Fabricating sheet metal stamping parts is simple and straightforward with the right information.
Whether you want to choose suitable material, adopt the best technique, or equipment – everything you’re looking for about sheet metal stamping is right here.
So, if you want to be a sheet metal stamping process expert, read this guide.
What is Sheet Metal Stamping?
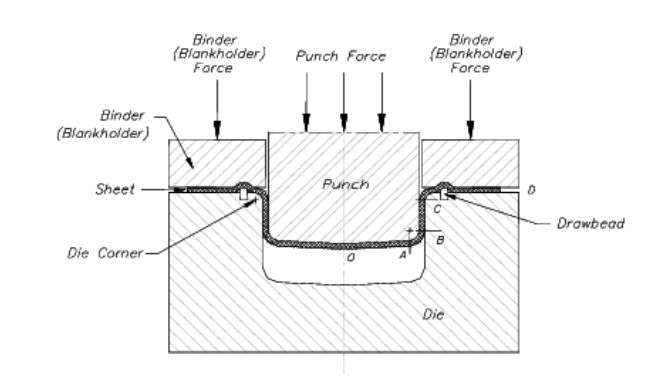
Sheet metal stamping process flow diagram, metal stamping is a cold-forming process, which uses a special tooling system and force to transform sheet metal into useful parts. The special tools may include dies, or stamping presses to form sheet metal parts.
Depending on the sheet metal part design, stamping may involve one or more processes.
Ideally, the stamping sheet metal requires:
- A sheet metal
- Suitable die system
- Stamping press
Stamping Sheet Metal Parts History
Stamping is a sheet metal fabrication technique that has evolved over the years. Some significant milestones include:
- The first coins were made in the 7th century B.C. through the hammering technique. The technique was popular until 1550
- By the 1880s, Marx Schwad used mechanical wheels in coin pressing
- 1880s, stamping greatly replaced forging, making it the main bicycle parts production technique
- 1890 – most stamping machines made in the U.S.A. with automobile companies like Ford adopting the technique
Today, there are many modern and fully automated sheet metal stamping techniques. They have reduced production costs, guarantee accuracy and allow for automation.
Benefits Of Sheet Metal Stamping Parts

Today, stamping sheet metal parts are popular in many industries. It is due to the numerous benefits the process offers.
These include:
- Easy and efficient way to shape sheet metal parts
- Suitable for producing complex and intricate parts
- Lower production
- Suitable for fast turnaround
- Tooling system is inexpensive
- Most stamped metal parts are accurate, hence require minimal finishing operations
- It is easier to achieve a high level of automation
However, the initial setup cost for a complete sheet metal parts stamping process is high.
Common Sheet Metal Stamping Processes
As mentioned earlier, stamping sheet metal may involve one or more processes and techniques. It will depend on the parts you want to make.
Let’s look at some common metal stamping techniques:
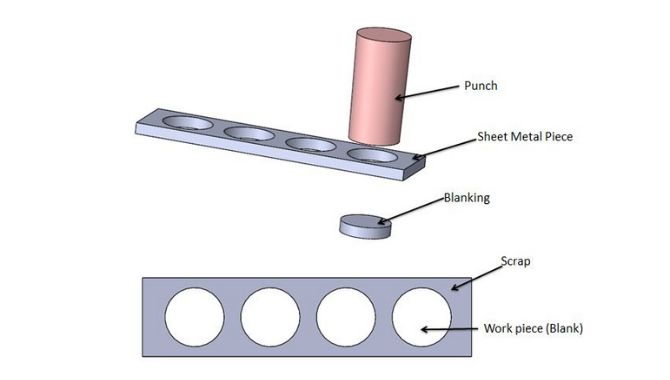
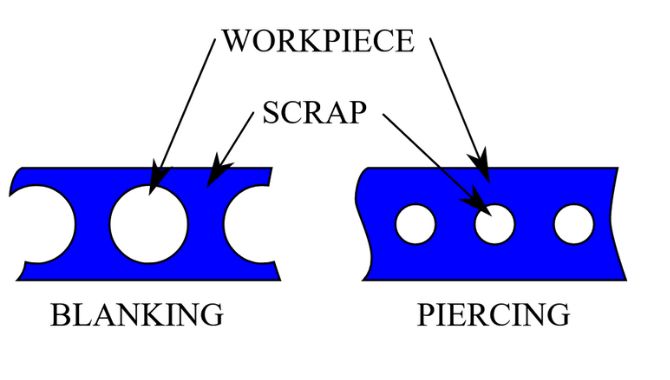
1. Sheet Metal Blanking
During blanking process, the machine will only cut useful sections according to your design. You can refer to the cut sheet metal section as finished blank or just blank.
Depending on your sheet metal fabrication requirements, you can process the sheet metal blank further.
2. Sheet Metal Punching
Punching is a popular process when you want to produce sheet metal blanks. During the punching process, the machine forces a tool through the sheet metal.
As a result, the tool cuts metal sections, resulting in holes.
3. Drawing Sheet Metal
During drawing process, you will force sheet metal into a cavity. By radially drawing sheet metal into the cavity, it must not stretch the material.
In this fabrication process, “sucking” sheet metal, it will “deep” shape.
4. Piercing Sheet Metal
Here, you will use a special tool to create holes or pierce through sheet metal. As a result, your final sheet metal part will have holes depending on your design.
Actually, sheet metal piercing is the opposite of sheet metal blanking. In fact, you can perform sheet metal blanking and piercing simultaneously.
5. Embossing Sheet Metal
An embossing tool will create either a recessed or raised section on the sheet metal surface. Of course, the process does not cut or remove any sheet metal section.
The recessed or raised section will depend on your pattern design.

6. Coining Sheet Metal
Coining is a unique stamping technique, which results in sheet metal bending. The process is popular for high accuracy and repeatability.
Usually, you will place the sheet metal between a die and punch.

7. Bending Sheet Metal
It is a process where you apply force to deform sheet metal into different profiles. Depending on the sheet metal bending technique, you can get:
- L shaped profile
- U shaped profile
- V-shaped profile
Of course, you can have custom profiles depending on unique design requirements.

8. Flanging Sheet Metal
Using dies or special machinery, you incorporate flange or flare on fabricated sheet metal parts. Depending on your design, you can incorporate:
- Tension flanges
- Compression flanges
Of course, you should carry out the flanging process along the sheet metal curved line.

Apart from these techniques, you may incorporate other sheet metal fabrication techniques to get better parts. These may include:
Cutting sheet metal – It involves separating sections or parts from the main sheet metal. You can use many techniques such as blanking, piercing, laser cutting, etc. So, during the metal stamping process, you can cut metal sections depending on your design.
Welding sheet metal – At times, you may stamp sheet metal parts separately which may require assembly at a later stage. That is where welding plays an important role. Broadly, you may choose TIG, MIG, or Laser welding to join different metal parts.
Spinning sheet metal – With spinning you will fabricate symmetrical round or circular parts. Therefore, you can form axially symmetric parts while stamping at the same time.
Machining sheet metal – It is a precisely controlled process where you remove sections from sheet metal to form a final product. Some common operations include sheet metal drilling, milling, or reaming.
Deep drawing sheet metal – The tensile and compressive pushes sheet metal into a die. Unlike other sheet metal drawing processes, here the depth of the drawn sheet metal part is equal to, or larger than the part radius.
With these in mind, it is important to choose the right sheet metal stamping operations.
Let’s look at the most common options.
Types of Sheet Metal Stamping Parts Operations
Whether you are planning to cut, emboss or bend sheet metal parts, choose stamping operations that guarantee cost-effectiveness, versatility, and accuracy.
When it comes to sheet metal stamping, you can consider these four options:
1. Progressive Die Stamping Sheet Metal Parts
During progressive die stamping, the sheet metal will pass through a series of die systems. For instance, depending on the sheet metal fabrication requirements, a single machine may have 3 to 4 stamping stations.
Therefore, once the die in station 1 stamps the sheet metal, the same part moves to stations 2, 3, and 4. By the end of the process, the machines stamp one section 4 times, but in different stations.
What makes the process unique?
- Producing complex sheet metal is easier through the stamping process
- Reduced production time
- Increases sheet metal stamping parts efficiency
- Progressive die stamping is suitable for long-run production processes
- Tooling system lasts longer due to reduced wear
- The process is highly repeatable
- Each station in the progressive dies stamping performs a unique or different function
- Reduces sheet metal wastage
In progressive die stamping, the final station will separate the part from the main sheet metal.
2. Transfer Die Stamping Sheet Metal Parts
The transfer die stamping sheet metal parts is similar to progressive die stamping. However, in this case, you will transfer the stamped part “mechanically” from one stamping station to another.
Transfer die stamping is characterized by:
- You will separate the stamped sheet metal part during the early stages
- It is suitable for stamping large sheet metal parts such as frames or structural parts
- Stamped sheet metal parts pass through one or more stamping dies
3. Four-Slide Stamping Sheet Metal Parts
If you are looking for versatile, functional, and practical sheet metal stamping parts, then four-side offers the perfect solution.
The process is also called 4-way stamping or multi-slide stamping.
In four slide stamping, 4 sliding tools deform sheet metal into various shapes or designs. They strike the workpiece, thereby transforming it through multiple deformations.
Depending on the multi-slide stamping machine, it may have more moving slides. Normally, four-slide stamping is suitable for complex sheet metal parts.
4. Fine Blanking Sheet Metal Parts Or Fine Edge Blanking
With fine blanking, you can produce flat and sheared edges on sheet metal parts. The process is precise and may not require additional processing.
You will achieve tight tolerances and smooth edges on sheet metal parts.
Generally, the process involves:
- Clamp sheet metal
- Blanking sheet metal part
- Eject the sheet metal
Unlike other sheet metal stamping processes, fine blanking uses a special tooling system. It is because the process requires high operating pressure.
As you can see, each sheet metal stamping operation offers unique fabrication features. Therefore, ensure you choose the right technique and operation for sheet metal stamping parts.
Choosing Material for Sheet Metal Stamping Parts
When it comes to stamping sheet metal parts, you can work with virtually any material. These may include:
1. Stamping Stainless Steel Parts
Stainless steel remains a popular material due to its excellent corrosion resistance properties. It is also due to its durability, sustainability, and superior performance in virtually all applications.
You can stamp sheet metal parts from the many stainless steel grades available. For example, the grade 300 series are common for most domestic and industrial applications.
Austenitic stainless steel remains popular for most sheet metal stamping processes. Other stainless steel materials suitable for the stamping process include:
- Martensitic SS such as the 410, 416, 420 and 502
- Ferritic SS for stamping parts are 405, 430F and 446
- Precipitation hardening SS grades are 15-5 PH and 17-7 PH
Stainless steel stamped parts are suitable for marine, medical, food, and energy industries.
2. Stamping Carbon Steel Parts
For carbon steel metal stamping you can choose any of these variations:
- Low carbon steel or mild steel – The carbon content varies from 0.03% to 0.08%. These steel alloys are easy to machine and weld.
- High strength low alloy steel – These alloys have 0.6% to 1.4% carbon. They are the strongest though very ductile.
Carbon steel offers the unlimited possibility of sheet metal stamping. You can make sheet metal housing, panels, bridge sections, etc.
Generally, stamped carbon steel parts are known for their strength-to-weight ratio. Additionally, it offers a cost-effective alternative in the metal stamping industry.
However, carbon steel is not corrosion-resistant like stainless steel. On the other hand, it has high thermal conductivity and better heat distribution.
3. Stamping Aluminium Parts
Aluminum is popular for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical properties, and lustrous appearance.
At the moment, stamped aluminum parts are common in the aerospace, construction, automotive, electronics, marine, and medical industries, just to mention a few.
Additionally, aluminum stamping operations you can adopt include blanking, coining, bending, piercing, etc.
Depending on the aluminum stamped parts, various alloys have varying performance characteristics. As a result, the application may also vary.
Take for example:
- 1100 series for chemical equipment
- 2024 and 7075 for aircraft parts
- 3003 for cooking utensils or furniture
- 5052 for metal ductwork system
- 6061 is suitable for architectural structures and aerospace components
- 6063 for making pipes and other extruded parts
Due to their lightweight and strength, aluminum stamping parts play an integral role in today’s industries.
4. Stamping Titanium Parts
Stamped titanium parts are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, easy to sterilize, and durable with excellent strength. For this reason, stamped titanium parts are common in:
- Medical industries
- Aerospace industry
- Petroleum industry
- Military industry
Although titanium stamped parts are slightly heavier than aluminum stamped parts, they have a good strength-to-weight ratio.
You can easily stamp titanium grade 9. Of course, this is not the case when it comes to titanium grade 5. Other available titanium grades include grades 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 11, 12, and 23.
5. Brass Stamping Parts
Stamped brass parts find applications in marine, medical, telecommunication, and power generation industries, just to mention a few.
It is due to brass corrosion resistance, and better surface finish. Shaping brass is easy and it conducts electricity.
Moreover, brass stamped parts are resistant to tarnishing and exhibit medium strength.
6. Stamping Copper Parts
You can easily stamp copper either in its pure form or after alloying. Some common alloys include brass and bronze. Generally, copper is corrosion resistant, ductile, easy to clean, has decorative appeal, and possesses antimicrobial properties.
Apart from these six common metals, the stamping process is also suitable for tin, silver, and gold parts
Whether it is ferrous or non-ferrous metals, stamping offers the perfect fabrication technique. Of course, choosing a specific material will depend on:
- Special features or properties the final product should have such as corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratios, etc.
- Cost
- Specific application
- Sheet metal availability
- Material formability for metal stamping
Therefore, before choosing any material for metal part stamping, you should be specific about your intended application requirements.
Choosing a Machine for Stamping Sheet Metal Parts
There are two fundamental aspects here:
1. Get an Efficient and Reliable Sheet Metal Stamping Machine
Today, there are many sheet metal stamping presses in the market. For example, you may consider:
- Mechanical sheet metal stamping press
- Hydraulic stamping press
- Mechanical servo stamping press
The type of sheet metal stamping machine will depend on accuracy and production capacity.

2. Invest in Better Tooling Systems
You should have quality sheet metal stamping dies. Remember, the dies form crucial tooling systems for the sheet metal parts stamping process.
In fact, an in-house tooling system is best for custom metal stamping parts. With this, it is easier to achieve precision sheet metal stamping parts.
After all, you will make all sheet metal stamping tools with the desired accuracy and precision.
It is the stamping dies that cut through the sheet metal. These metal stamping tooling systems are made from tool steel, hence they are resistant to wear.
Depending on the stamping die, you can use it for:
- Single operation
- Multiple operations
Of course, there are compound dies and multi-station dies. So, the choice will depend on the sheet metal stamping operation.
Stamping die design is critical. Remember, it resembles the exact part design you want to fabricate.

Stamped Sheet Metal Parts Finishing Processes
Although stamping sheet metal may produce accurate parts with better finish – at times it is not always enough.
A reason you should add a surface finish. The surface finishes on sheet metals enhance aesthetic value, alongside better physical, chemical, and mechanical properties.
In fact, sheet metal stamping finishing help to fix imperfections on the surface.
The most common custom stamped parts finishing include:
Polishing – The finishing will give stamped metal parts a mirror-like surface finish.
Powder coating – You will apply powder on a stamped metal surface. In most cases, you will apply the powder electrostatically.
Deburring – it helps to remove rough sections on the stamped parts. You can use mechanical or electrochemical means to remove burrs on stamped sheet metal parts. As a result, you will improve the stamped metal part quality, aesthetic, and functionality.
Plating – Here, you will coat stamped metal parts with a thin layer of a metal substrate.
Anodizing – The electromechanical process decorates stamped sheet metal parts. Depending on the substrate, it can make the surface corrosion-resistant or more appealing to the eye.
Etching – It involves cutting into stamped metal parts to create designs.
Apart from these, you may also opt for custom surface finishing. You can discuss this with the sheet metal parts stamping provider.
Here are more resources:
Common Sheet Metal Stamping Defects
Although stamping sheet metal parts produce accurate parts and components, some challenges may include:
Hole deformation – Punching then bending holes may cause significant deformation near the edge.
Burrs formation – At times, shearing metal edges can be a common phenomenon. This causes imperfections that require deburring.
Cracking during bending – metals with little plasticity may crack. You should know the material type, then follow sheet metal bending rules.
Others include unwanted deformation, broken edges, ununiformed bending, and surface scratching.
It is important to follow the best practices when using any sheet metal stamping technique.
Bonus: Once you stamp sheet metal parts, it is important to adopt reliable assembly techniques.
These may include:
- Riveting
- Welding
- Mechanical assembly techniques
You can learn more about: Sheet Metal Assembly Techniques.
Stamped Metal Parts Applications

From specialized computer parts and aircraft components to home appliances – stamped sheet metal parts are the perfect choice for many industries.
Whether it is fabrication cost, fast turnaround, or reliability, the stamped sheet metal parts applications may include:
Automotive Industry – automotive sheet metal stamping process, from brackets, vehicle parts, engine components, steering assembly parts, piston assembly switches, etc. There are many stamped automobile components and metal parts.
Power Generation Industry – turbine parts, power distribution equipment, windmill parts, and power transmission accessories are mostly metal stamped parts.
Medical Industry – stainless steel stamping is popular in the medical industry. Stamped parts for medical applications may include surgical equipment, probes, implantable devices, instrument connectors, etc.
Aerospace Industry – titanium stamping and aluminum stamping are common in making aircraft parts and components such as flaps, stabilizers, spoilers, panel components, etc.
Electrical and Electronics Industry – Heat sinks, switches, covers, enclosures, and many other accessories are made from stamping. These may include steel electrical parts in various electrical parts.
Home Appliances – stamped electronic enclosure parts, heat sink components, casing, covers, switches, lock systems, etc.
Telecommunication industry – there are many stamped steel parts in the telecommunication industry. From switches, casing, transmission equipment, panels, etc.
Even when you want precision metal stamping parts, there are many parts available. They feature tight tolerance and accuracy.
In short, the stamped metal parts applications are unlimited.
In Short:
With all these in mind, we can summarize the sheet metal stamping process step by step as:
- Design the sheet metal part you wish to make – of course, you must follow the recommended sheet metal stamping design guidelines
- Choose a suitable material – the material may come as a coiled or blanked sheet
- Design sheet metal tooling system
- Choose a cost-effective and efficient sheet metal stamping machine
- Depending on part requirements, choose a suitable sheet metal stamping technique
- Consider any of the four sheet metal stamping operations
- Start the sheet metal stamping process
- Check the quality of stamped sheet metal parts
- Apply appropriate surface finishing
- Check stamped sheet metal part quality
- Package stamped sheet metal parts ready for shipping
KDM Sheet Metal Stamping Parts Capability
At KDM, we offer many possibilities when it comes to sheet metal stamping parts. Our key benefits include:
- Complementary tooling to reduce lead time
- Fast production with our advanced stamping machines and accessories
- Competitive cost – we offer the best prices in the market
- Our stamped metal parts must conform to industry standards. We are an IATF16949, ISO 9001, and ISO 14001 certified company.
Whether you need part design, low-volume production, high-volume production, or custom-stamped metal parts – KDM has both capacity and capability.
Our team will help you with custom-stamped part design. Whether you want standard or precision sheet metal stamping parts, KDM can maintain tight tolerances.
Additionally, many custom finishes are available for your specific needs.
You can contact us today for all your sheet metal stamping parts.
Conclusion
As you can see, sheet metal stamping parts is a fabrication technique involving many techniques and operations. It is a simple, cost-effective process you can use to make many sheet metal parts and components.
For any questions or inquiries about our capability in stamping sheet metal parts, contact us now. Or request sheet metal stamping process pdf for more information.
More Resources:
Deep Drawn Metal Stamping – Source: KDMFAB
High Speed Metal Stamping – Source: KDMFAB
Stamping in Metalwork – Source: Wikipedia
Types of Metal Stamping – Source: IQS Directory
Understanding Metal Stamping – Source: Thomansnet




