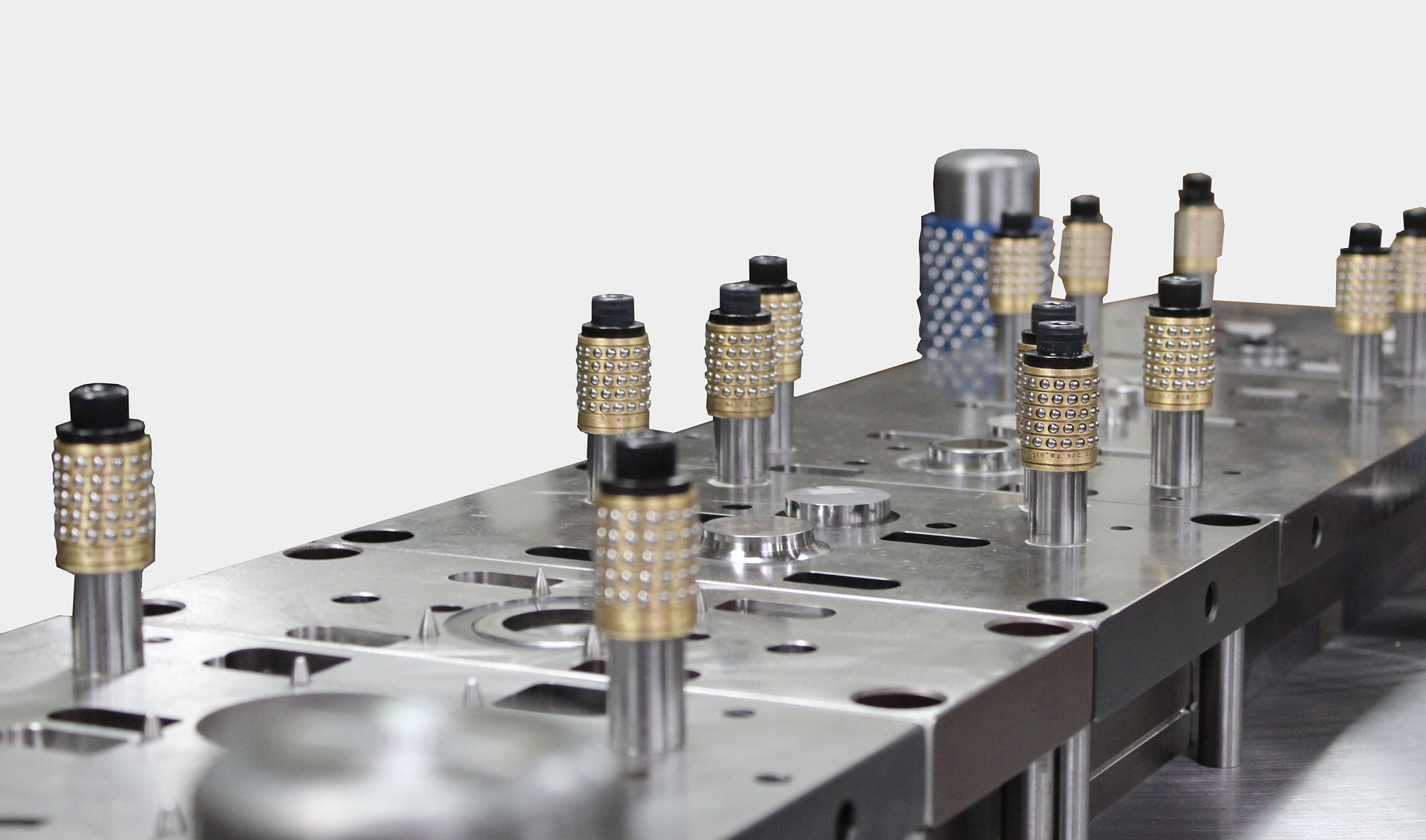

Now, let’s look into the progressive die stamping design guide. Here,you get to understand how the process works and what goes into it:
Basic Steps Involved In Progressive Die Stamping
The progressive die-stamping process can be complex. However, when done right, it creates a lot of room for efficiency and high-volume production.
In all, using a progressive stamping machine requires precision with tooling, an infusion of automation, and a sequential approach that allows you to create different apartswith the necessary efficiency and speed. Here’s how the process goes:
Die Design and Construction
The progressive die stamping process starts with a design and conceptualization of the progressive die. This die will comprise different stages or stations, each containing different elements – stamping die punches, etc.
In most cases, the progressive dies are custom-engineered for the specific parts that are being built. Your designer will need to be careful while planning the layout, especially considering the order of operations needed to create the proper features.
Material Feeding
Moving on, the real stamping process begins with just a strip or coil of the material – say, metal This metal feed is important if you hope to ensure efficiency, especially in high-volume production.
You uncoil and guide the material into the die press, where you position it properly as you prepare to start the stamping process.
Progressive Movement
The progressive tool & die press comes with a hydraulic or mechanical system that advances the strip through the die. With this sheet metal feeder, you can ensure that the strip is properly exposed to each station in the die with an accurate order.
As the material strip moves from one station to the other, different operations are performed to shape it properly.
Station Operations
Different stations within the progressive die complete specific operations to bring about proper progressive metal forming. Some of these include:
- Piercing and Cutting: This is the creation of slots and holes, as well as the process of cutting the material to the desired shape.
- Bending and Forming: Incorporating curves, angles, and forms into the material’s shape.
- Coining: Accuracy in shaping the part’s surface.
- Embossing: Adding any intricate patterns into the material’s surface
Scrap Removal
At specific stations, you can take out waste materials from the strip. This is usually done via cutting or shearing, and it goes a long way in optimizing the integrity of the remaining material.
Assembly and Attachment
In some setups, components are attached within the die. For instance, you could have clips, screws, and fasteners added to the part as it moves through the stations.
Finished Product
Once the material goes through every station, you’re left with the finished products. From here, you ensure proper quality control to ensure that each part meets your required specifications.
Post-Processing
There’s also a need for additional finishing once the parts are separated from the carrier strip. Coating, deburring, heat treatment, and more will help to enhance the material’s appearance and properties.
You finally have your finished product, and you can package and send it out easily.
How To Enhance Efficiency and Accuracy In The Process
As we explained earlier, the progressive die stamping process itself is quite efficient. When done properly, the process helps to significantly reduce costs while also optimizing productive efficiency.
However, the effectiveness of the process can also be optimized using different strategies – including the following:
Optimized Die Design
Invest heavily in properly designed progressive dies that have been built to accommodate the parts you’re producing. This helps to cut scrap and minimize material waste.
Material Selection
Be deliberate in selecting the right material to work with your progressive stamping die. It should be thick enough, formable, and strong enough to minimize die wear.
Maintenance and Die Tooling
It’s important that you inspect and maintain your progressive stamping tool to ensure that it is in top condition. Worn-out components should be sharpened, and you can replace them where necessary.
Lubrication and Cooling
You need the right lubrication systems to take out friction between the die and the material. This helps you to prevent wear and optimize the tool’s operating life as much as possible.
Die Setup and Adjustment
With standardized procedures, you’ll be able to streamline the setup process considerably. Implement automation and quick-change tooling to reduce downtime as much as possible.
Process Monitoring and Control
Implement real-time monitoring systems to detect defects, deviations, or process anomalies.
Press Automation
Modern, automated presses with programmable controls help to ensure accurate and repeatable stamping operations.
Training and Skill Development
Anyone operating a progressive die stamping machine will need to be trained and properly skilled. This leads to improved troubleshooting and enhances your ability to solve problems.
Data Analysis and Process Improvement
All through the stamping process, collect and analyze critical production data. This helps you to identify possible bottlenecks and possible areas where improvements can be made. To do this, you can implement Lean manufacturing or Six Sigma methods to ensure process streamlining.
Quality Assurance
This is one of the most important parts of your efficiency optimization. With proper quality assurance and control, you can notice and treat defects as soon as they appear.
Advantages of Progressive Die Stamping
Advancements in the use of progressive metal stamping dies have come in handy in several forms. What are the advantages of progressive die stamping? Some of the major benefits of the progressive stamping process include the following:
High Efficiency and Speed
Most notable among the many benefits of this process is its ability to optimize speed and efficiency in manufacturing. The process is continuous and automated, enabling high output rates and quick production.
Cost-Effective Production
With high speed and efficiency, a die-stamping machine also reduces per-part production costs considerably. You don’t have so many labor requirements, and you can also cut down on material waste. All of these contribute to cost savings.
Consistency and Precision
A progressive stamping tool is designed to optimize precision and repeatability. Just as well, parts made using this method show consistency in quality and dimensional accuracy.
Complex Part Geometry
The progressive die and stamping process offers parts with intricate features, shapes, and geometrical tolerances. However complex the design, a progressive stamping machine should be able to handle it.
Reduced Material Waste
Progressive die stamping is also built to cut down on material waste. Most of the scrap metal is taken out at different stations, so material waste is considerably reduced.
Minimal Manual Labor
One of the critical features of progressive die stamping is automation. This reduces the need for manual labor – thus eliminating labor costs and optimizing safety.
High Production Volume
Progressive die stamping is well-suited for high-volume production runs, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency even when producing millions of parts.
Speed to Market
With its ability to produce materials quickly, progressive die stamping helps to improve the speed with which products can be taken to market. This is critical in industries where customer demands switch quickly.
Material Versatility
As we showed earlier, you can use progressive die stamping on different materials – steel, plastics, copper, etc. This versatility makes it easy for manufacturers to select the best material for their needs.
Besides the fact that the process works with different materials, you should also note that progressive die stamping can easily be scaled to meet switching production demands. For instance, if you need to increase order volumes, then you could easily add more shifts or presses.
Environmentally Friendly
With minimal scrap generation and efficient material usage, progressive die stamping can be quite eco-friendly in manufacturing.
All in all, the process is efficient and cost-effective across the board. With its ability to also work with complex metal parts, progressive die stamping is definitely one process that works quite well.
Progressive Die Stamping vs Transfer Die Stamping
When it comes to metal stampings, most experts tend to compare progressive stampings with transfer die stamping on different grounds. Both of them share many similarities, but they also differ on several fronts.
The comparison between them includes the following:
Process Flow & Operations
In progressive die stamping, you have a single continuous material strip that moves through a sequence of stations within a single die. Each station performs a specific operation, from bending and cutting to stamping die punches and forming. As the part moves through the die, it is separated from the material strip.
As for transfer die stamping, the material is cut into separate banks from a coil or strip, then transferred between different dies. Each die station is responsible for a specific operation, and the part is moved from one die to the next with a transfer mechanism.
Material Usage
Progressive die stamping does better in this regard as it cuts down on wastage. Scrap is usually removed within the die during the process, making it especially perfect for minimizing material usage in high-volume production.
On the other hand, there’s a possibility for transfer die stamping to generate more scrap as each blank is individually cut from the material strip before going into the die stations.
Part Complexity and Size
Progressive die stamping is better suited for small and medium-sized parts that also come with complex builds and can be produced efficiently in a single pass. At the same time, it works better with high-volume production for components like fasteners, connectors, and other electronic parts.
The reverse is pretty much the case for transfer die stamping as it works better for larger parts that require multiple production steps.
Production Speed
Thanks to its continuous nature, progressive die stamping is generally faster. As such, it works perfectly for high-volume, high-speed production. With its use of more steps, transfer die stamping is a bit slower.
Tooling Costs
Expenses are definitely important when considering this comparison.
For progressive stamping, you might find that initial tooling costs will be higher since the single progressive die is more complex. However, the incorporation of higher production volumes means that tooling costs can be reduced.
Lower initial tooling costs for transfer die stamping tend to be the order of the day since each die station is simpler. But, you can see these costs increase when you need different dies to produce some complex parts.
Versatility
In terms of size and part complexity, you’d find that progressive die stamping is generally more limited. The process is better suited for small to medium-sized production with highly accurate components, allowing you to optimize efficiency from there.
As for transfer press stamping, you get more flexibility in producing larger and more complex parts. Note, however, that you might need more tooling changes for transfer die stamping if you hope to incorporate different part geometries.
All in all, both processes work quite well when done right. Your choice will depend on your part requirements, production volume, and how much you’re willing to spend.
How To Design for Progressive Die Stamping
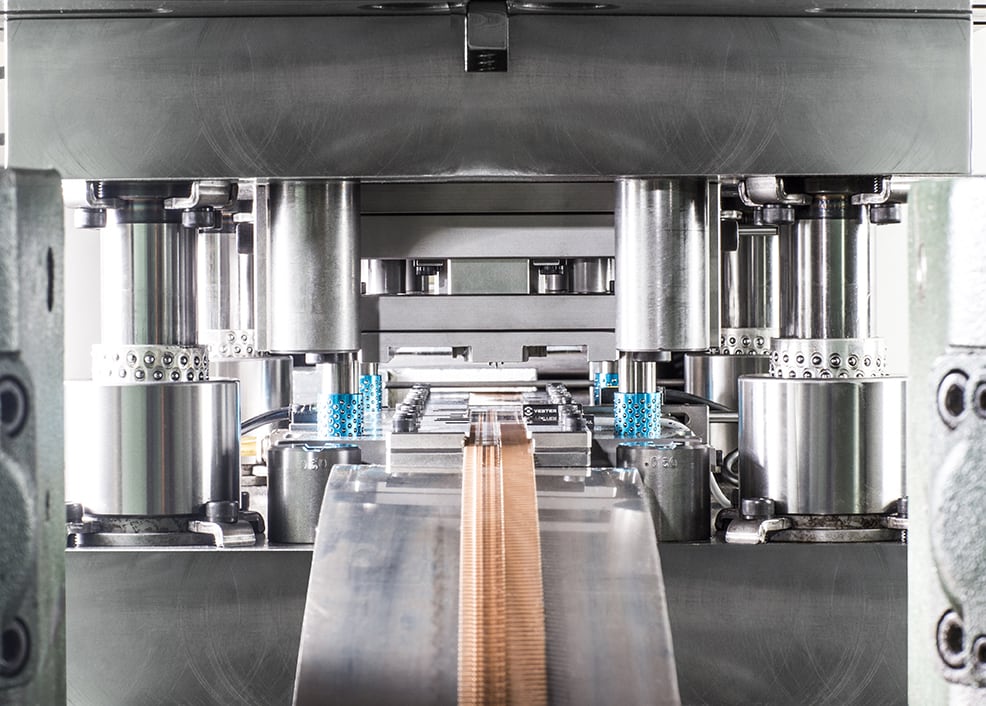

At the end of the day, the success of your progressive die-stamping process will depend considerably on how well you’re able to consider several factors. These include:
Part Design and Feasibility
Per usual, start with a properly designed part that works perfectly with progressive die stamping. Features should be designed in a way that allows them to cut down on material waste while still allowing for effective material feeding.
Material Feeding and Straightening
You need to optimize material feeding systems in order to ensure continuous, smooth flow into the die. To ensure that you don’t come across a coil set in the material strip, you can implement material straightening across the board.
Lubrication and Cooling
Proper lubrication will help to cut down on friction between the die and the material. Just as well, cooking systems can help to manage the generation of heat all through the stamping process.
Die Protection Systems
Install a die protection system to prevent damage to the tool and the die. All of these can help to detect issues such as double feeds and misfeeds, while also stopping the press to avoid any further damage.
Press Selection and Setup
When selecting a press to fit into your progressive die design, ensure that it matches the die’s specifications and your part production needs. Also, remember the place of proper setup and calibration as you hope to achieve consistent results.
Quality Control Measures
Always implement in-process quality control checks and inspections at different stages of the stamping process. This way, you’re able to identify possible deviations and defects.
Scrap Management
In your progress tool and die design, focus on reducing scrap material as much as possible. This will help ensure optimal material utilization and cost savings.
Operator Training
Technicians and operators should be trained on how to effectively use equipment and troubleshoot any common problems.
Continuous Improvement
A culture of continuous improvement should be fostered within your operations. As long as suggestions can help to enhance efficiency, they should be encouraged.
Environmental Considerations
At KDM Fabrications, we fine-tune our operations to ensure that they are beneficial to the environment. Our progressive die stamping operations focus on disposing waste materials, and we also use eco-friendly lubricants to minimize the environmental impact of the entire process.
Production Planning and Scheduling
Effective production planning will be needed to meet any customer demands while ensuring production efficiency. We at KDM FAbrications have implemented the right systems to ensure that we meet your needs comfortably.
Supplier and Vendor Relationships
It’s important to maintain the right relationships with tool vendors and material suppliers to ensure that you get the highest in quality materials. Just as well, timely support will be needed in case you need to conduct repairs and maintenance.
At KDM Fabrications, we have access to a broad field of manufacturers and suppliers, allowing us to easily optimize our operations across the board.
Parts Made Using Progressive Die Stamping
All in all, progressive die stamping is versatile and can be used to design several products and components in different industries. A few of these include:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, the process can be used to create components such as connectors, clips, and fasteners. These components require consistency and high accuracy, and the incorporation of a progressive stamping press ensures safety and optimal vehicle performance.
Electronics and Electrical Industry
Terinals, contacts, connectors, and more can be produced using progressive die stamping. They require fine features and tight tolerances, making the process perfect.
Aerospace Industry
For aerospace operations, progressive die stamping is used to produce different precision parts like fasteners and brackets. Considering the fact that many of these components have to meet strict safety standards, the process is especially important.
Appliance Manufacturing
Progressive die stamping helps in producing household appliances such as hinges and panels that are cost-efficient and functional at the same time.
Construction and Building
Components like clamps and brackets that are used in structural and building applications are important for ensuring the integrity and stability of buildings and other structural components.
Medical Devices
In the medical space, you can incorporate progressive die stamping to produce surgical equipment, sensor components, and more. Once again, the place of quality and precision can’t be overemphasized here.
Telecommunications
Any small components used in telecommunications equipment are made using this process. Its objective is to ensure that these parts meet the demanding requirements for operation.
Renewable Energy
Components for solar panels and wind turbines are manufactured using progressive die stamping.
Conclusion
Progressive die stamping is an impressive process with several critical applications. And as the market for these tools continues to mature, we expect to see even more uses for the process itself.
If you’re a manufacturer looking to incorporate this step into your manufacturing process, then contact us at KDM Fabrication and let us help you out!
More Resources:
Step-by-step Stainless Steel Stamping Process – Source: KDM




